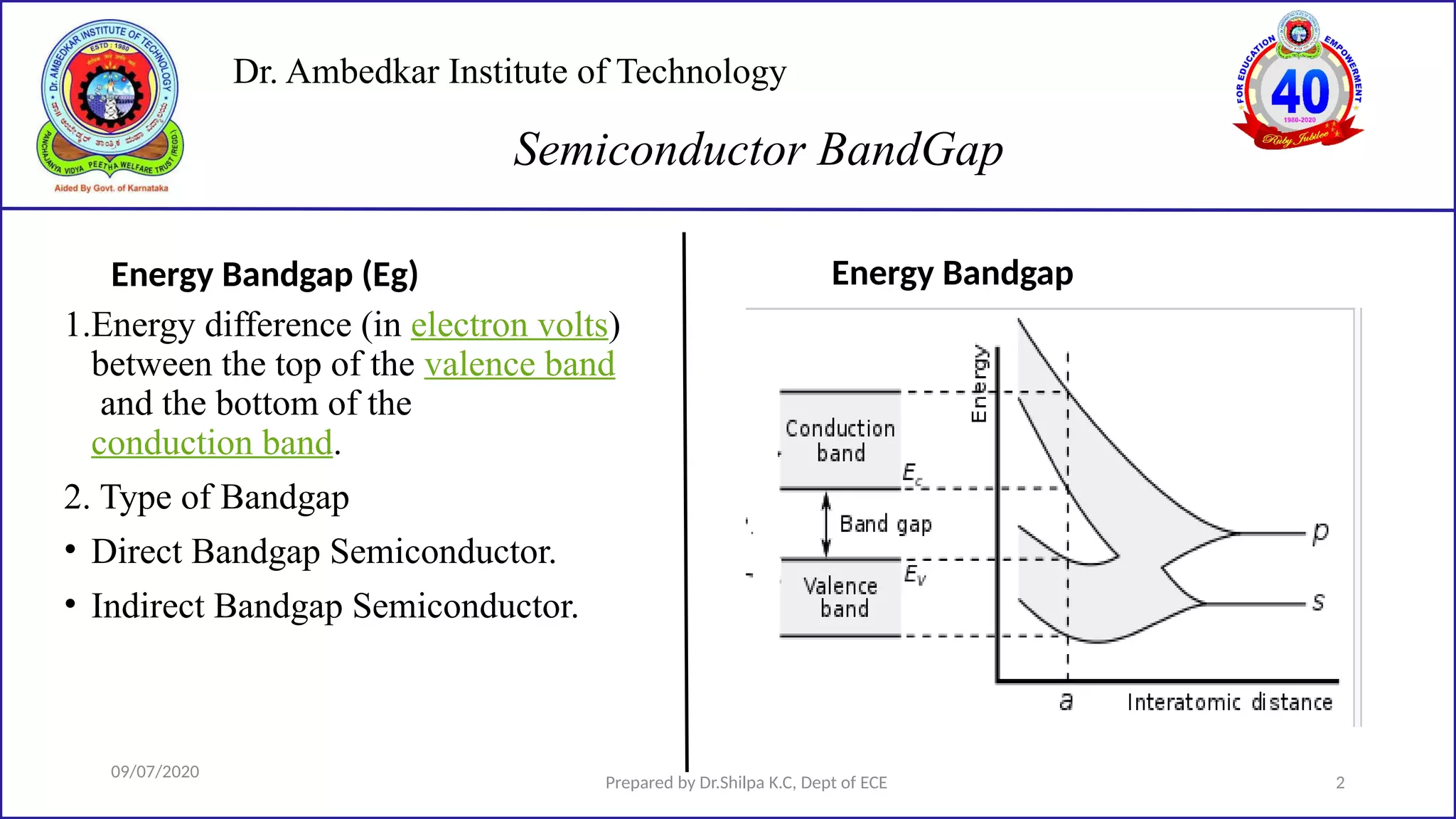
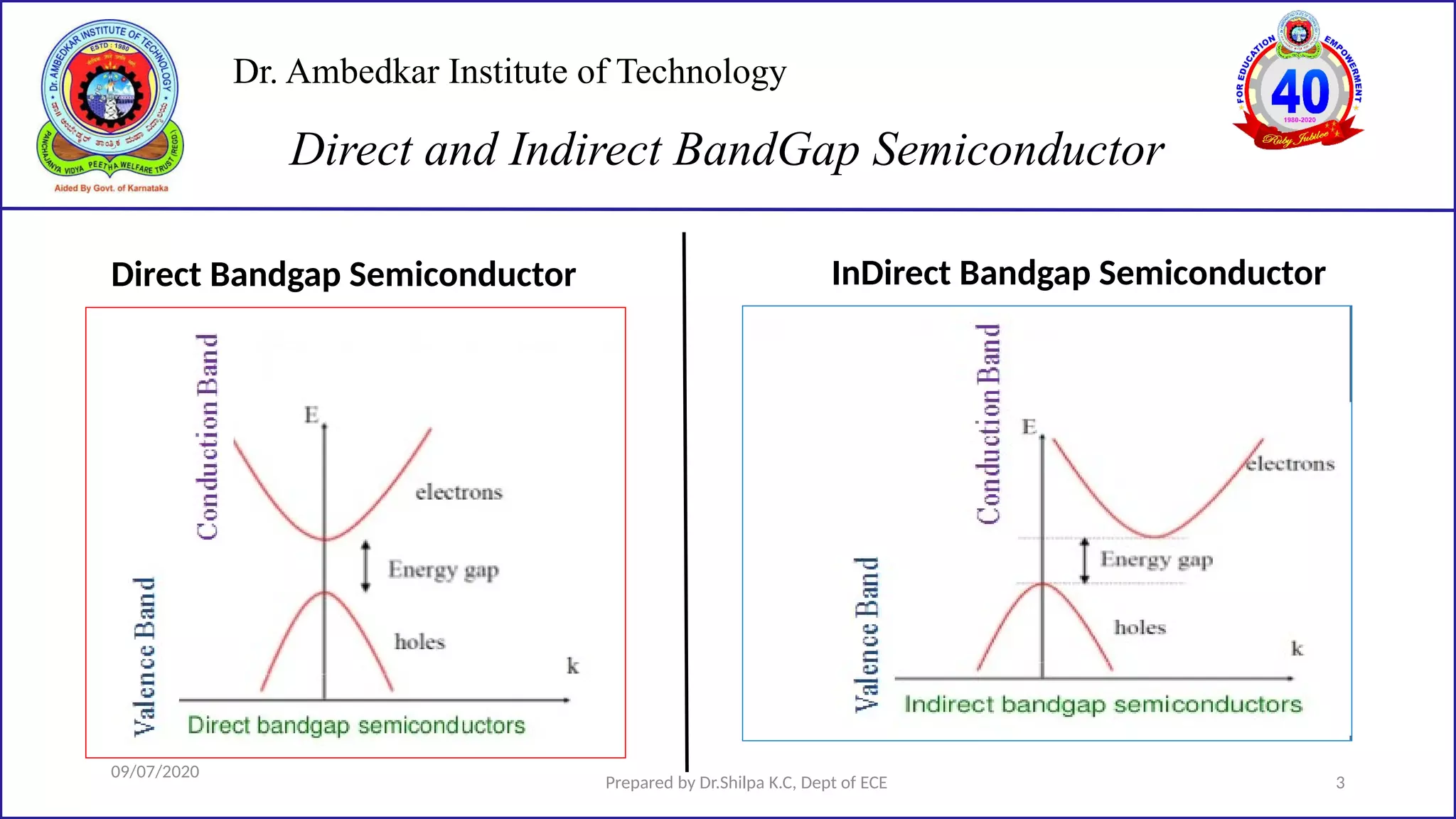
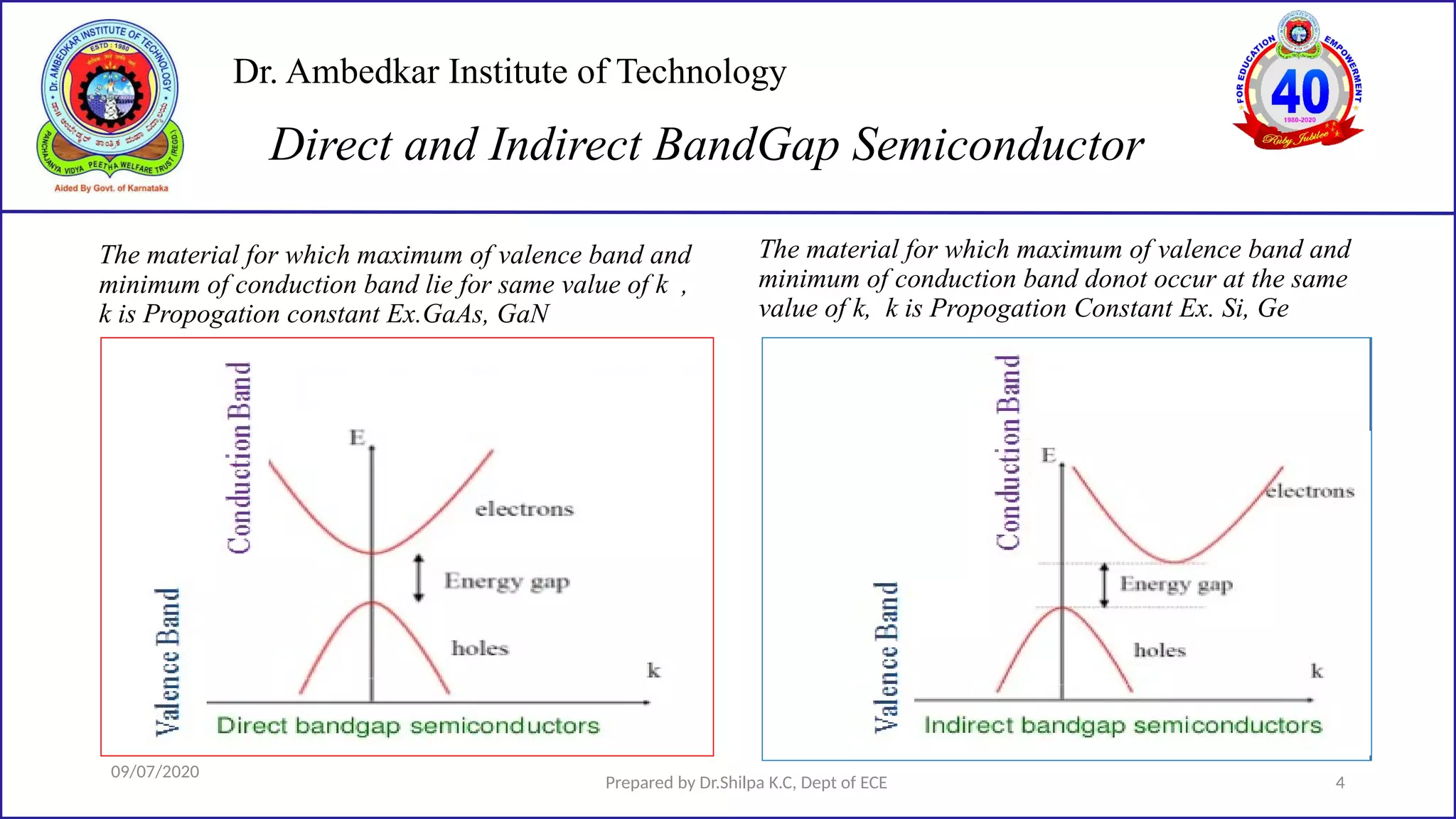
