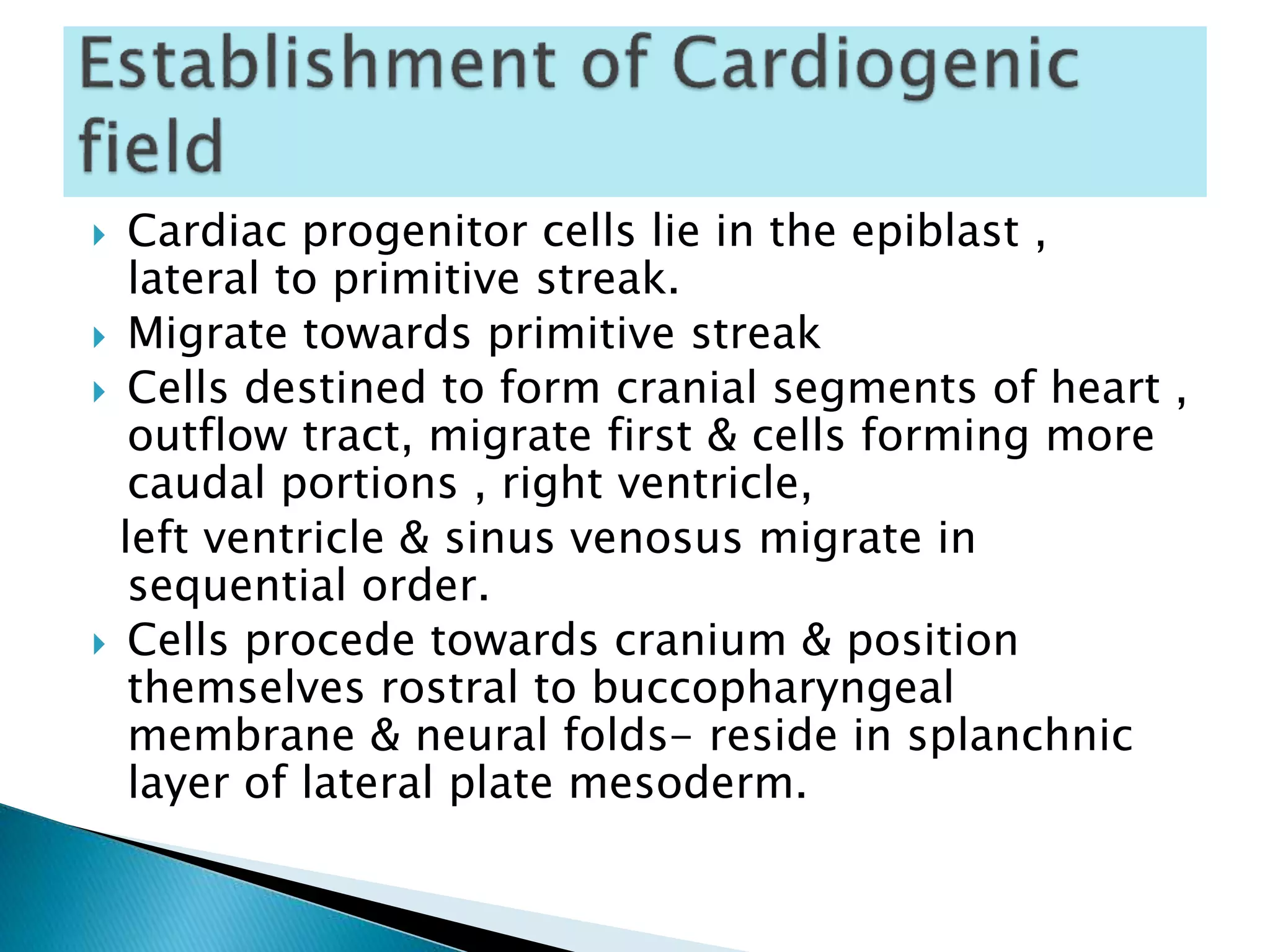
