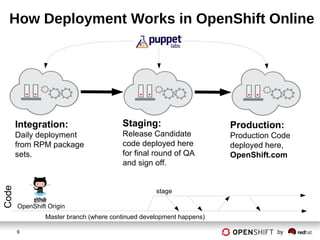
The document discusses OpenShift DevOps, focusing on the relationship between OpenShift Origin and OpenShift Online, including how code transitions from development to production. It outlines key concepts in DevOps, the architecture of development environments, and the roles of tools like Jenkins in environment creation and management. The document concludes with a brief overview of deployment processes and the environments involved.