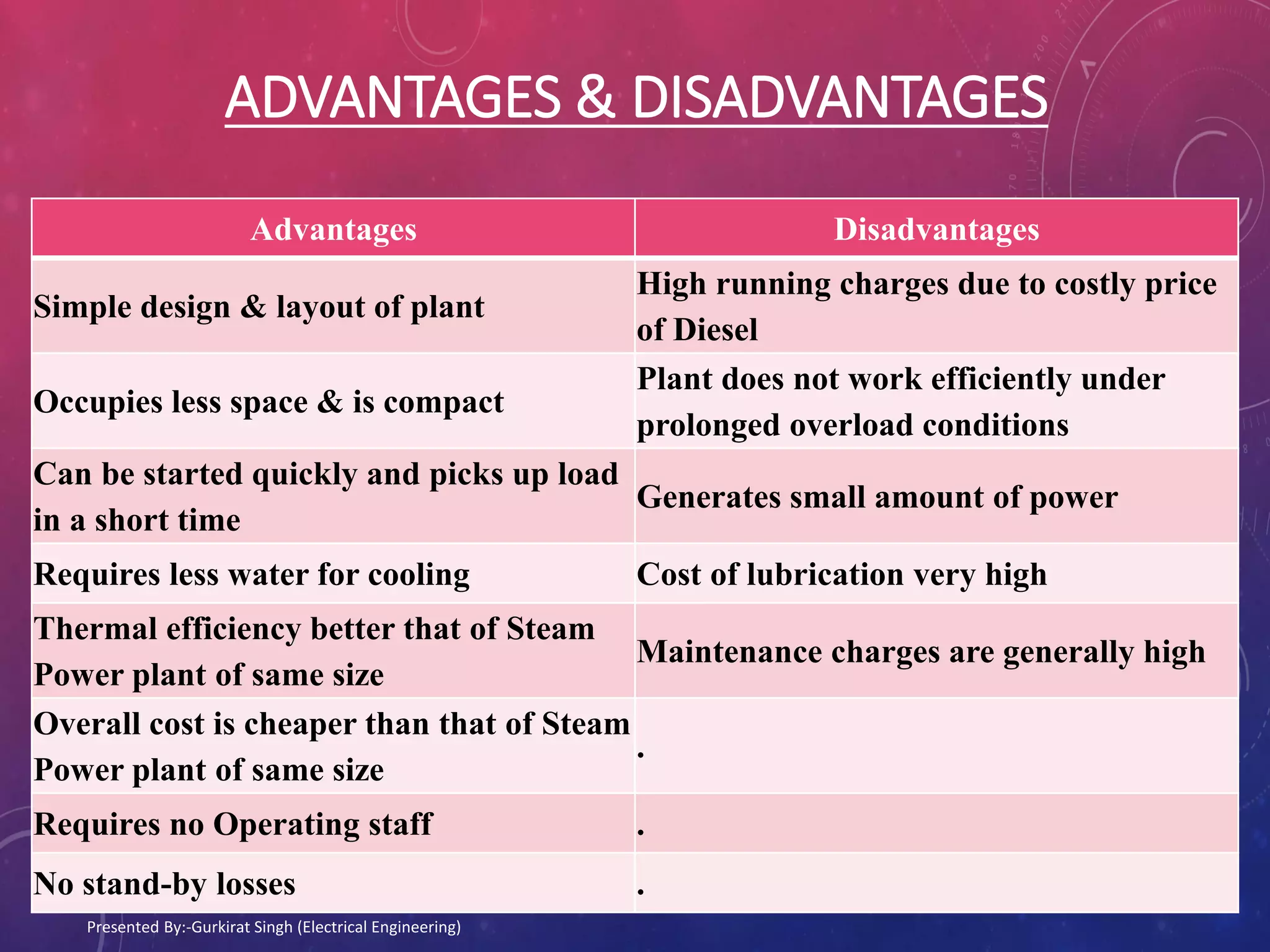
The document presents an overview of diesel power plants, detailing their working principles, advantages and disadvantages, and factors influencing site selection. It contrasts two- and four-stroke diesel engines, highlighting their operational differences, efficiency, and design complexities. Additionally, key terms related to internal combustion engines and operational mechanics are defined to provide a comprehensive understanding of diesel engine technology.