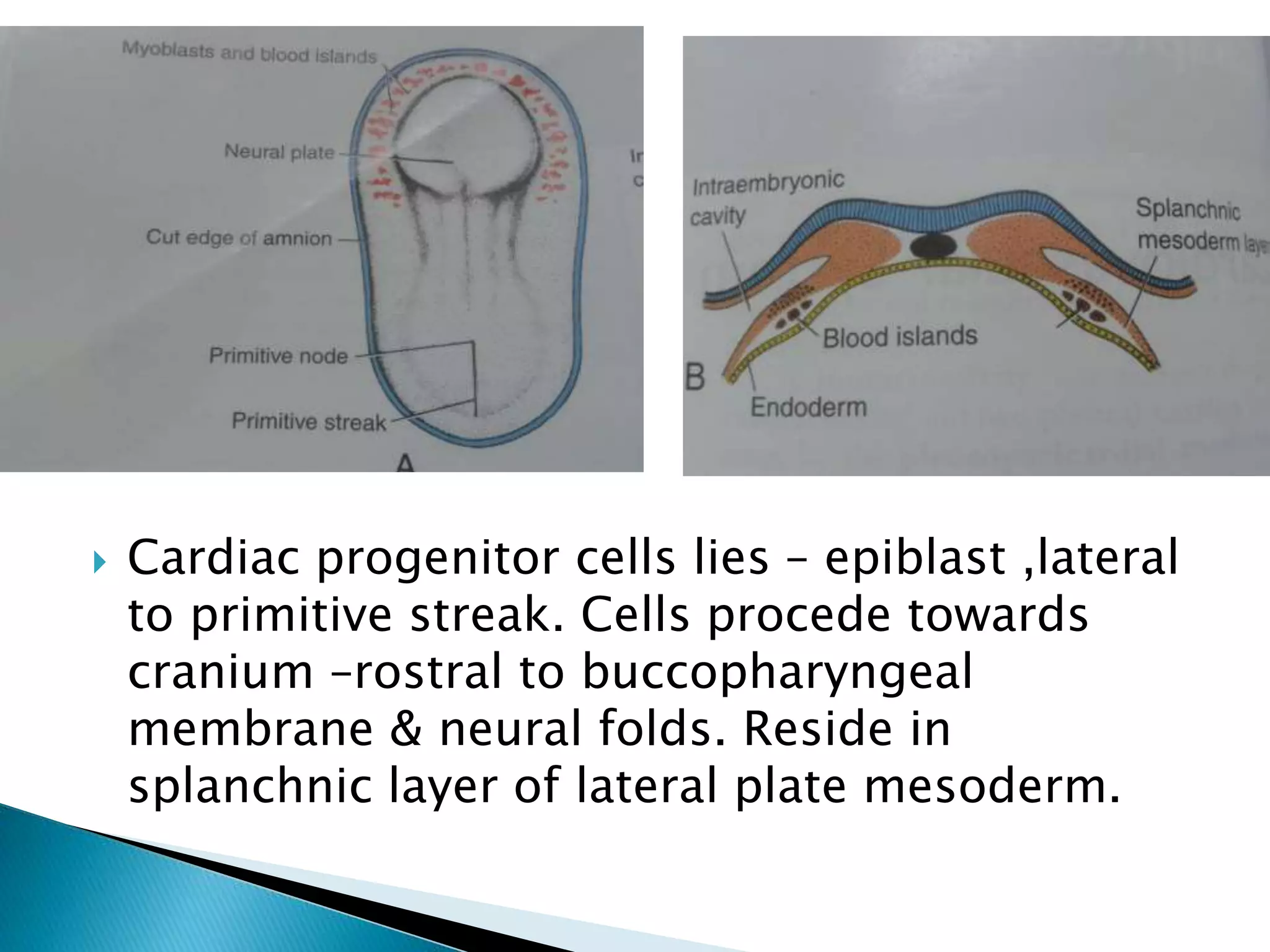
