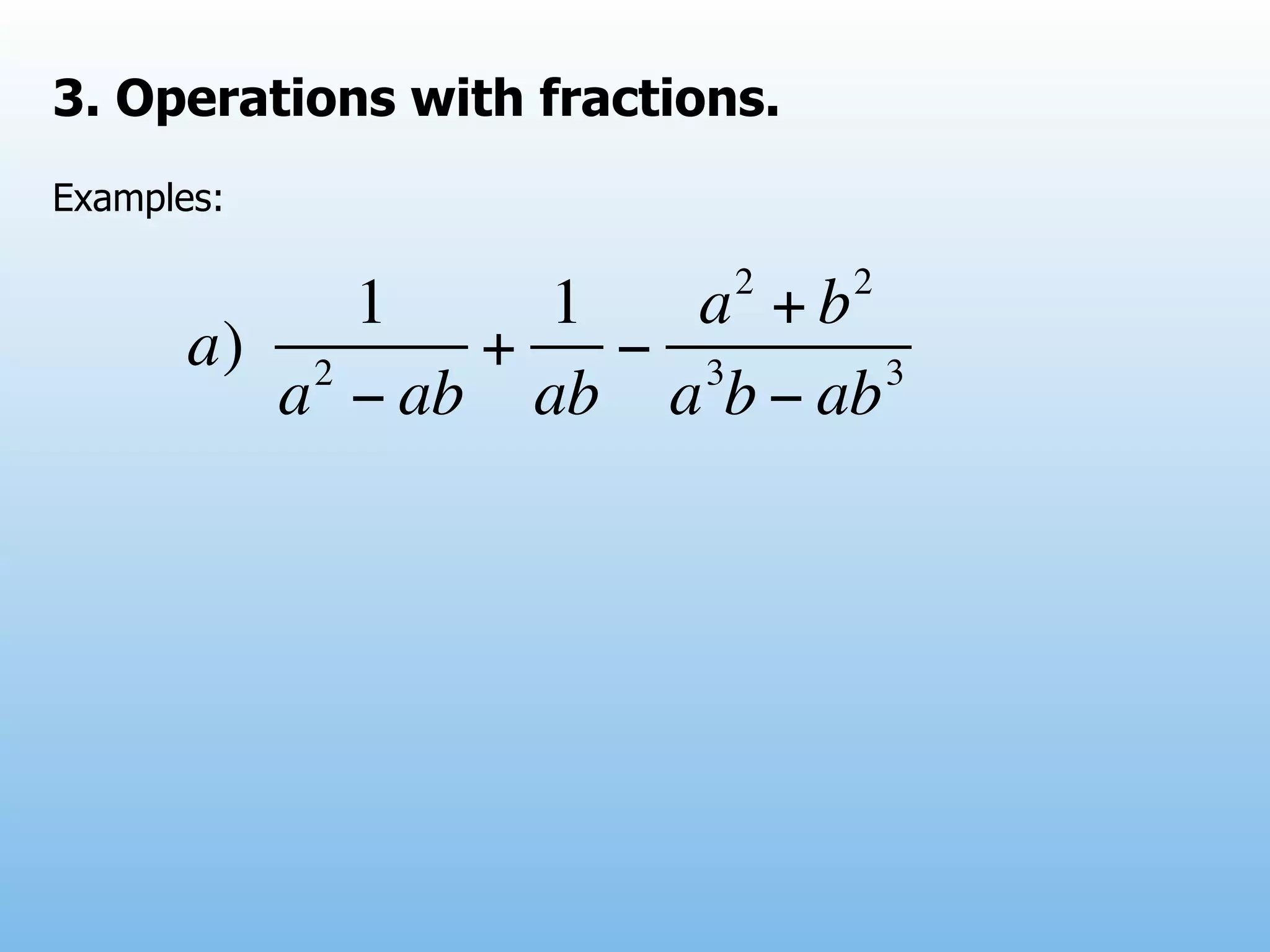
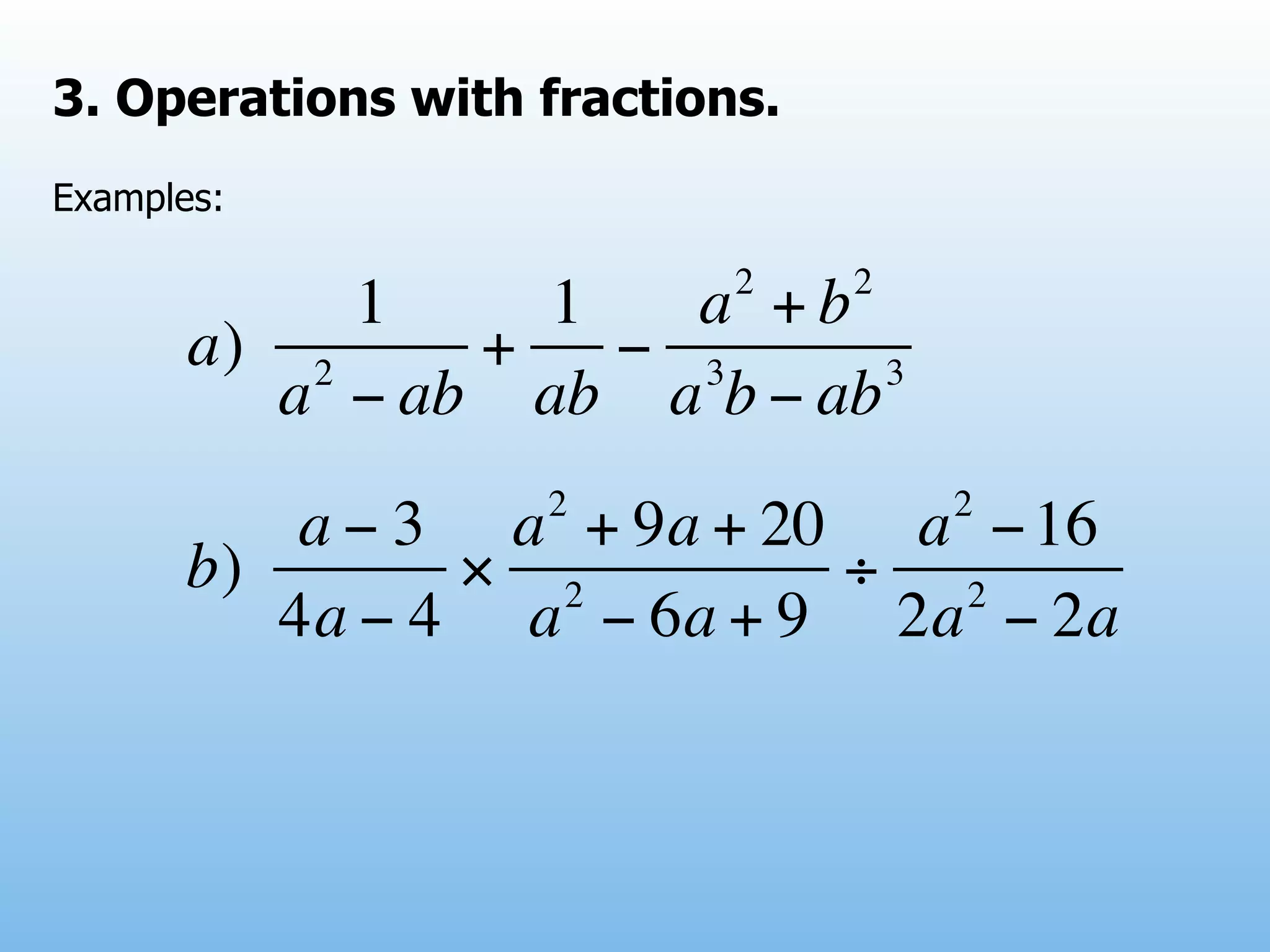
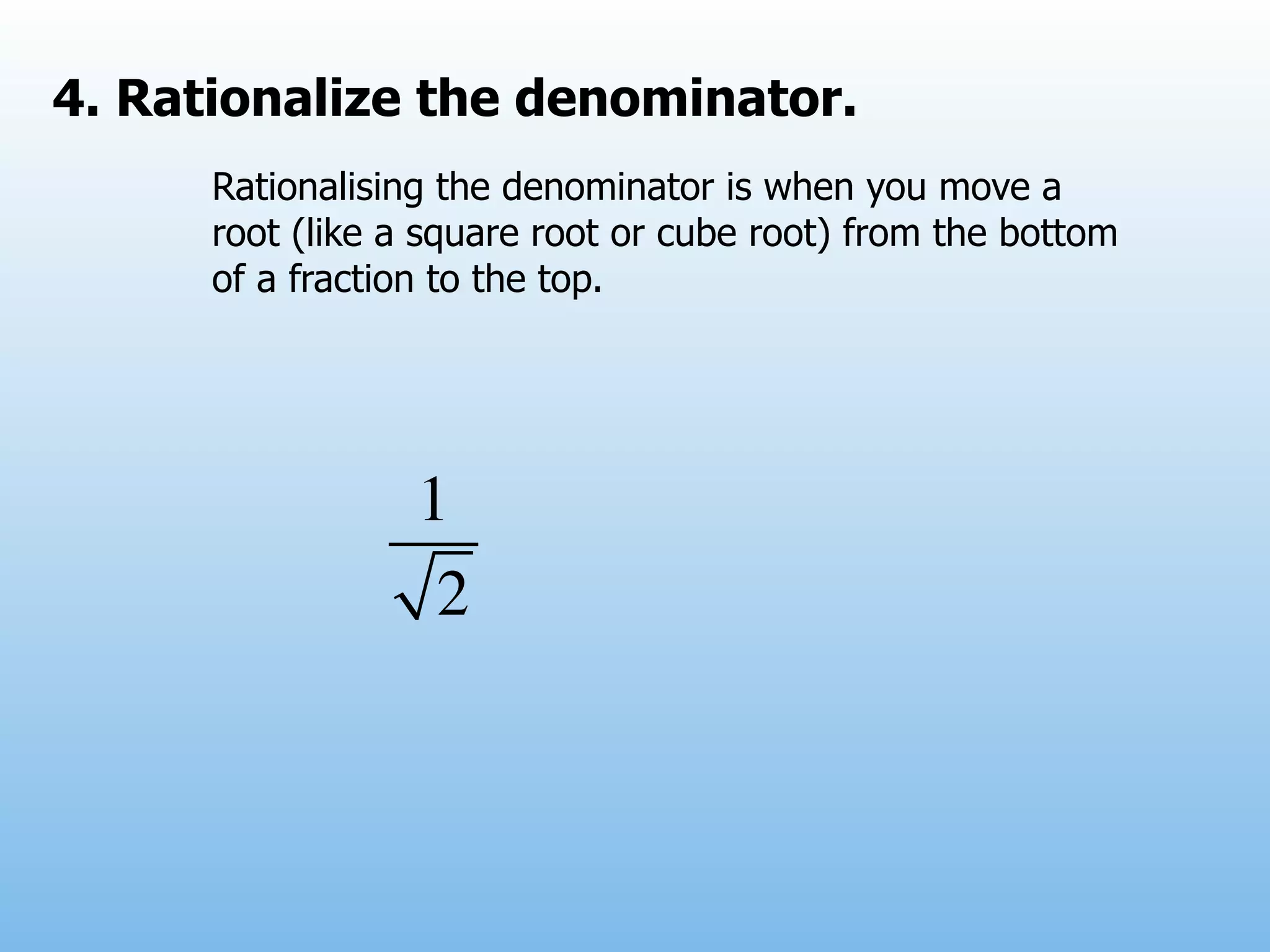
