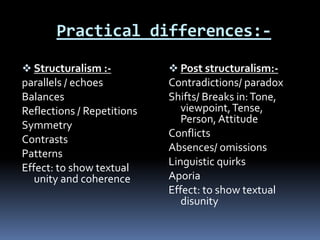
This document compares structuralism and post-structuralism. Structuralism derives from linguistics and aims to find reliable truths by observing patterns in a logical, systematic way. It views language as an orderly system. Post-structuralism derives from philosophy and questions assumptions with a skeptical, emotive tone. It sees language as threatening and meaning as fluid. While structuralism seeks to understand reality through categorization, post-structuralism fundamentally questions concepts of human beings and civilization. In practice, structuralism looks for parallels and patterns in texts, while post-structuralism finds contradictions and shifts to show textual disunity.