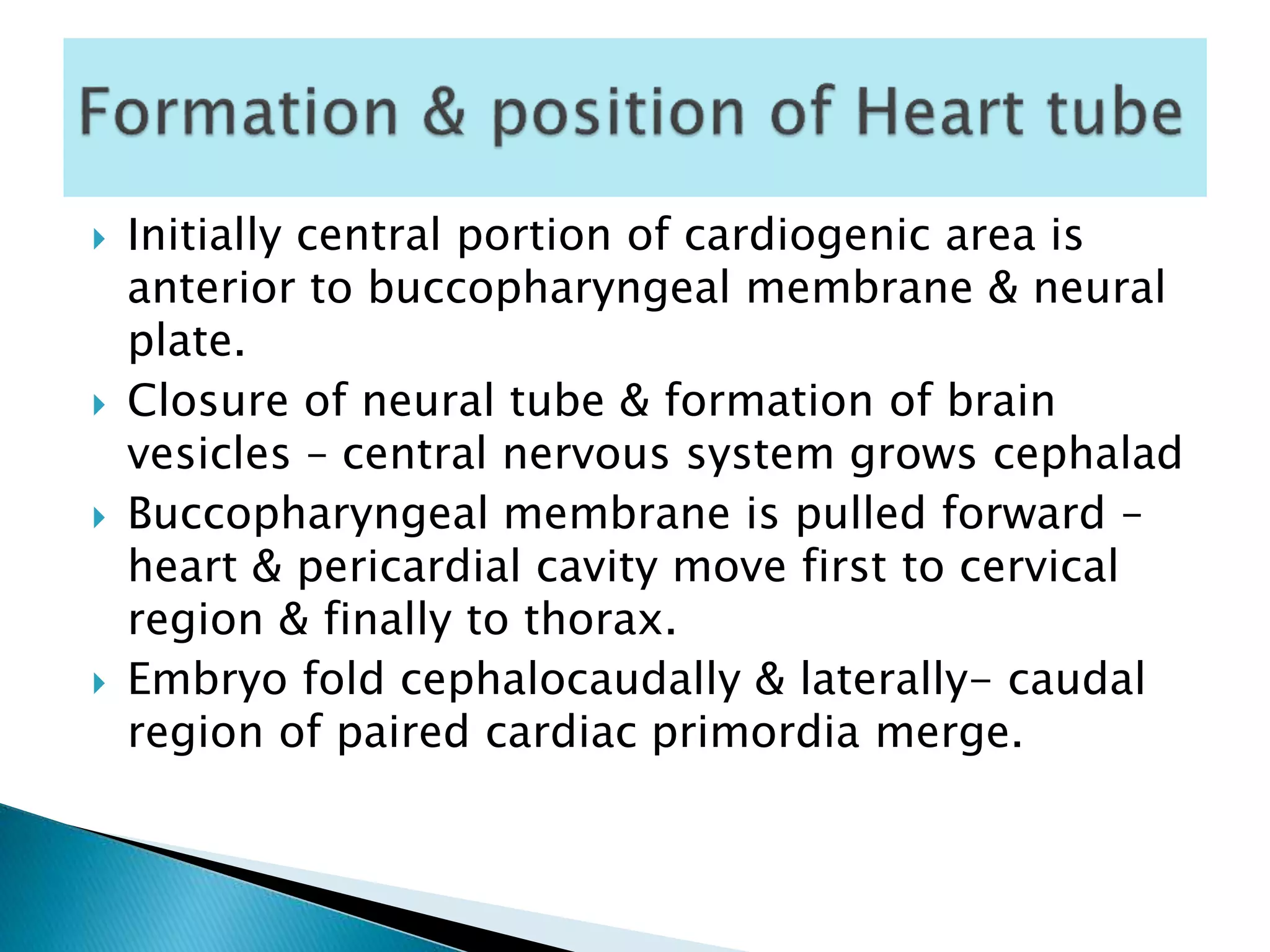