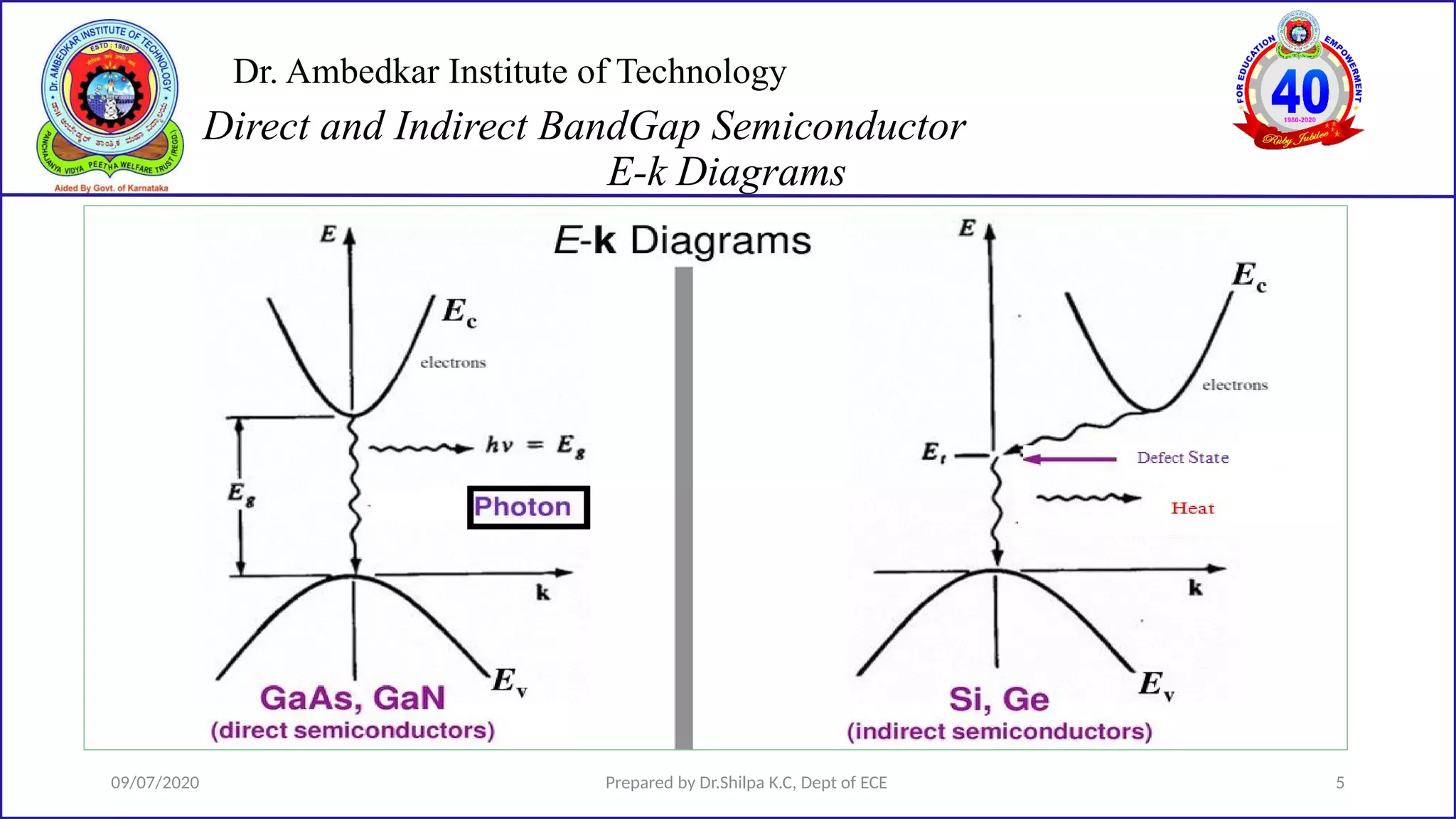
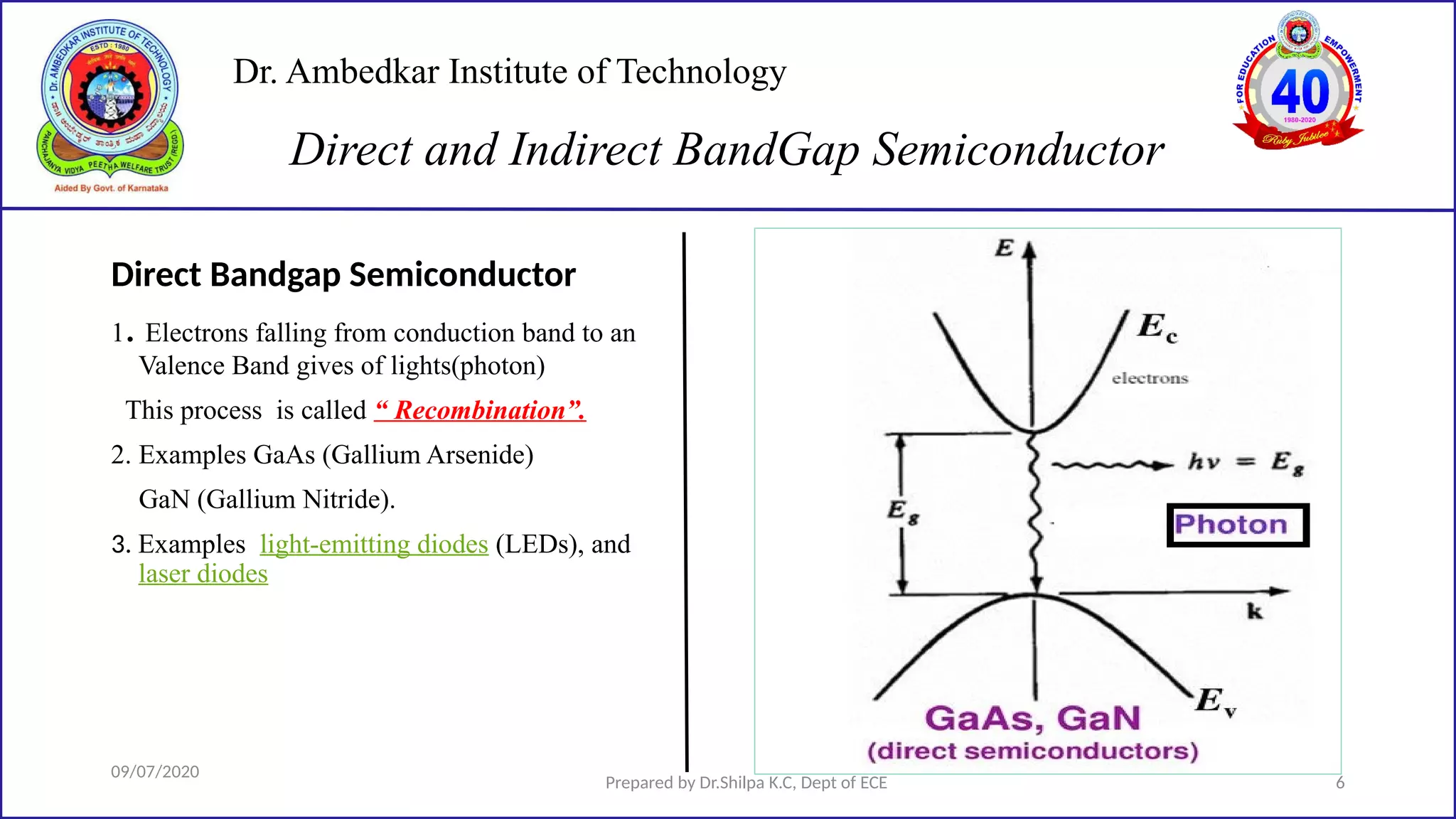
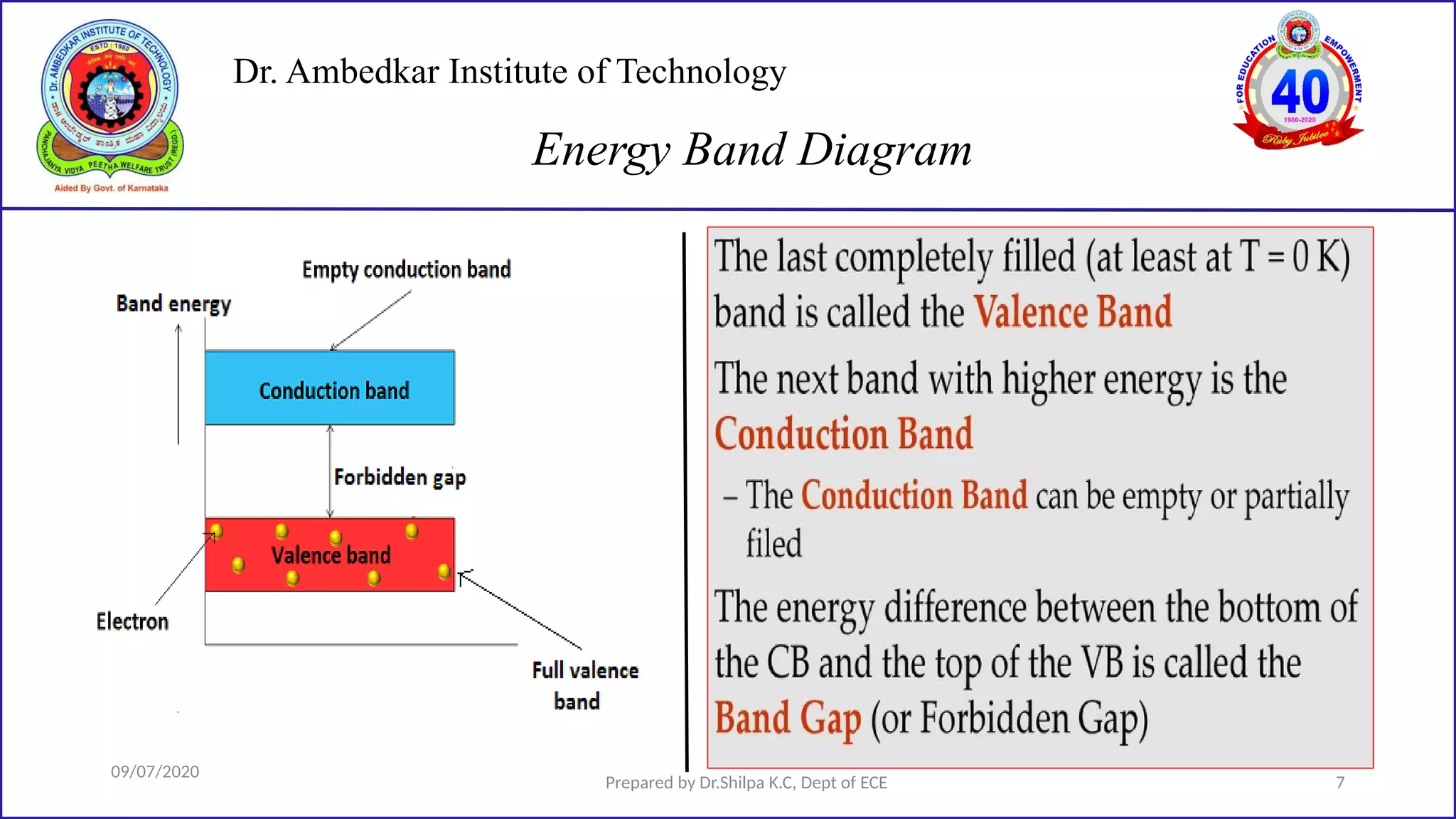
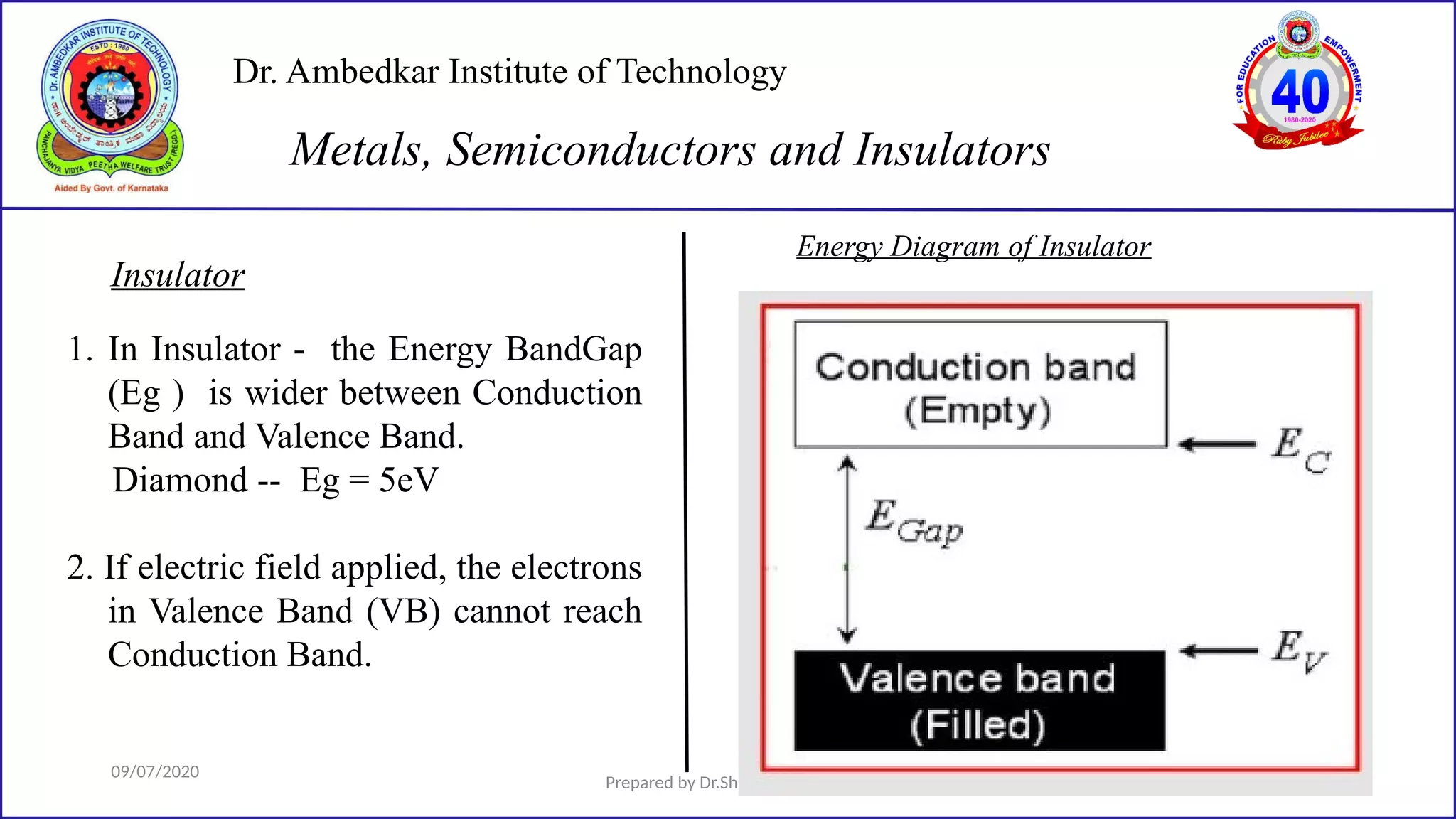
