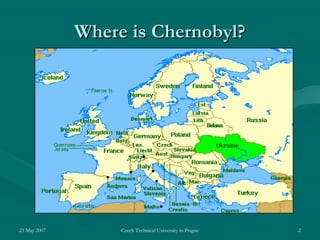
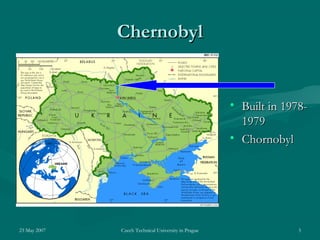
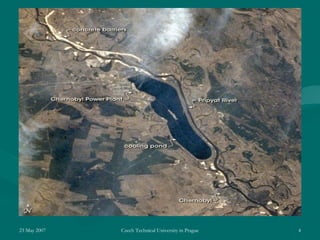
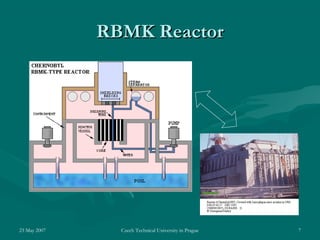
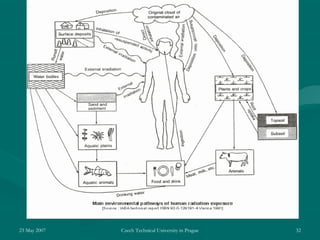
On April 26, 1986, a reactor explosion at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in Ukraine released radioactive material into the atmosphere. Due to operator errors, explosions destroyed the reactor and started fires that lasted 10 days. Over 7 million people in nearby areas were exposed to radiation, with thousands dying or suffering long-term health effects. It was the worst nuclear disaster in history.