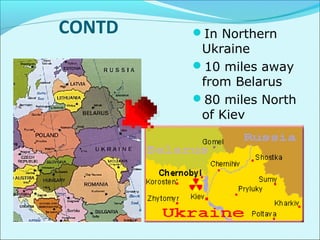
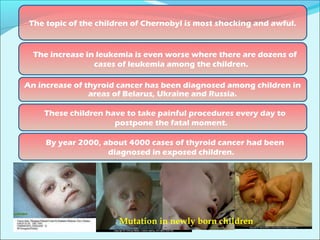
The Chernobyl nuclear disaster of 1986 in Ukraine was the worst nuclear power plant accident in history. When the reactor core was damaged during a safety test, it caused two explosions and released large amounts of radioactive material into the atmosphere. Over 100,000 people had to be evacuated from the surrounding area. Many people suffered long-term health effects such as increased cancer rates, and the environment was also contaminated over a large region. The accident highlighted issues with the Soviet nuclear reactor design and lack of safety precautions that led to the disaster.