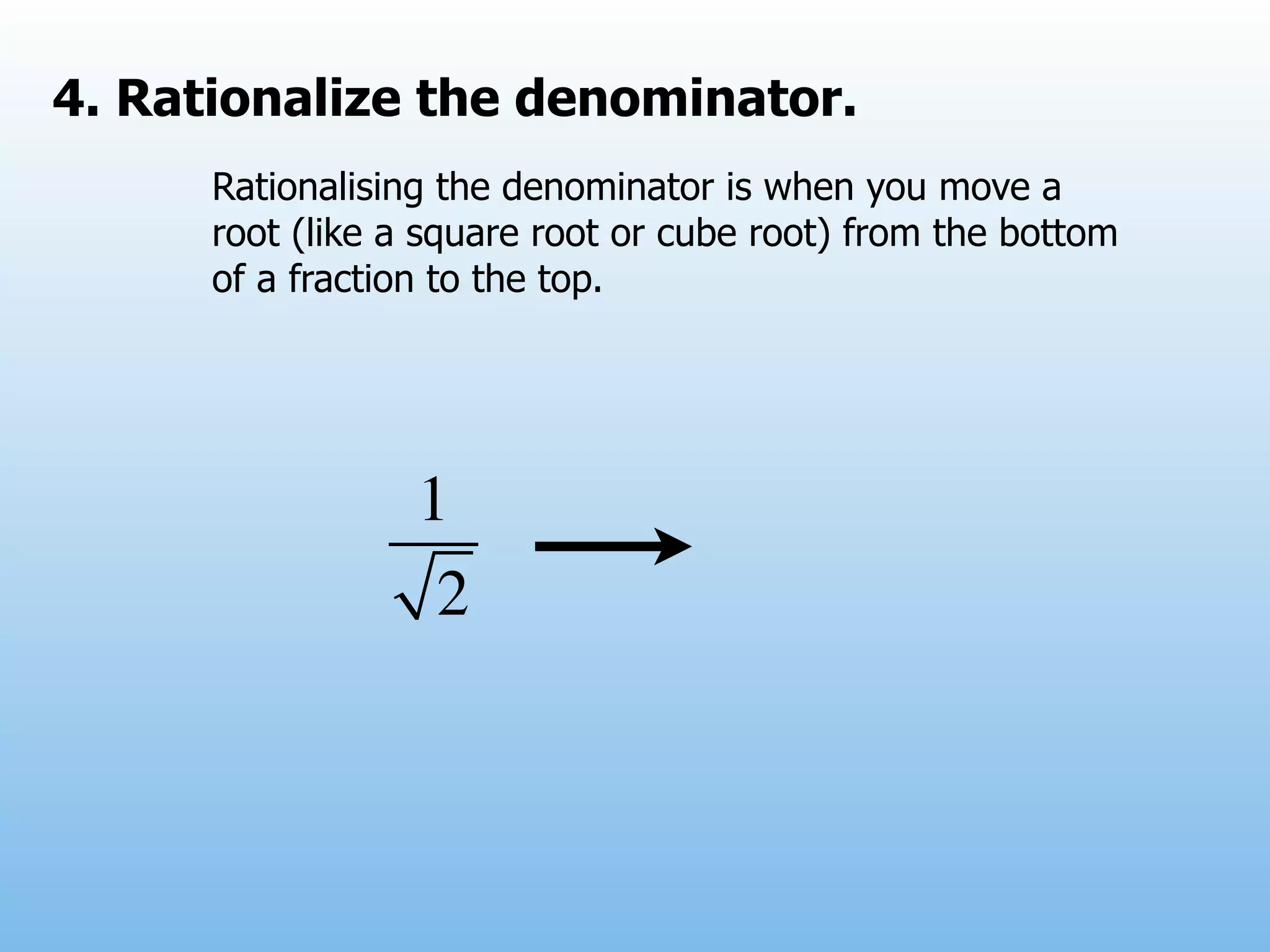
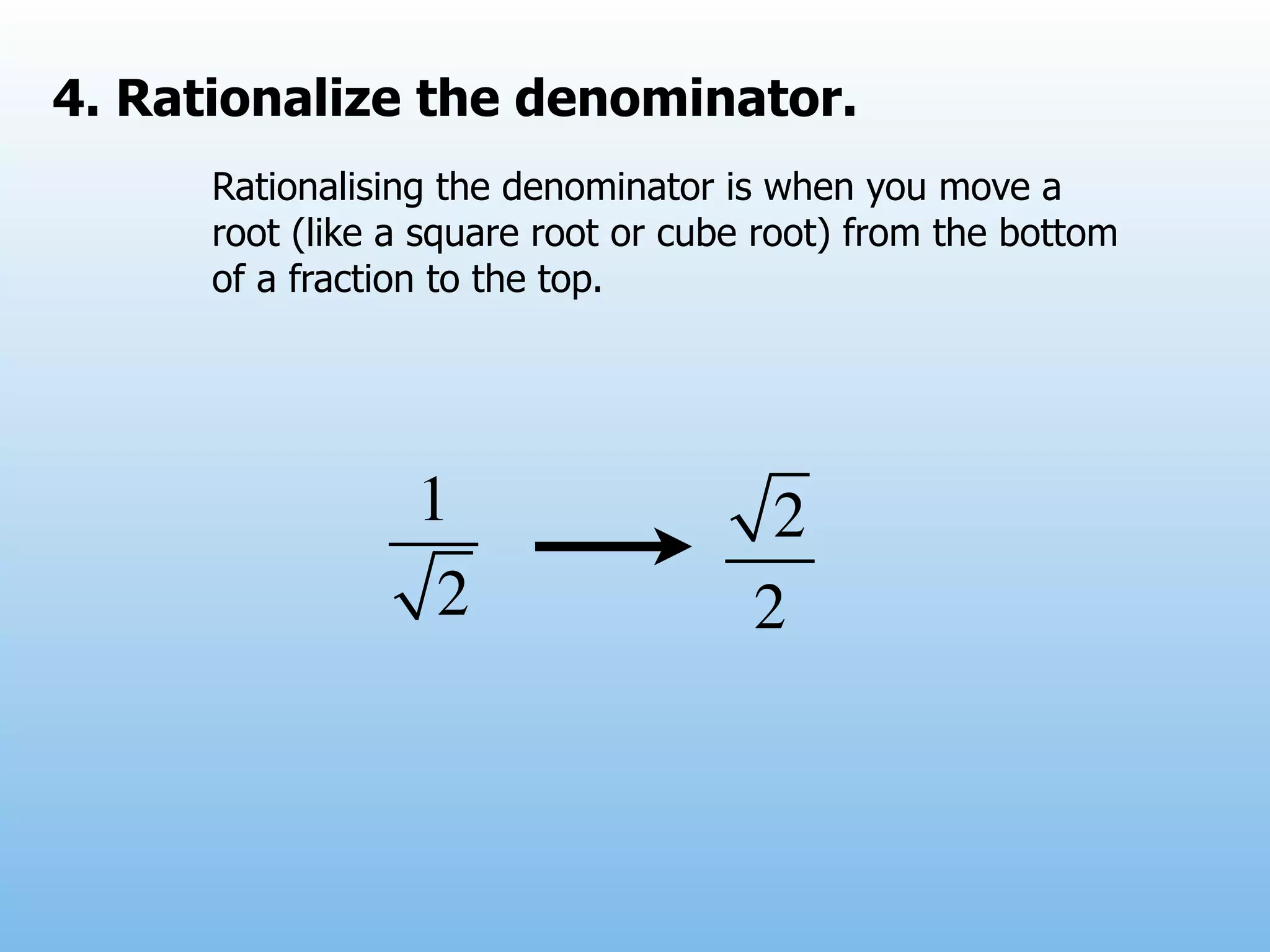
