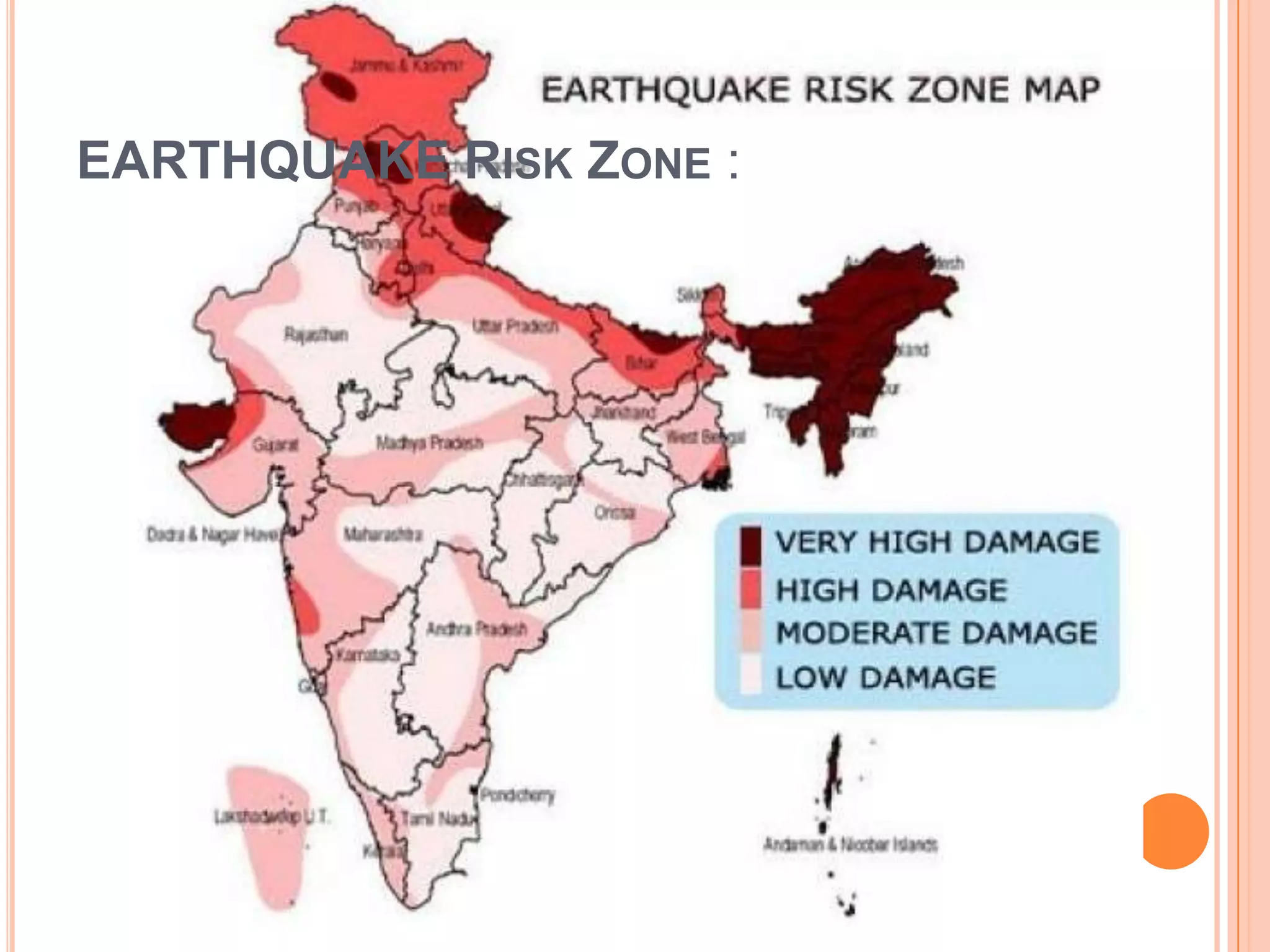
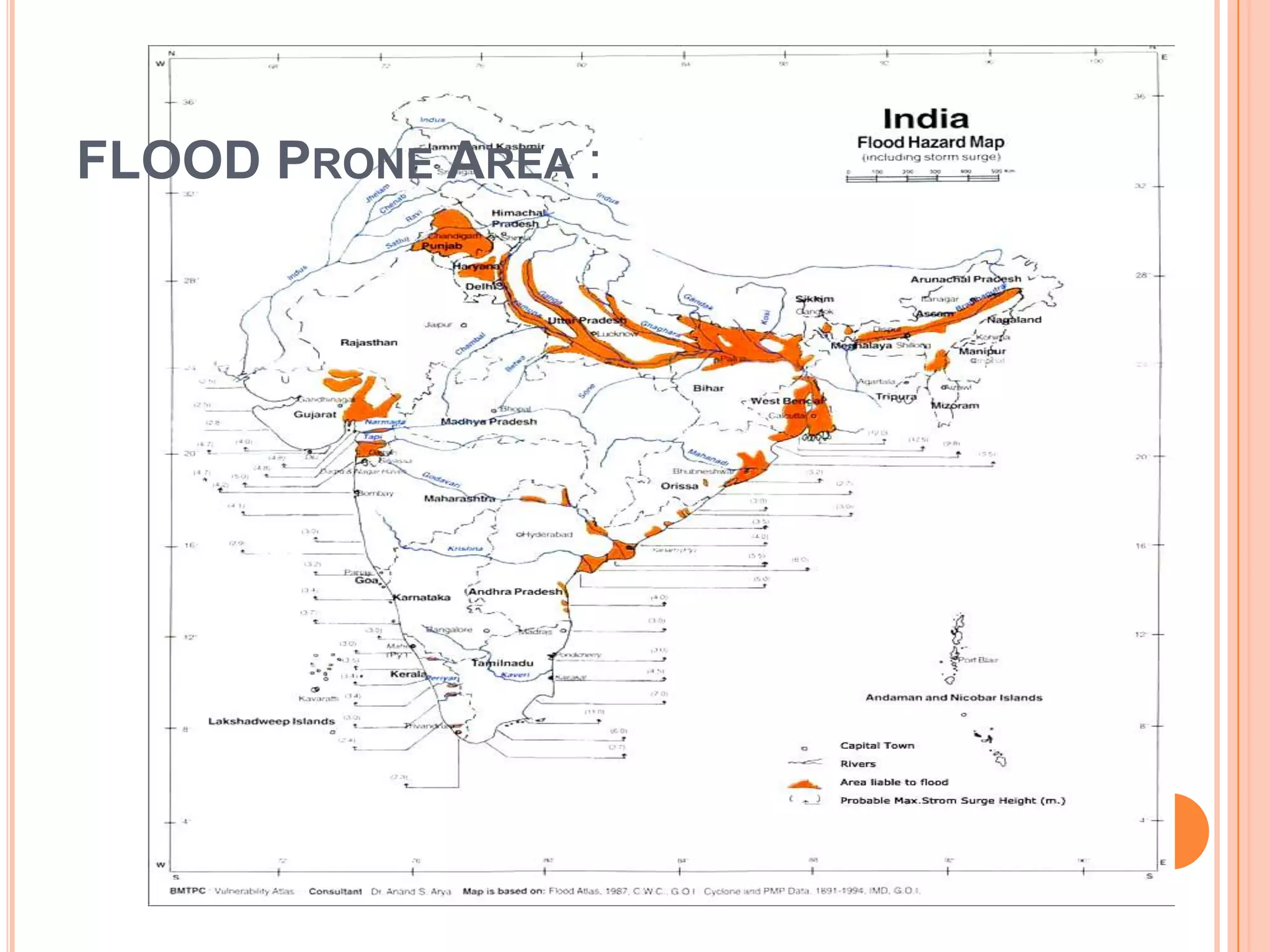
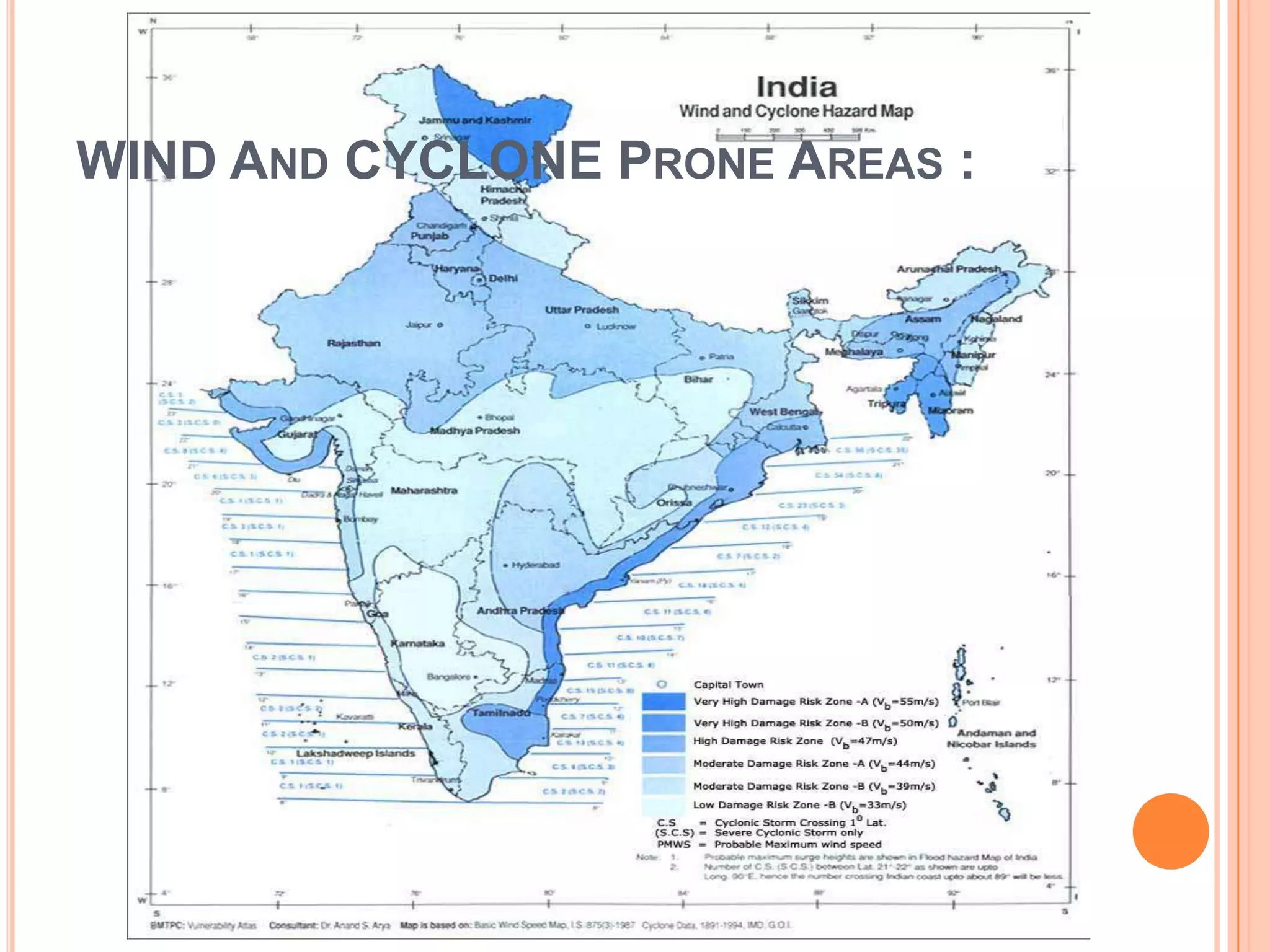