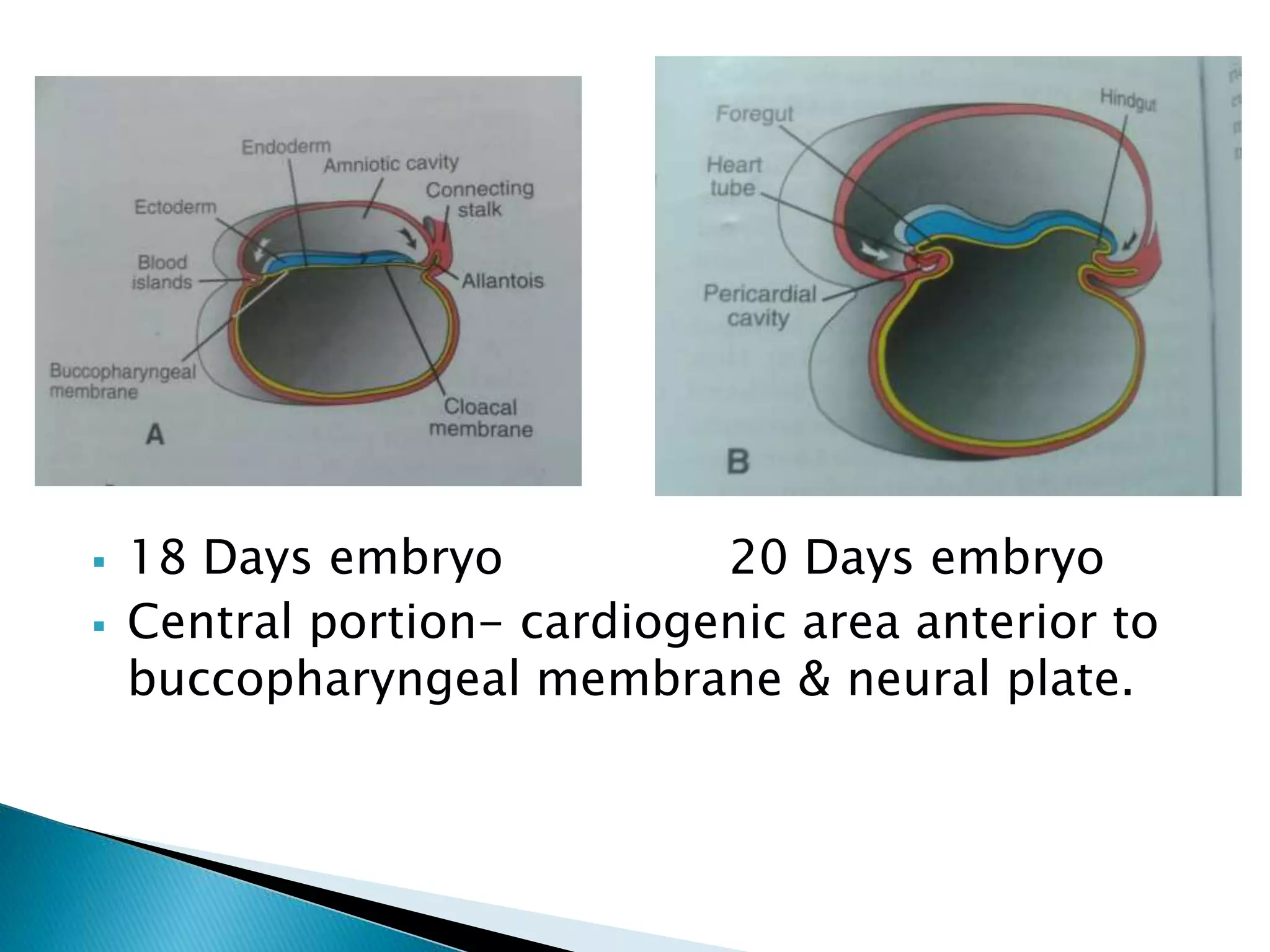
