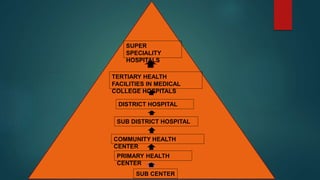
The document discusses discharge summaries, referrals, and death certificates. It defines discharge as the process of shifting a patient out of the hospital with medical summaries ensuring stability. Referral is defined as the process of seeking help from a better resourced facility. A death certificate establishes the date, fact, and cause of death and is required for legal and benefits purposes. It also outlines the required components of discharge summaries, referrals, and medical certificates of cause of death.