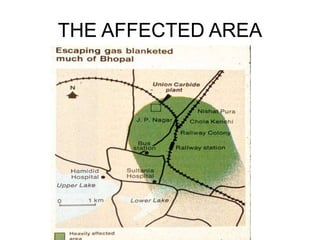
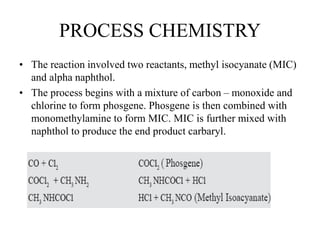
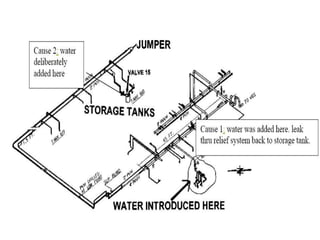
The Bhopal gas tragedy occurred in 1984 when toxic methyl isocyanate gas leaked from a Union Carbide pesticide plant in Bhopal, India, killing thousands. Several factors contributed to the disaster, including improperly designed safety systems, non-operational safety equipment, and lack of emergency planning. While the cause of the leak is still debated, lapses by both Union Carbide and the Indian government exacerbated the incident. The tragedy highlights the need for inherently safer chemical plant design and hazardous material handling procedures.