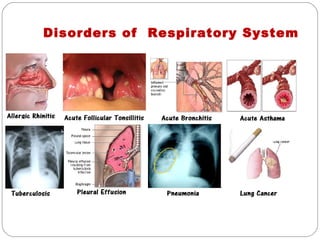
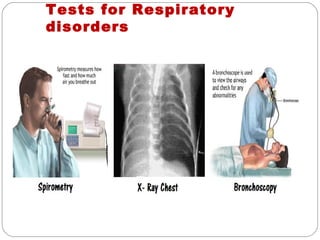
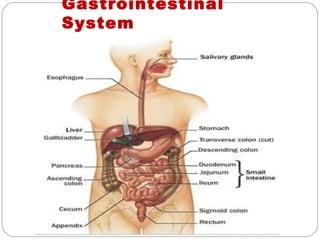
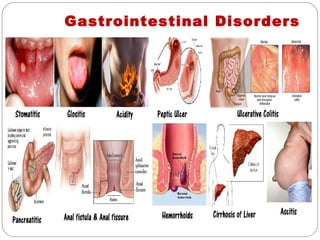
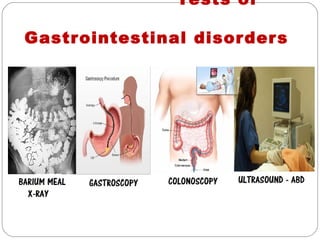
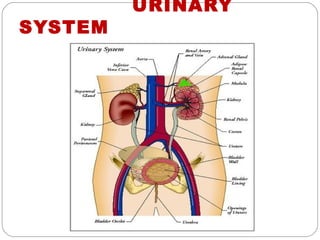
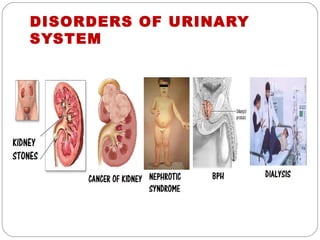
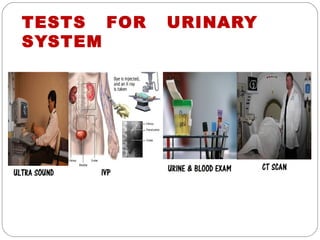
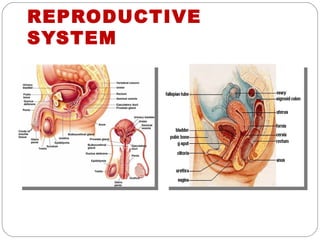
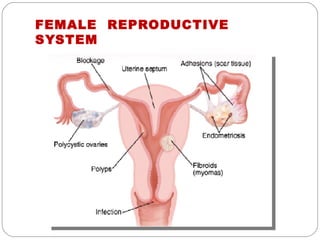
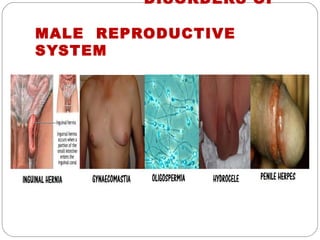
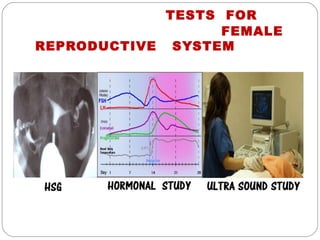
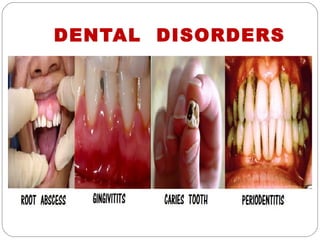
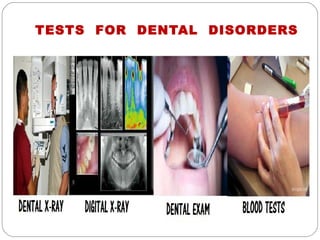
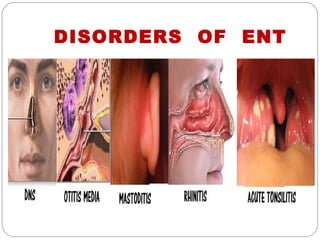
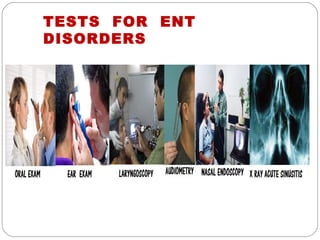
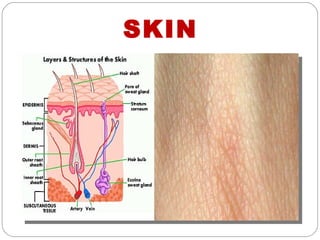
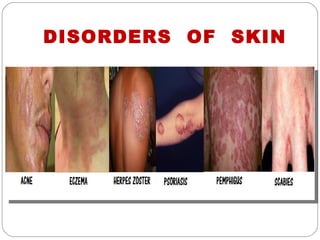
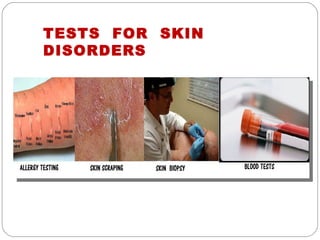
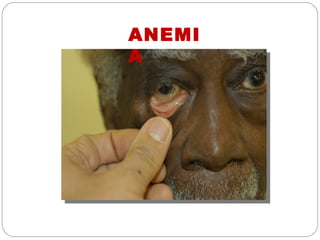
The document provides information about the major body systems including:
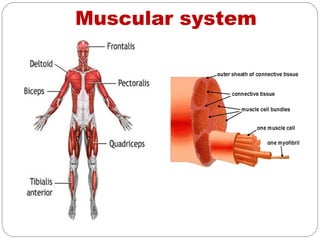
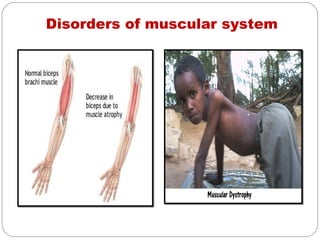
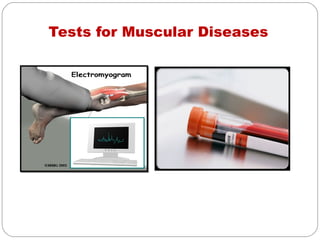
- Muscular system which produces movement through skeletal muscles, cardiac muscles and smooth muscles. It discusses disorders like muscle pain, spasms and reduction in size.
