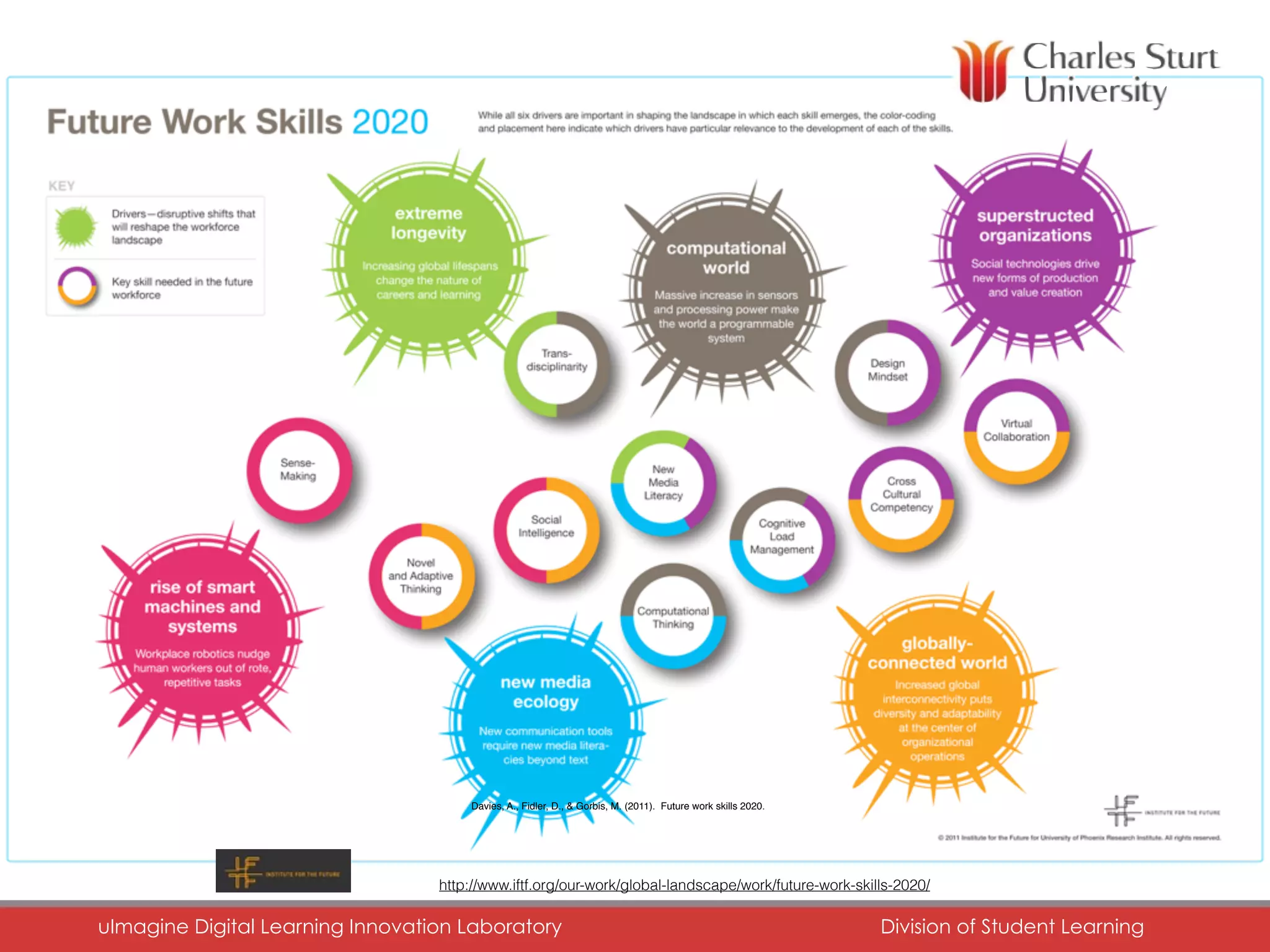
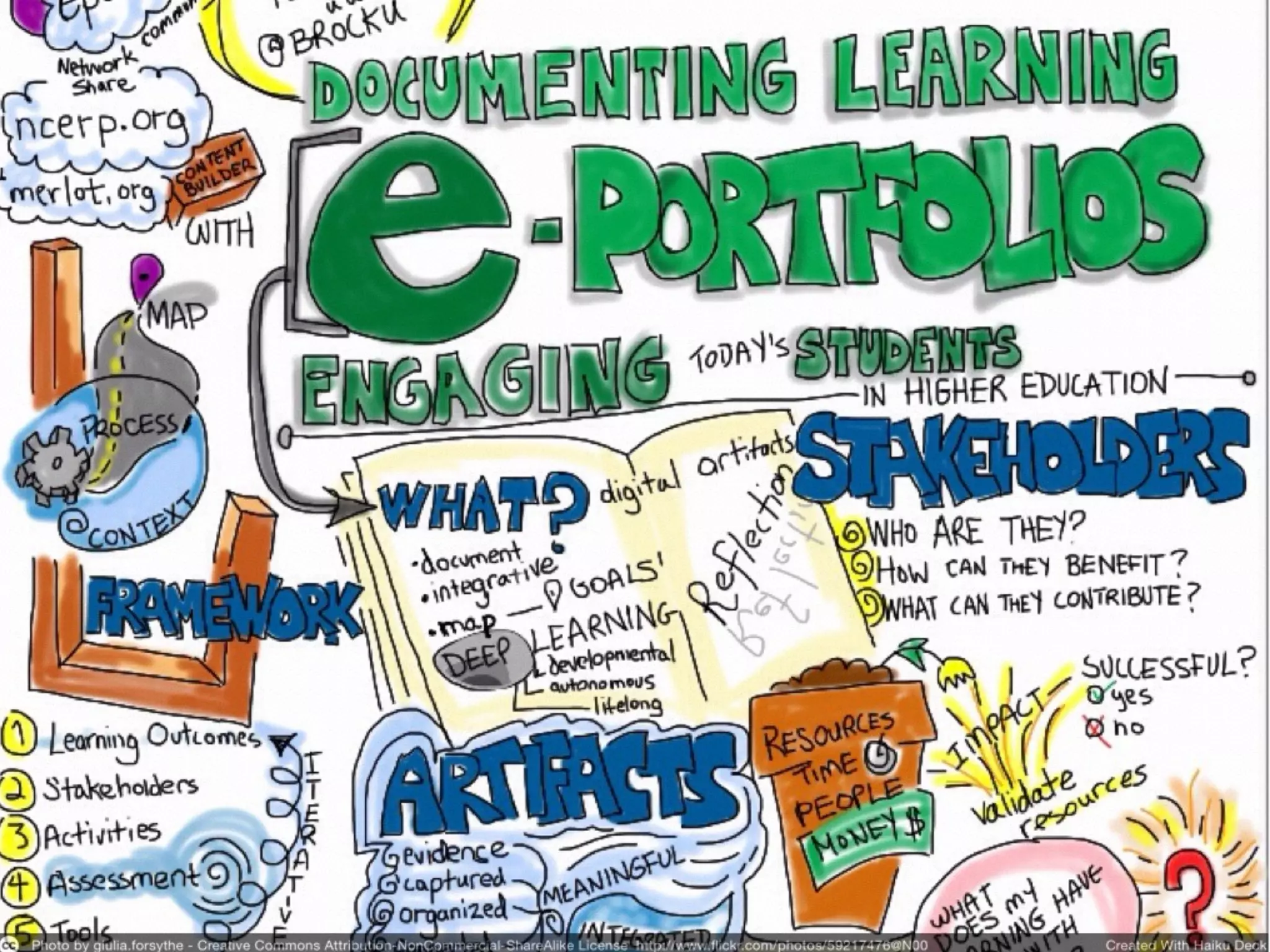
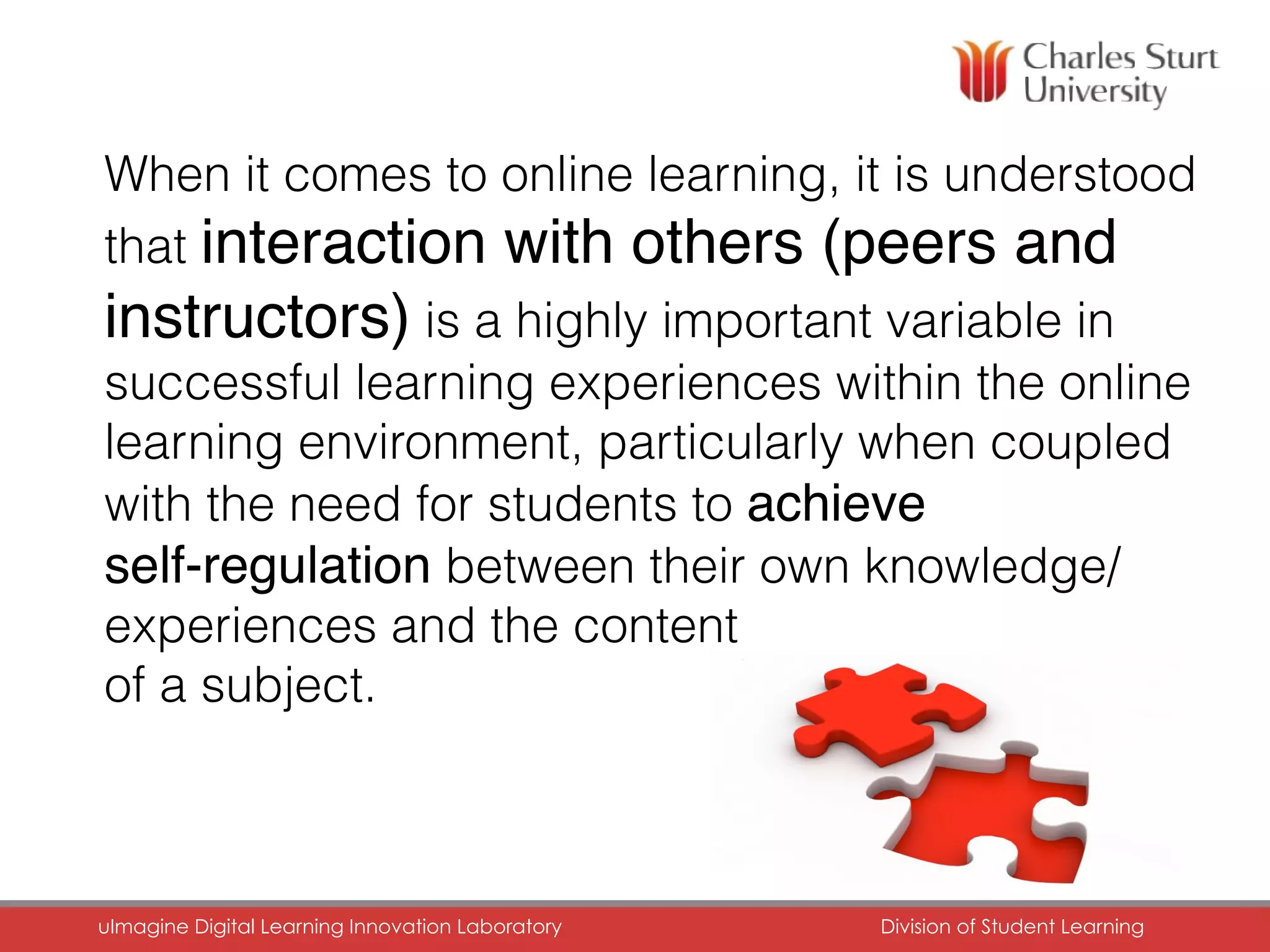
The document discusses the role of digital portfolios in enhancing learning experiences in higher education by fostering reflection, self-assessment, and professional engagement. It emphasizes the importance of adapting pedagogical practices to leverage digital environments, supporting skills in digital literacy, collaboration, and critical thinking. Ultimately, it advocates for a redesign of academic programs to integrate portfolios as a means of demonstrating competencies in an interconnected learning context.