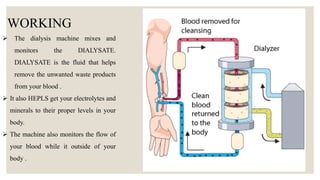
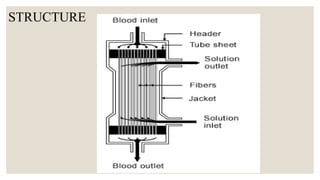
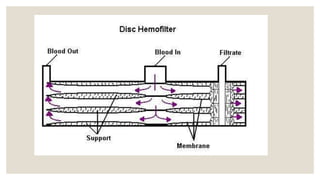
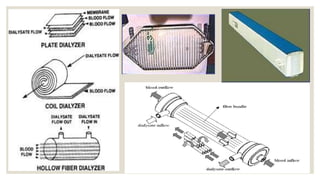
The document discusses dialysis machines, specifically dialyzers, which act as artificial kidneys to assist patients with renal failure by clearing toxins and balancing blood constituents. It highlights the history of dialysis, the components and working principles of dialyzers, and various types of dialyzers, including their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it mentions potential reactions to different dialyzer membrane types and the overall application of hemodialysis in medicine.