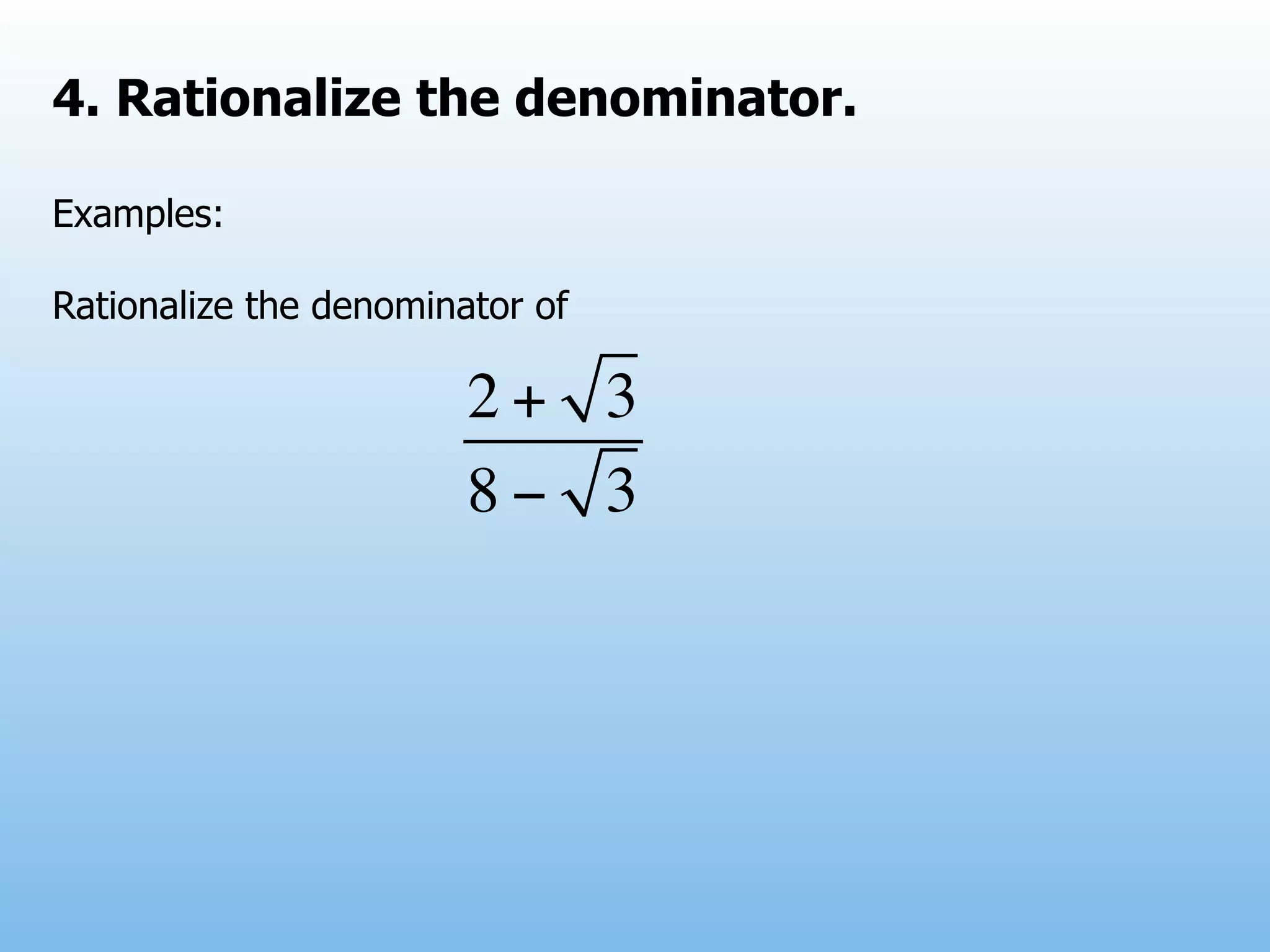
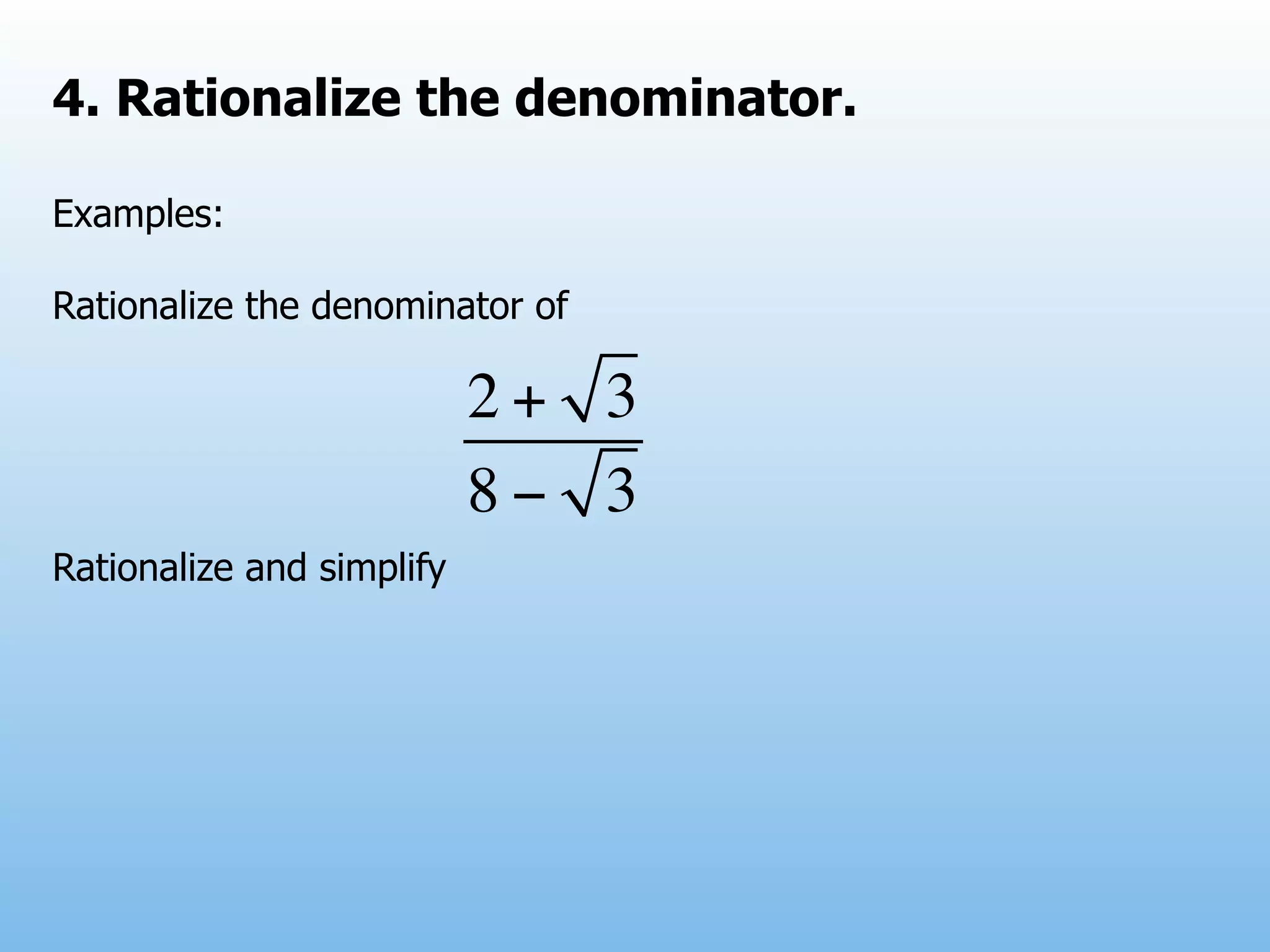
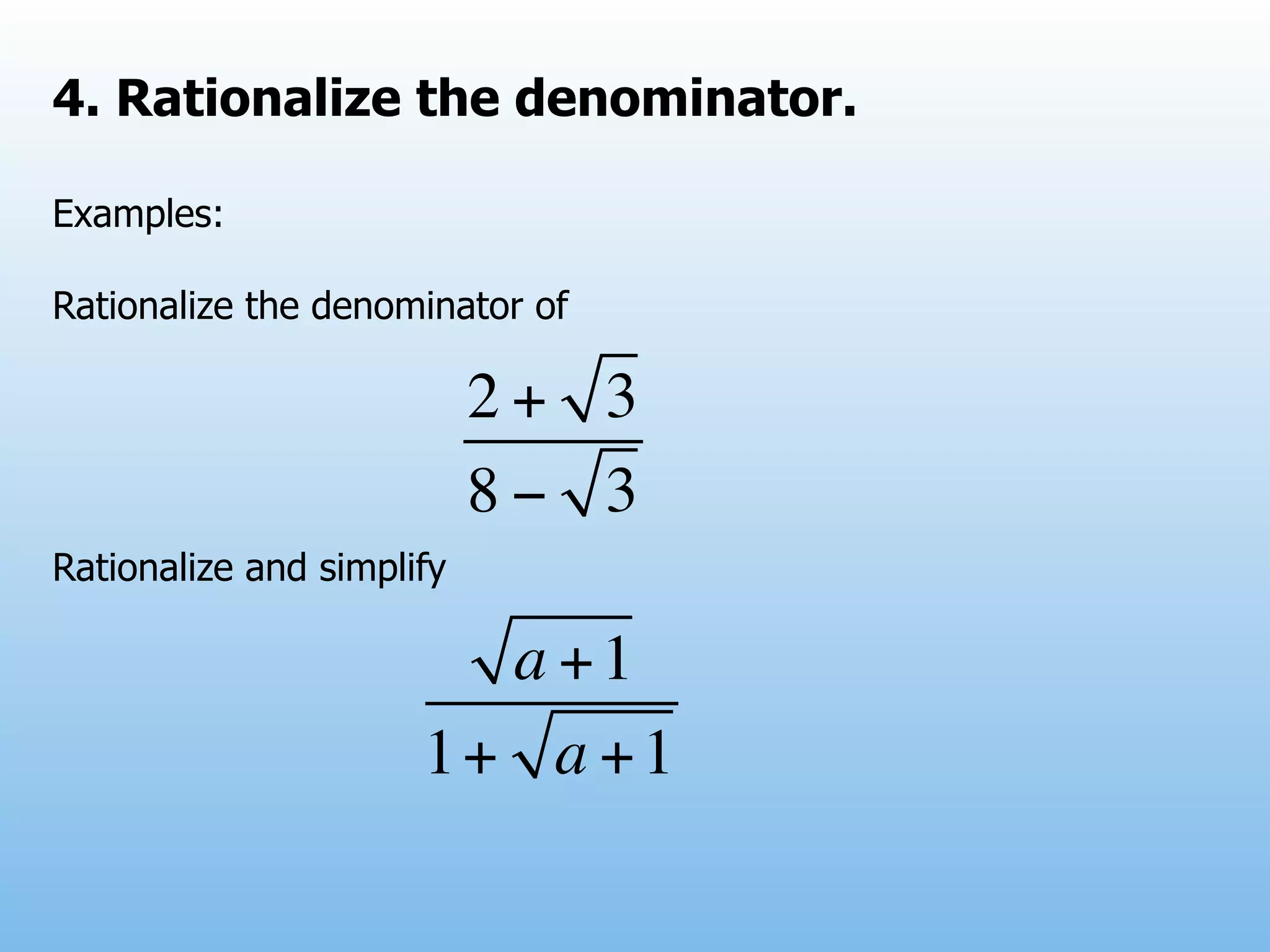