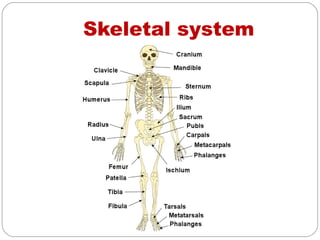
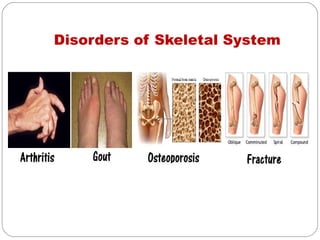
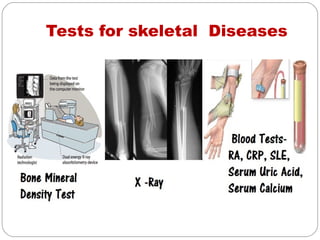
- Skeletal system which provides structure, movement and protection through bones, ligaments and joints. Disorders cause pain, swelling and stiffness in joints.
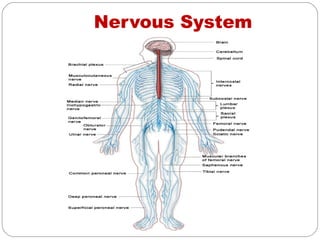
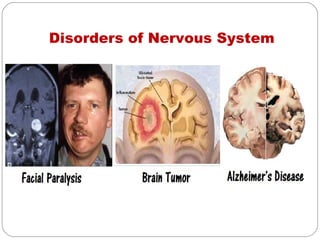
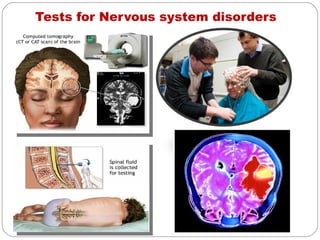
- Nervous system which communicates information through neurons in the peripheral and central systems. Disorders result in tingling, numbness, pain and loss of sensation or muscle power.
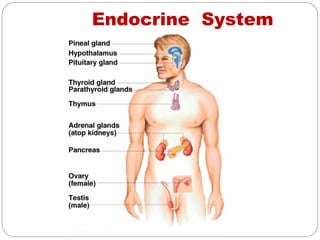
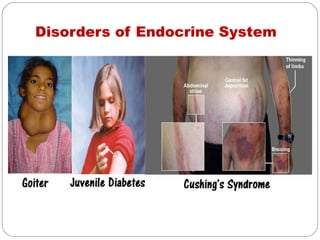
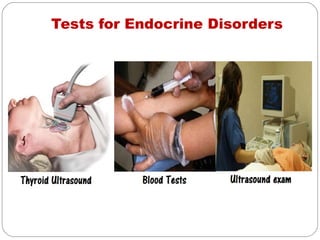
- Endocrine system which regulates body processes through hormone-producing glands. Disorders cause changes in growth, metabolism and sexual function.
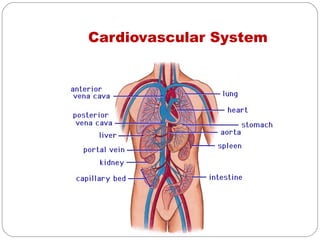
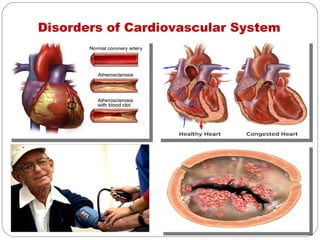
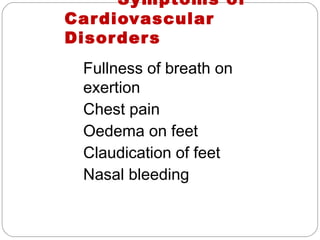
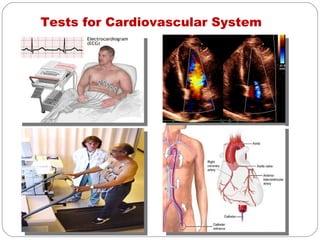
- Cardiovascular