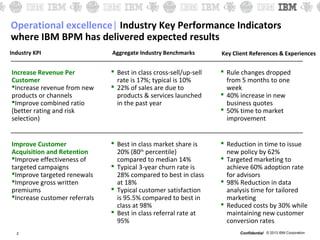
This document contains a briefing on operational excellence through business process management (BPM). It discusses how BPM can help organizations improve key performance indicators such as increasing revenue per customer and improving customer acquisition and retention rates. Industry benchmarks are provided for these metrics. The document defines BPM and its expected benefits, including improved visibility, accountability and adaptability of processes. A brief history of process management is given followed by typical challenges companies face today. It is noted that BPM bridges business and IT and that most processes will continue requiring human involvement. The document stresses that achieving operational excellence through BPM requires sponsorship from senior leadership and empowering cross-functional teams to continuously improve processes.