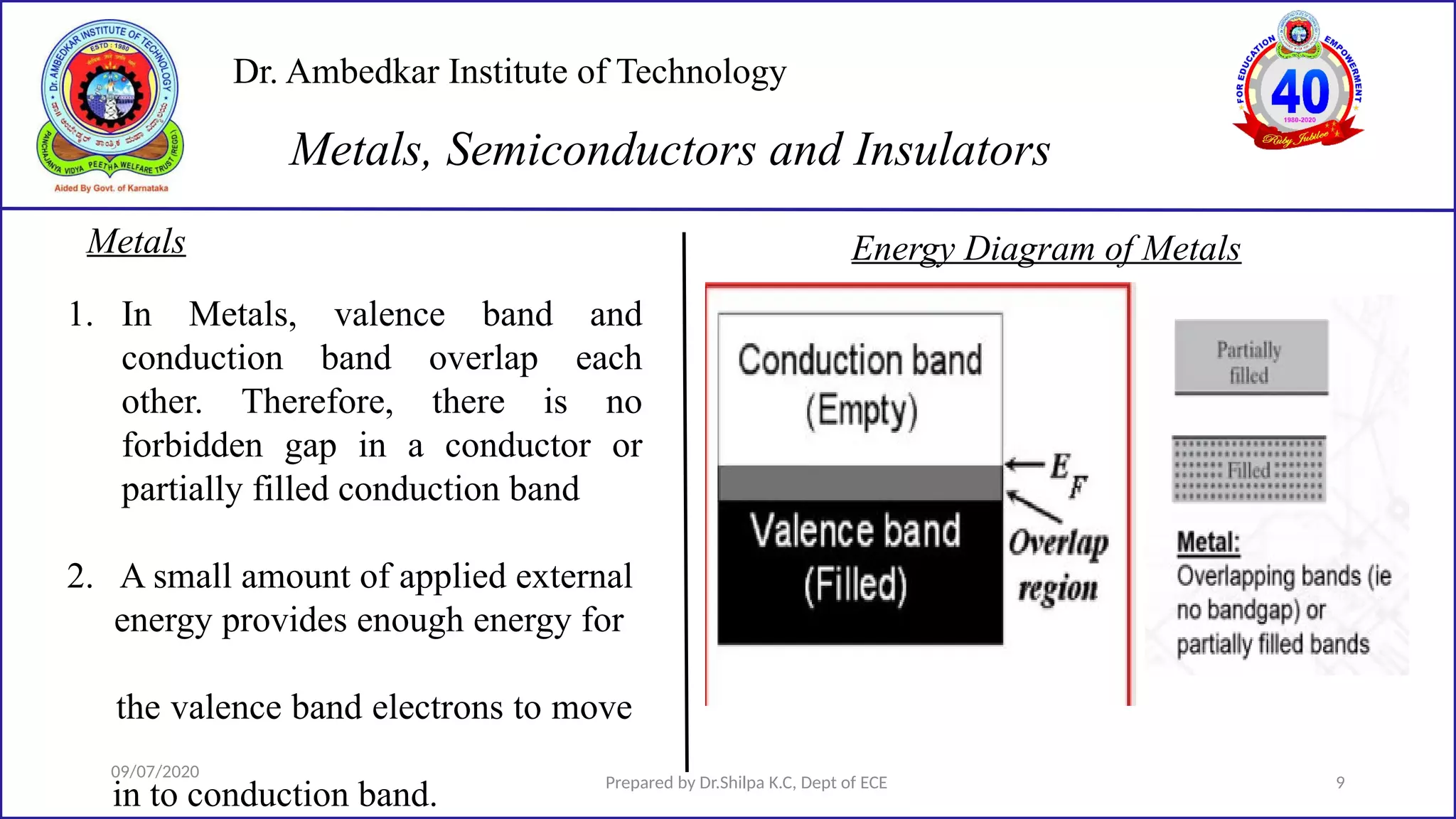
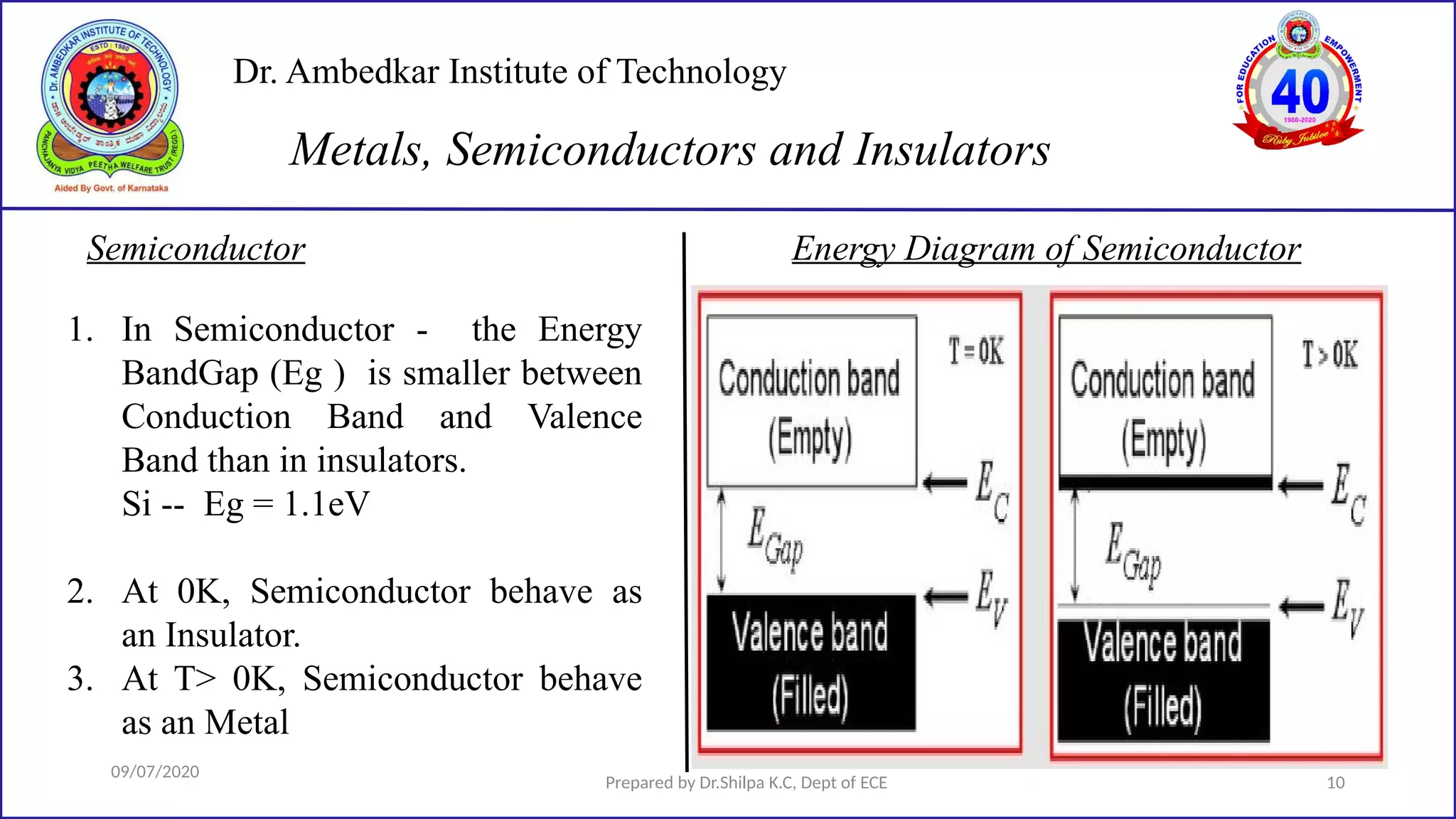
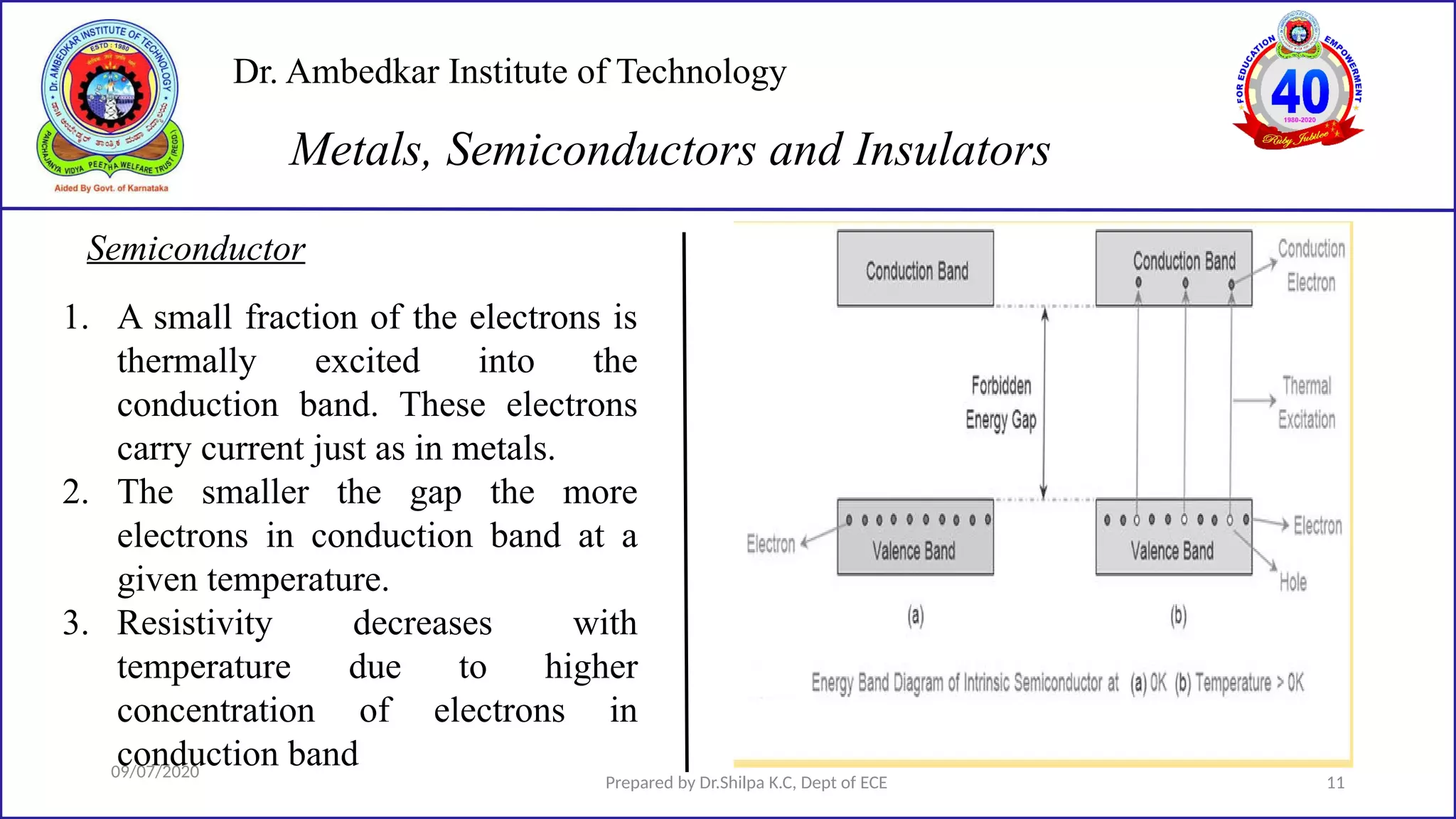