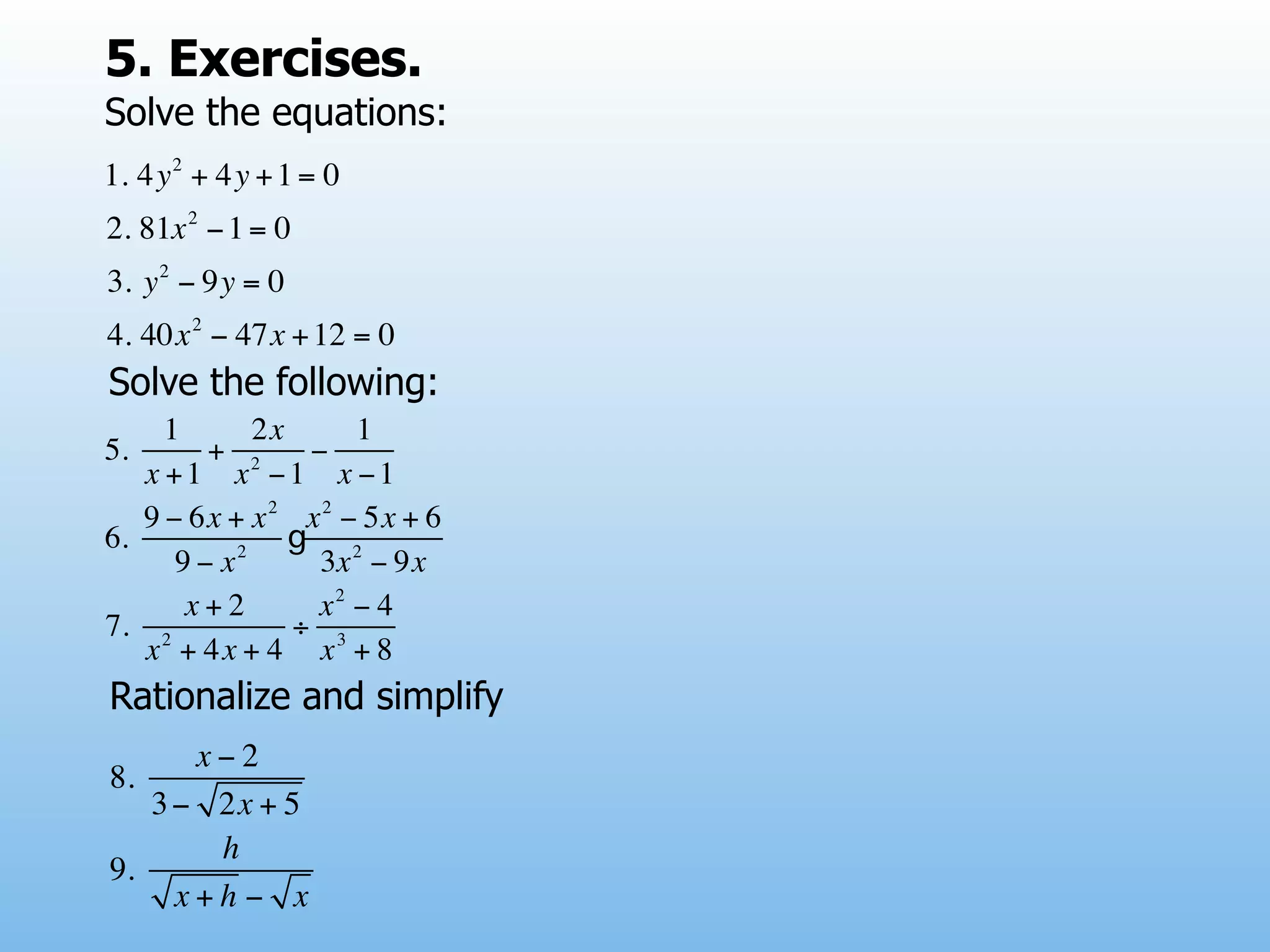The document provides examples and explanations of operations with fractions, including adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing fractions. It also explains how to rationalize the denominator of a fraction by moving a root from the bottom of a fraction to the top. Some examples of rationalizing denominators are shown. Finally, it lists some exercises involving solving equations, rationalizing denominators, and performing operations with fractions.