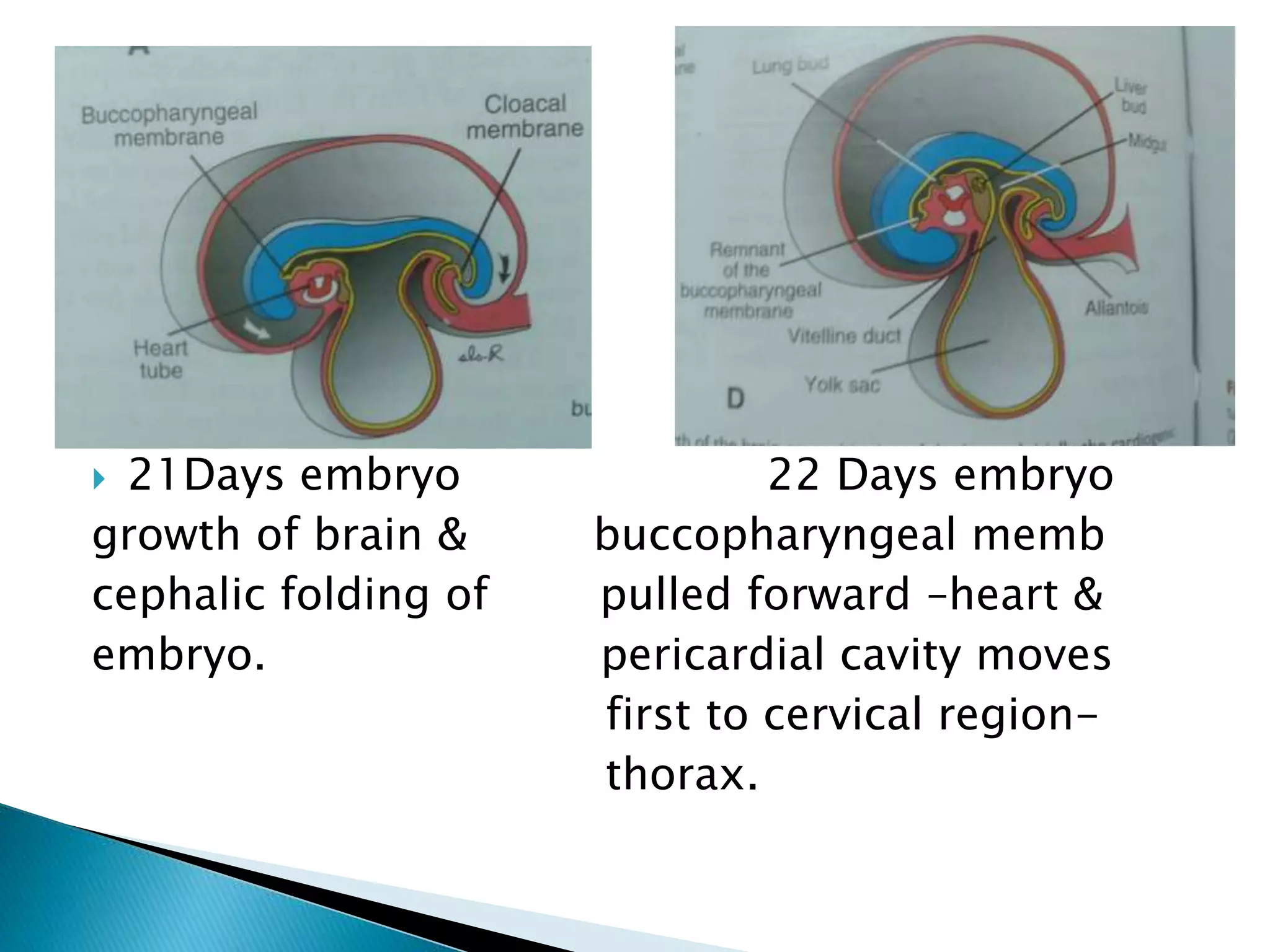