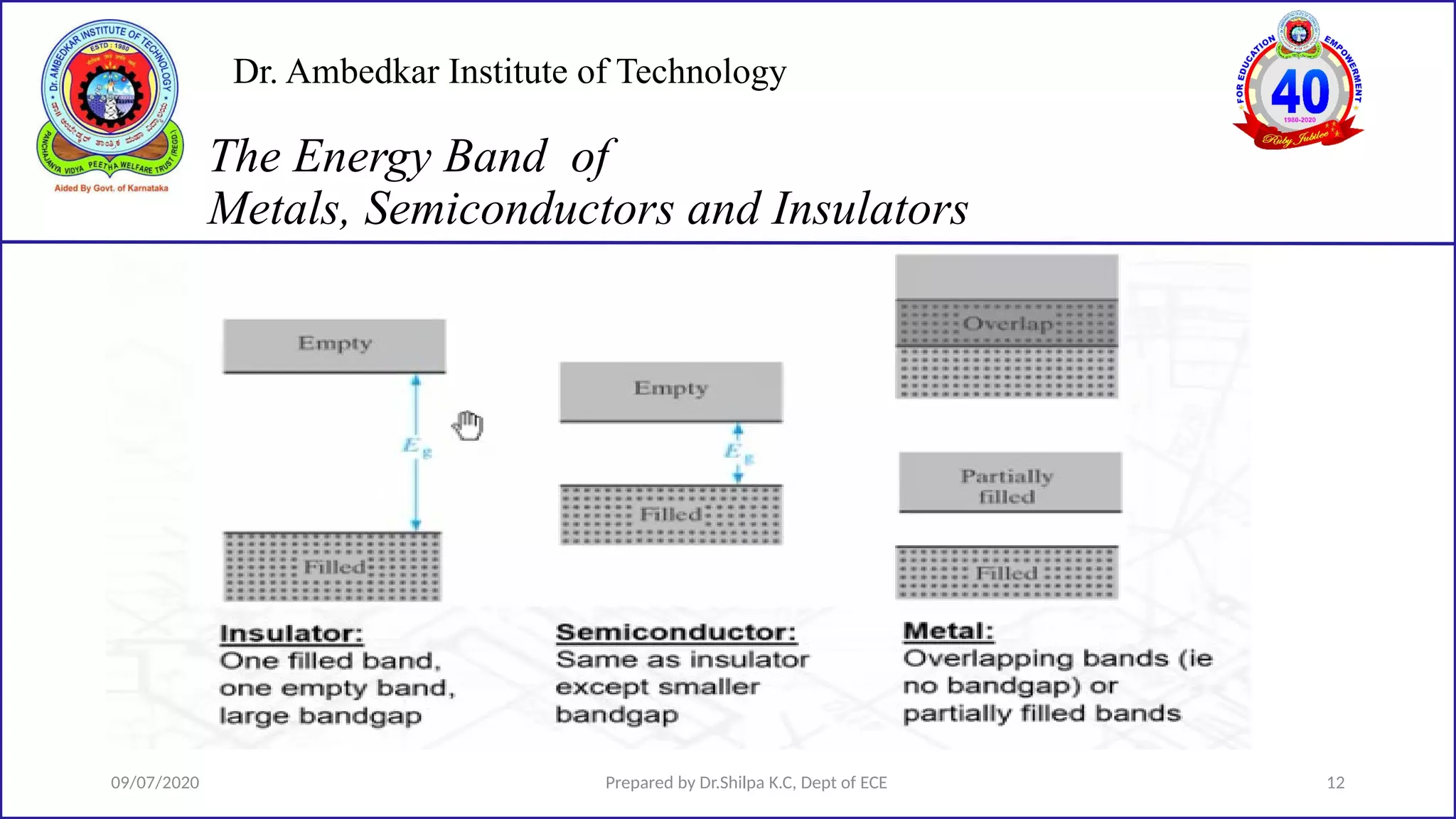
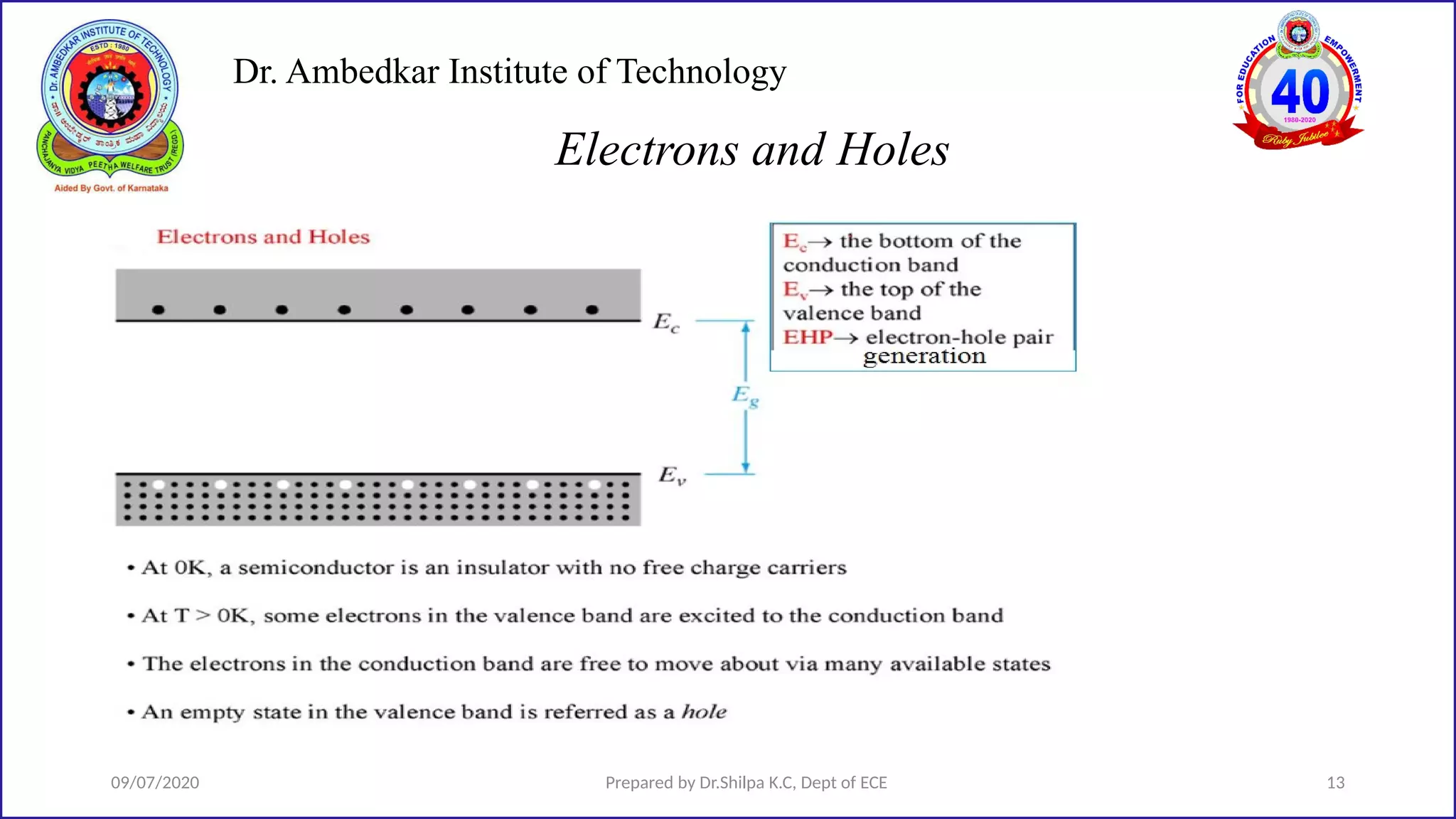
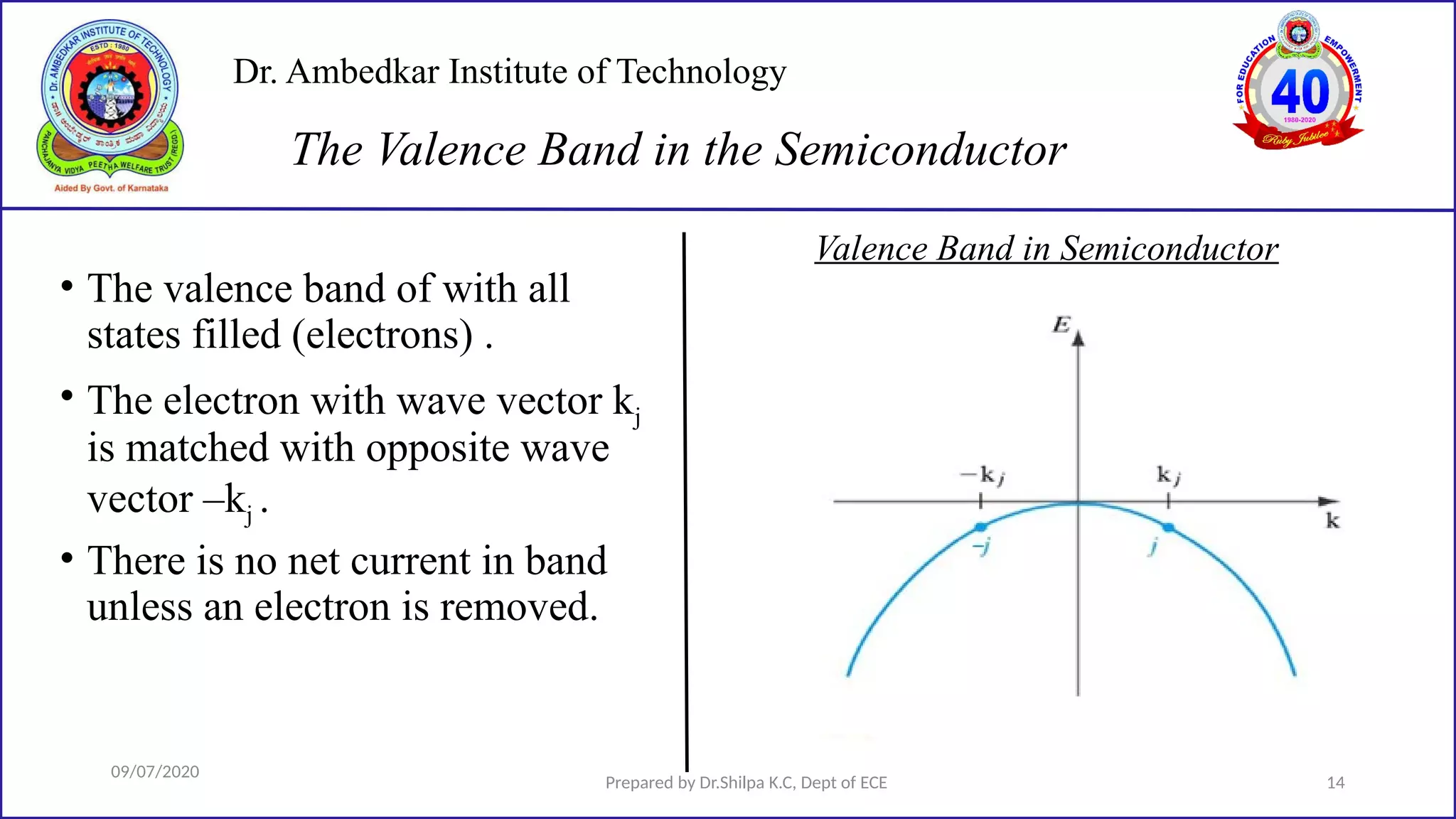
