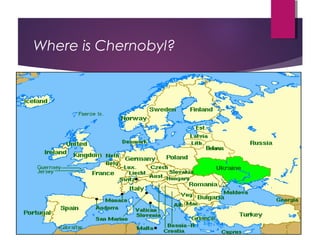
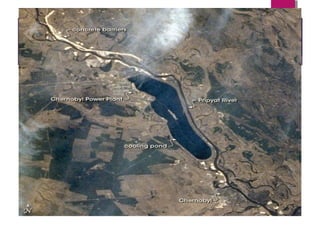
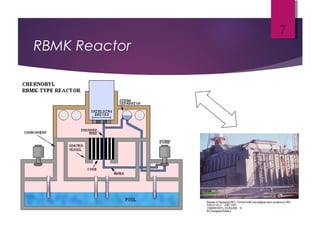
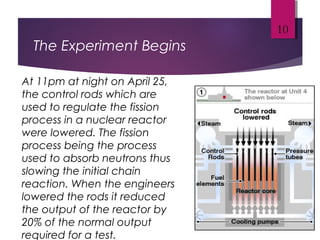
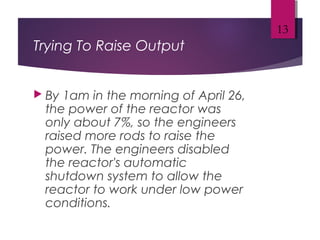
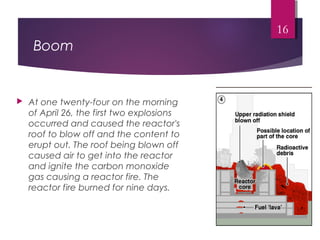
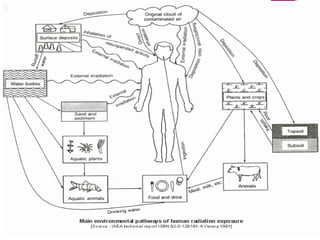
The Chernobyl disaster, a catastrophic nuclear accident on April 26, 1986, resulted from operator errors during a test at reactor number four, leading to an explosion that released 190 tons of radioactive material and contaminated vast areas, primarily affecting Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia. The aftermath involved extensive cleanup efforts and resulted in immediate and long-term health effects, including radiation sickness and increased cancer rates among affected populations. Initial blame was placed on operators, but later reports also scrutinized the reactor's design, highlighting the disaster as the worst man-made catastrophe in history.