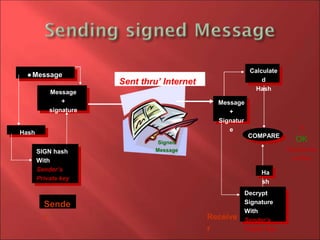
This document discusses digital signatures and how they provide authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation for electronic documents. It explains that a digital signature is created by encrypting a hash of a message with the sender's private key. The recipient can then decrypt the signature using the sender's public key to verify their identity and confirm the message has not been altered. Digital signatures are commonly used for software distribution, financial transactions, and anywhere tampering detection is important. They allow for secure electronic communication and commerce by helping to prevent forgery over the internet.






![Caesar Cipher
The shift is linear and equidistributed 3
changes
I agree lcdjuhhKey Cipher
The shift is linear (cyclic) 269
k.n.gupta 62 mewam3rzjba
i+3=l
Space=c
[+3]
k+2=
m
(dot)=e
[+6]
n=w
[+9]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/digitalsignature-160912142432/85/Digital-signature-7-320.jpg)