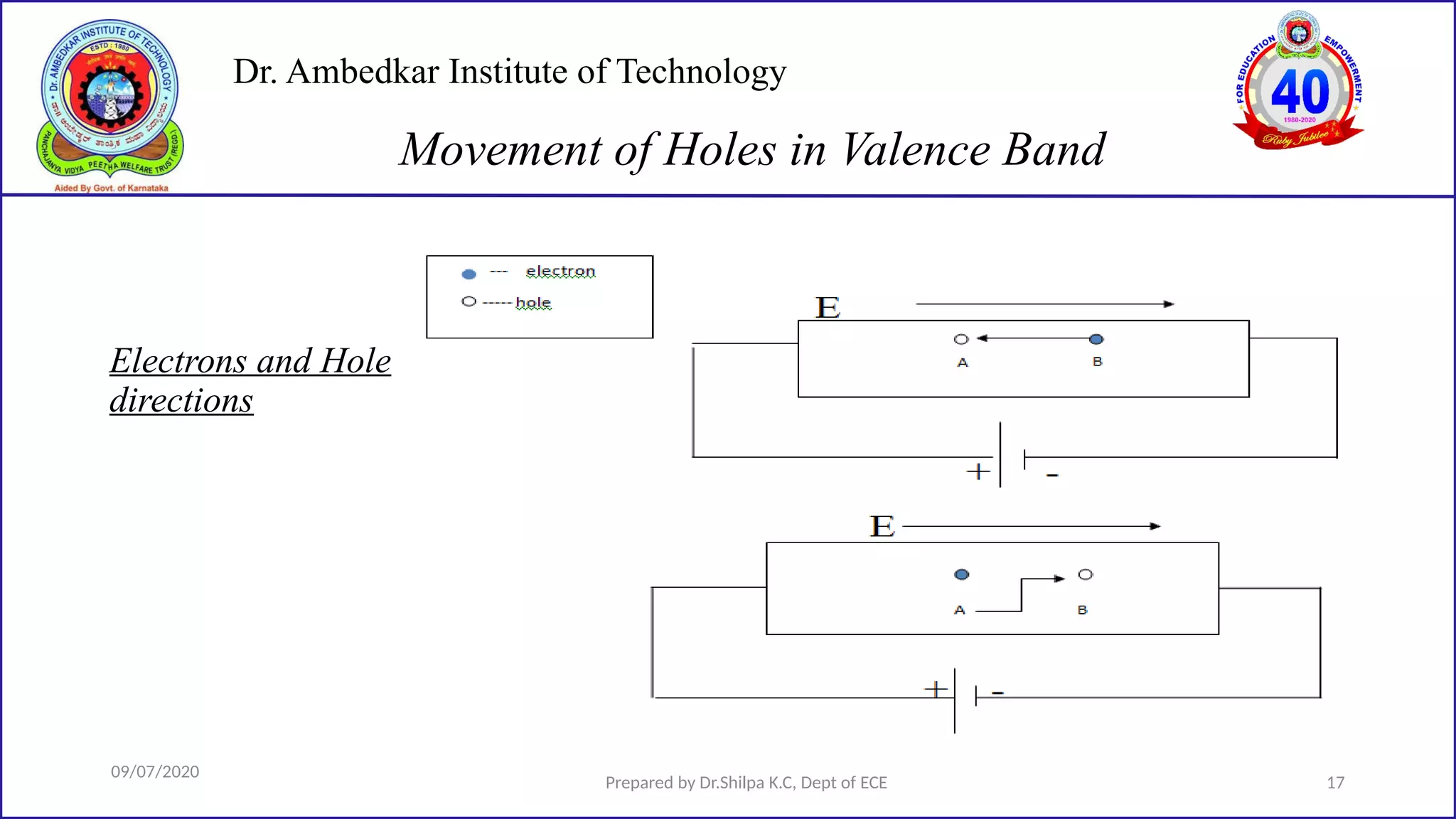
This document is a lecture on semiconductor physics presented by Dr. Shilpa K.C. of Dr. Ambedkar Institute of Technology. It discusses energy bandgaps in semiconductors, including the differences between direct and indirect bandgap semiconductors. It also examines the band structure and energy diagrams of metals, semiconductors and insulators. Finally, it introduces the concept of holes and how their movement in the valence band allows current to flow, similar to the movement of electrons in the conduction band.