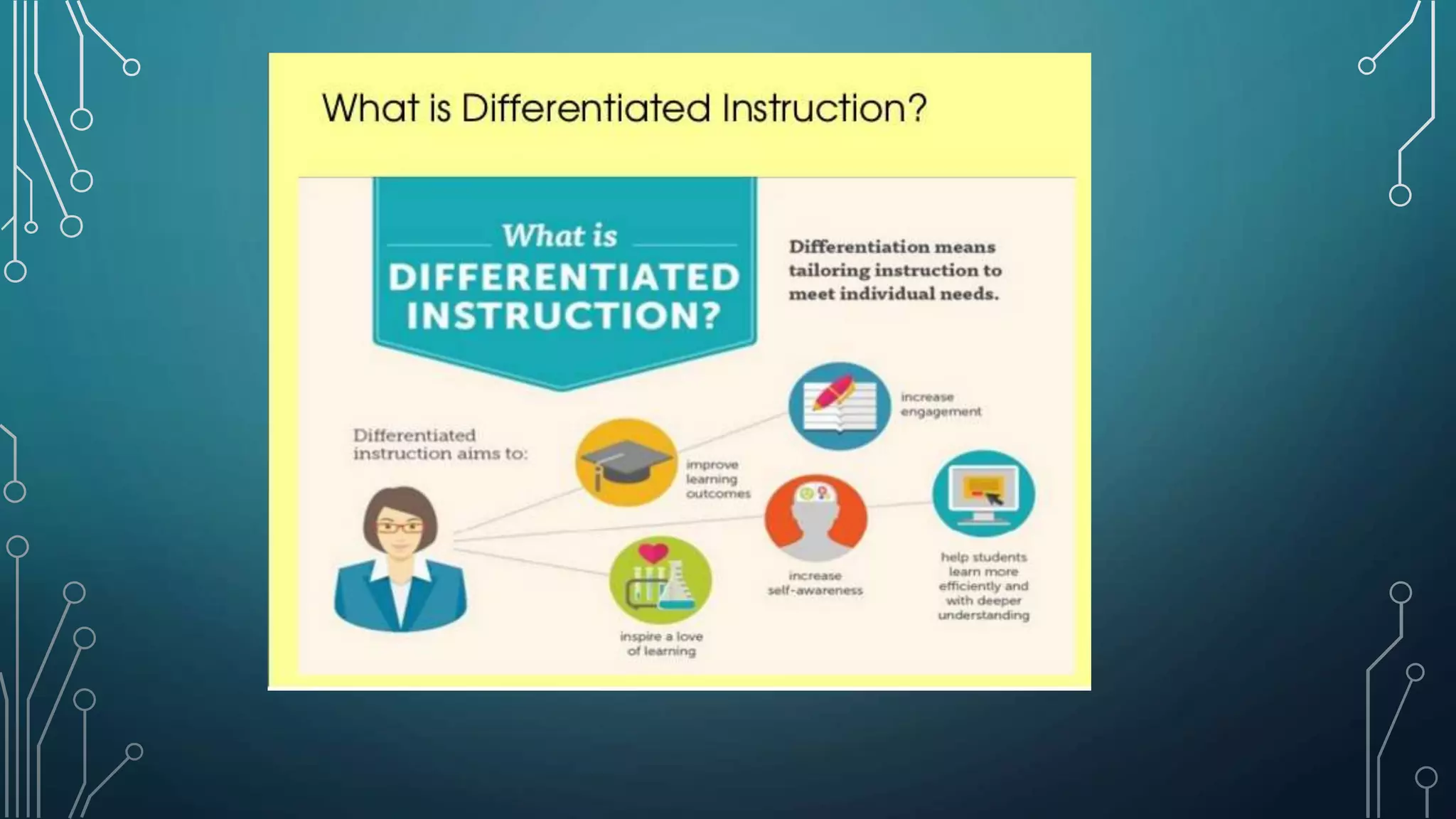
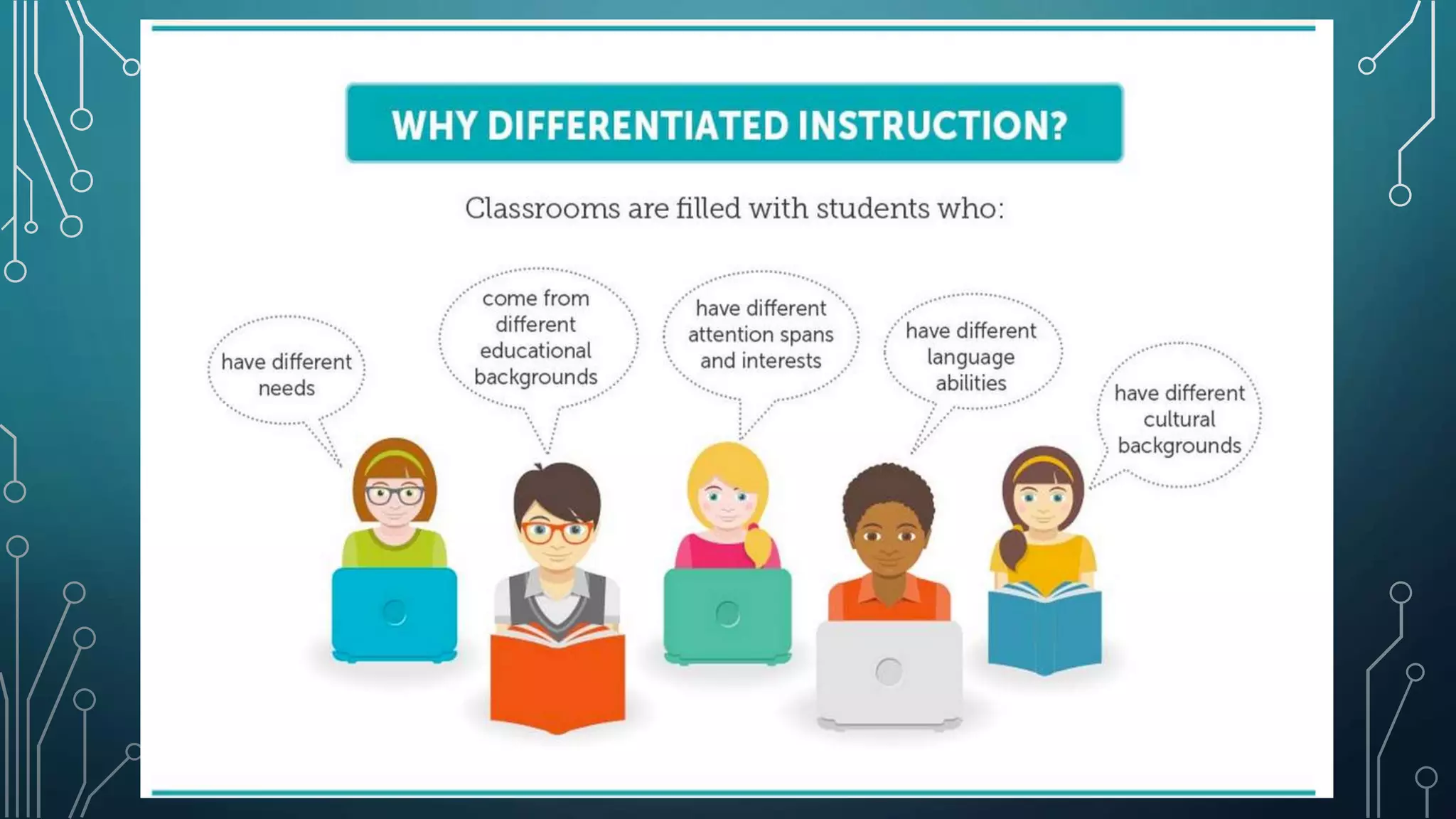
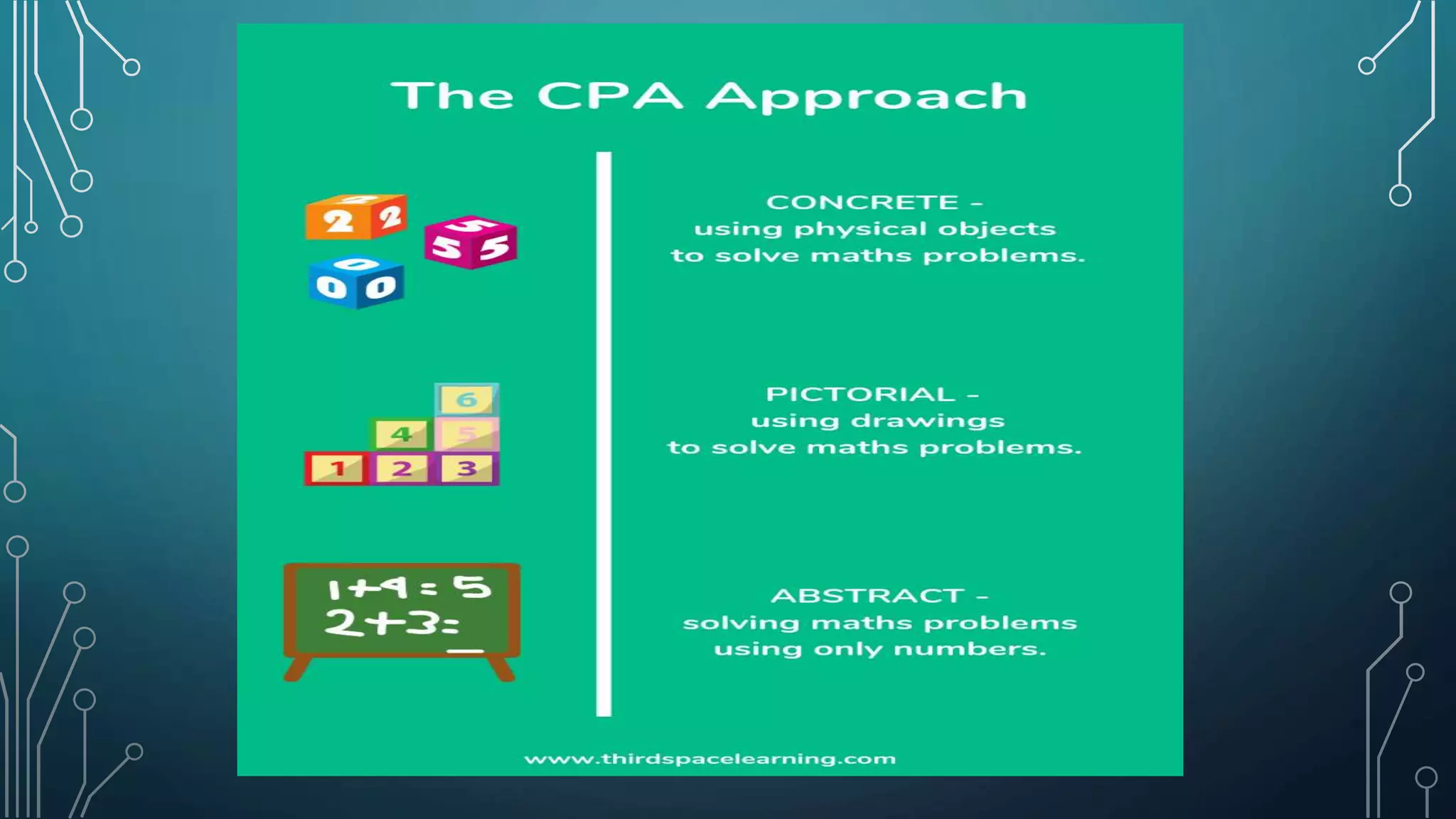
Differentiated learning in mathematics involves adapting instructional strategies to meet the varied needs of students, considering their readiness, interests, and learning profiles. Key principles include collaborative learning, flexibility in instruction, and the use of diverse teaching materials and assessment methods to promote individual growth. Effective differentiation enhances students' problem-solving and reasoning skills while connecting mathematical concepts to real life.