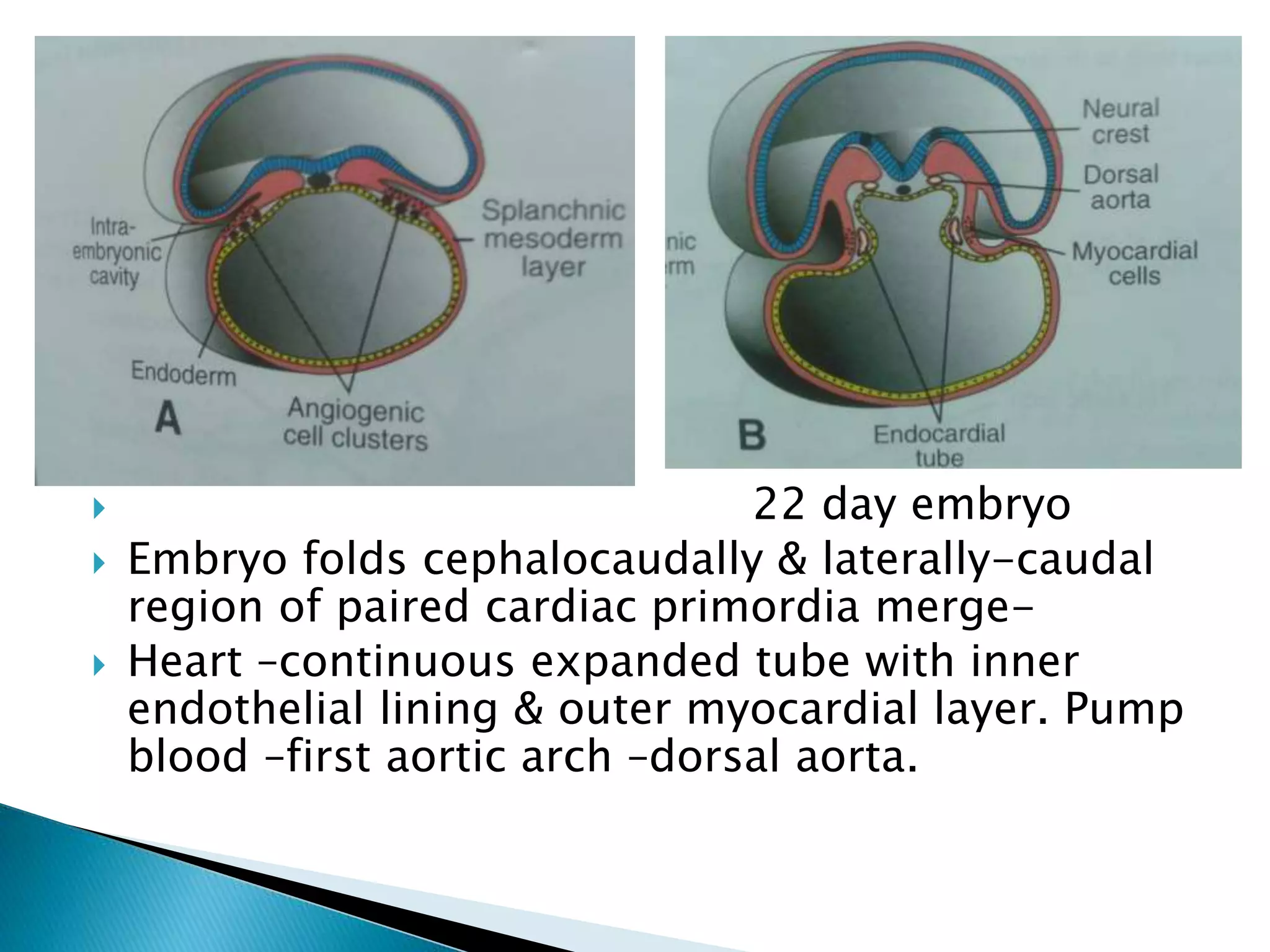
