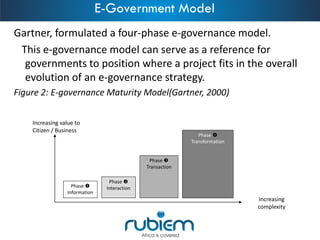
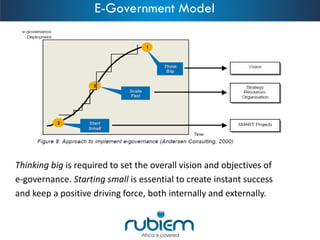
1. The document discusses e-government and outlines a 4-phase model of e-government maturity from information to transformation.
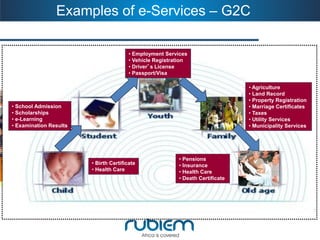
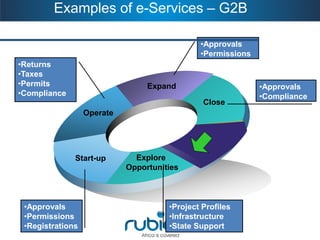
2. It provides examples of e-services from government to citizens and businesses.
3. The benefits of e-government to government are described as better delivery of services, cost cutting, and increased transparency and revenues.