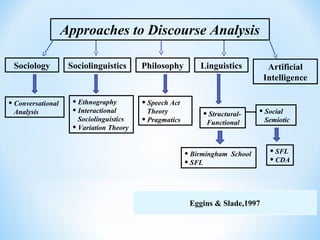
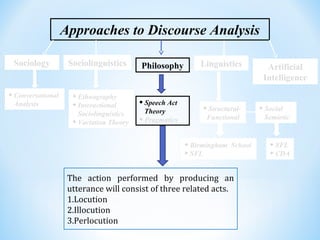
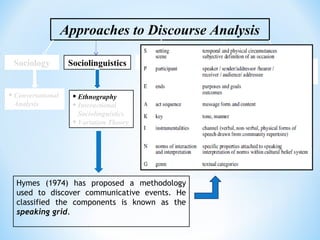
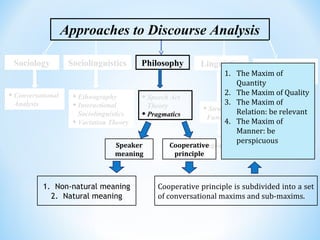
The document discusses different approaches to discourse analysis including sociology, sociolinguistics, philosophy, linguistics, and artificial intelligence. It also discusses speech act theory, pragmatics, Grice's cooperative principle and conversational maxims, Hymes' speaking grid for analyzing communicative events, and natural vs. non-natural meaning.