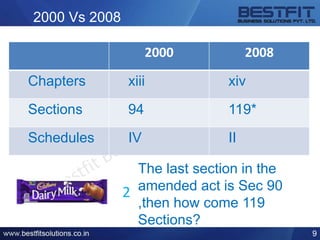
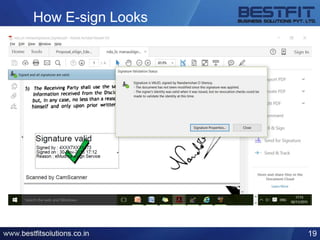
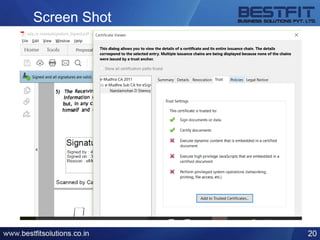
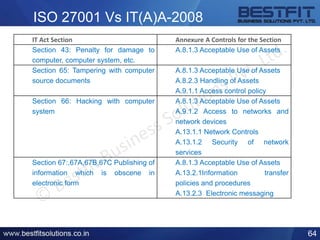
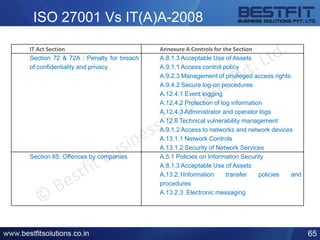
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Information Technology (IT) Act of 2000 and its subsequent amendments in 2008 and beyond, detailing its evolution, important provisions, and significant incidents leading to its updates. Key highlights include the shift in focus from e-commerce in 2000 to data protection and cybersecurity in 2008, along with the introduction of legal recognition for electronic records and signatures. Additionally, the document outlines penalties for computer-related offences and emphasizes the necessity of reasonable security practices to protect sensitive personal data.