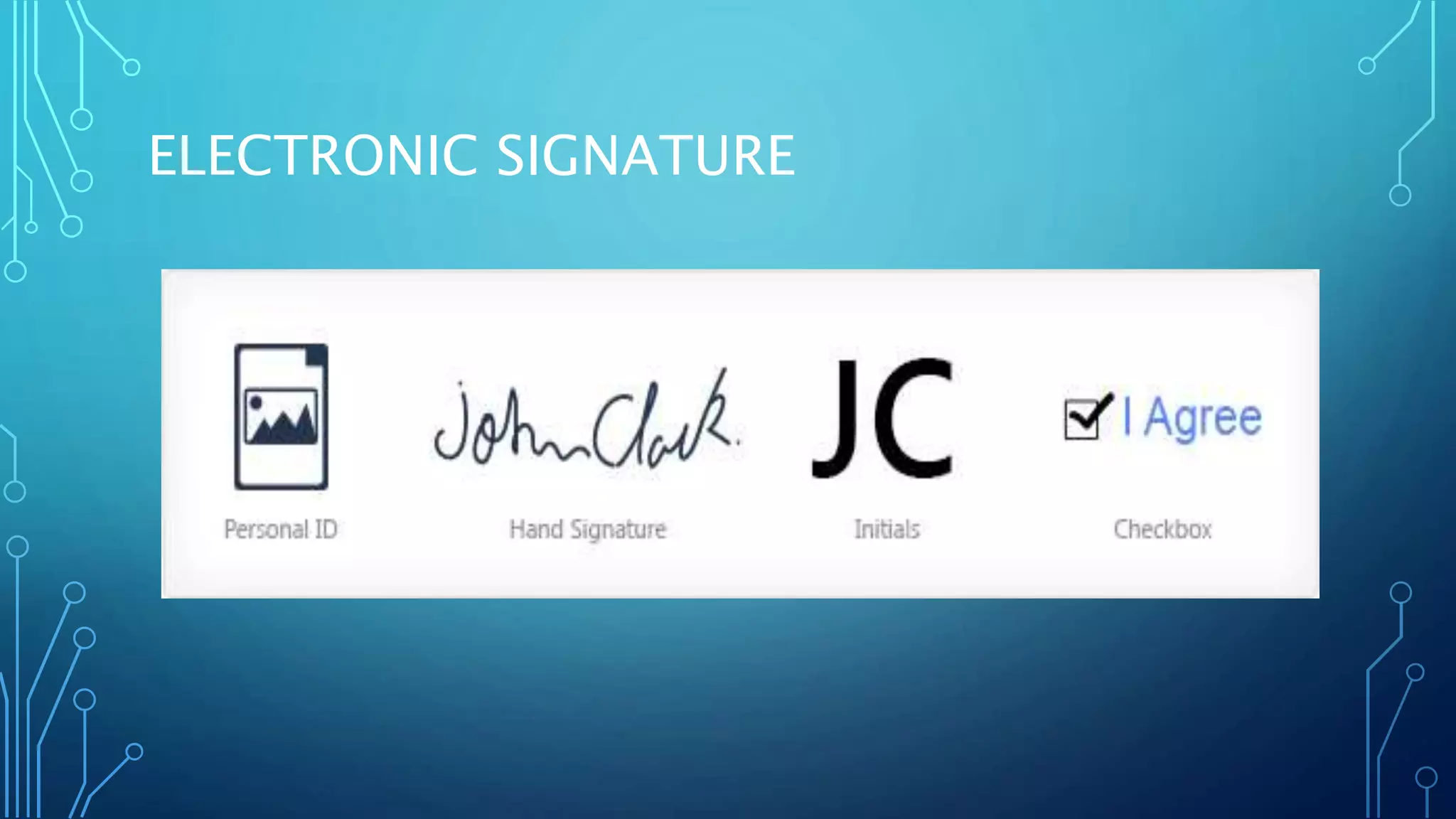
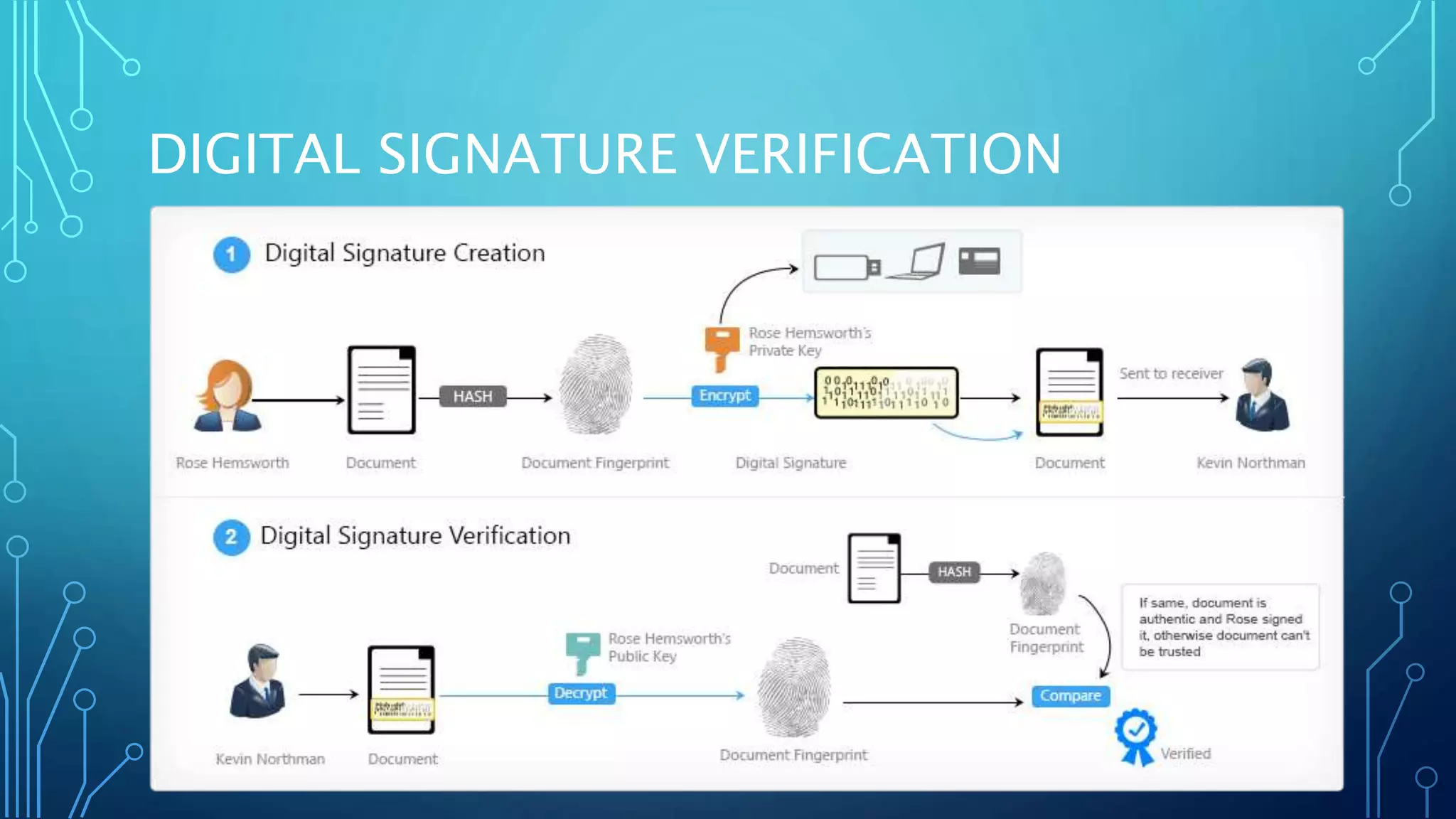
Electronic signatures and digital signatures are often confused but have distinct features and functions. An electronic signature captures a user's intent to sign a record and includes their method of signing, data authentication, and user authentication. A digital signature uses encryption to secure the data associated with an electronically signed document and helps verify its authenticity. When used together, electronic and digital signatures provide a simplified and secure way to electronically sign documents and transactions.