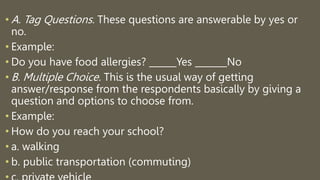
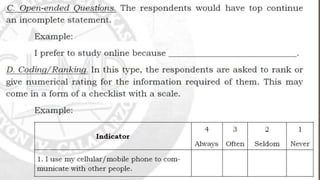
1. There are several ways to collect data for research including mechanical devices, clerical tools, and common methods like interviews, questionnaires, tests, observation, and focus groups.
2. The choice of research instruments is an important decision for the researcher as it is the channel through which they will gather needed data.
3. Good data collection instruments should be brief, efficient, systematically sequenced, valid and reliable, and researcher and sample friendly to easily collect rich information.