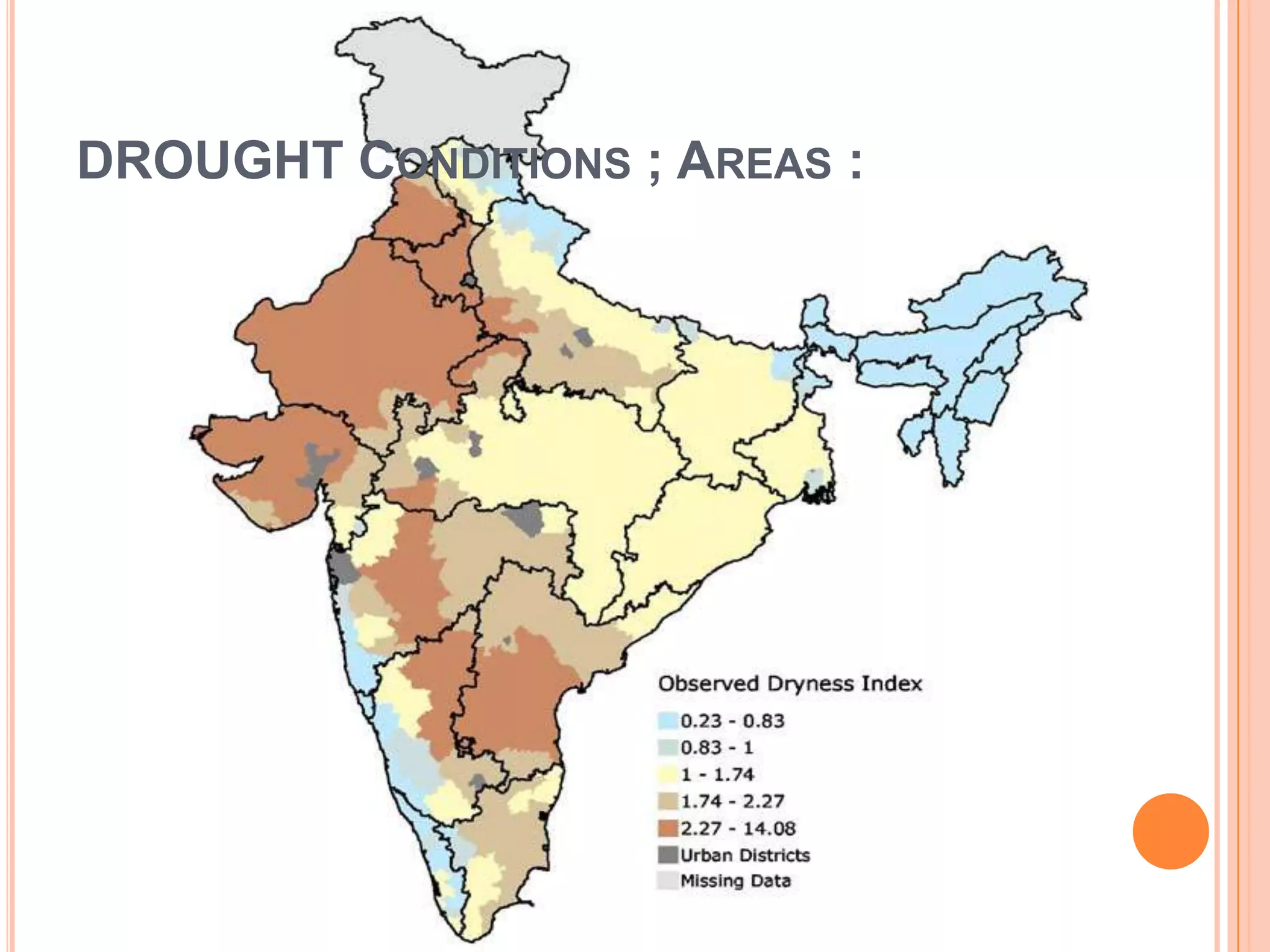
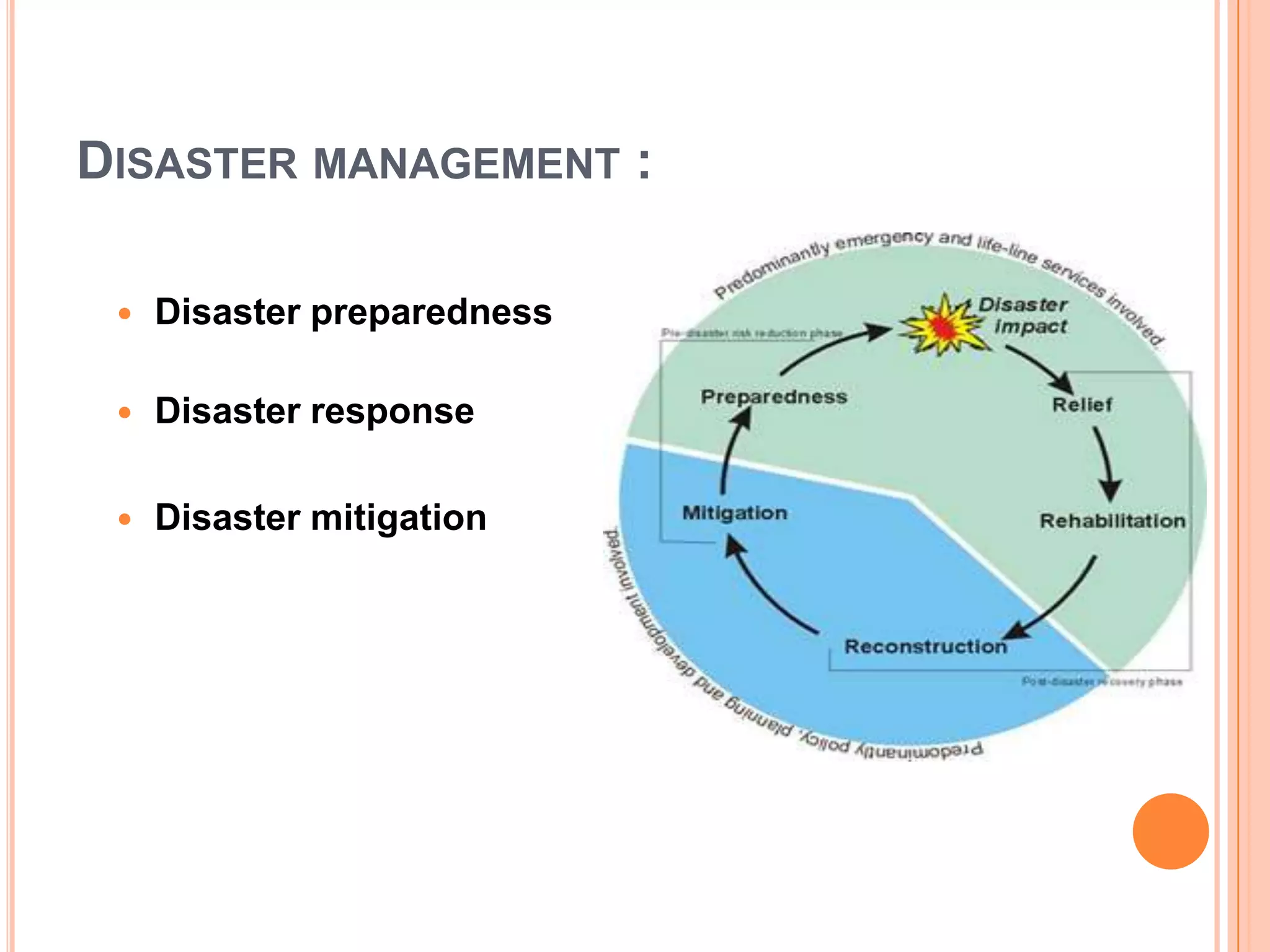
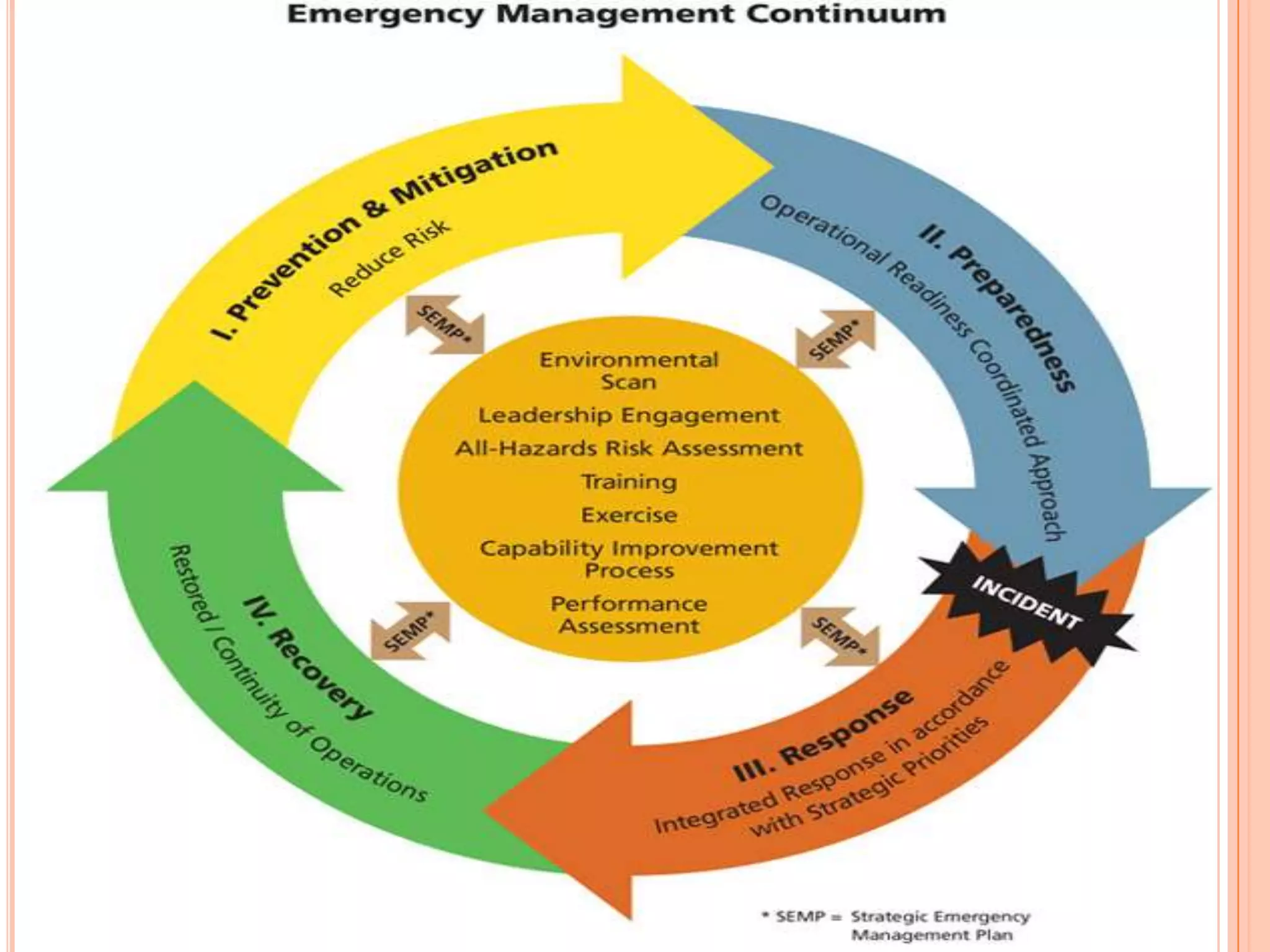
The document discusses various types of natural and human-induced disasters. It defines a disaster and outlines the disaster management paradigm. It describes key phases of a disaster and provides examples of major natural hazards like earthquakes, cyclones, floods, droughts, and tsunamis. For human-induced disasters, it mentions fires, industrial accidents, bomb blasts, and road accidents. The document also discusses disaster preparedness, response, and mitigation efforts. It outlines precautions for different types of disasters and highlights India's disaster management framework and warning systems.