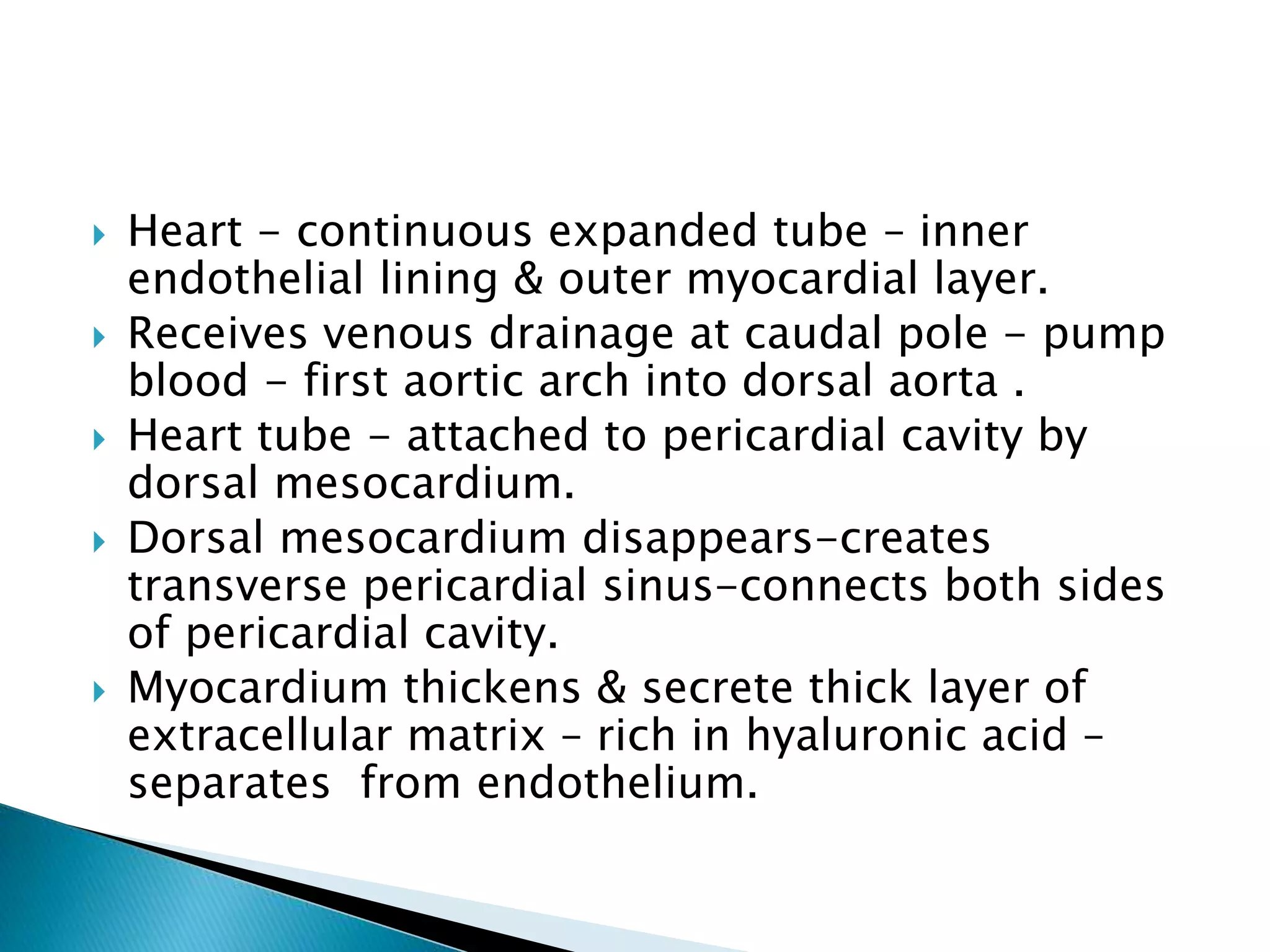
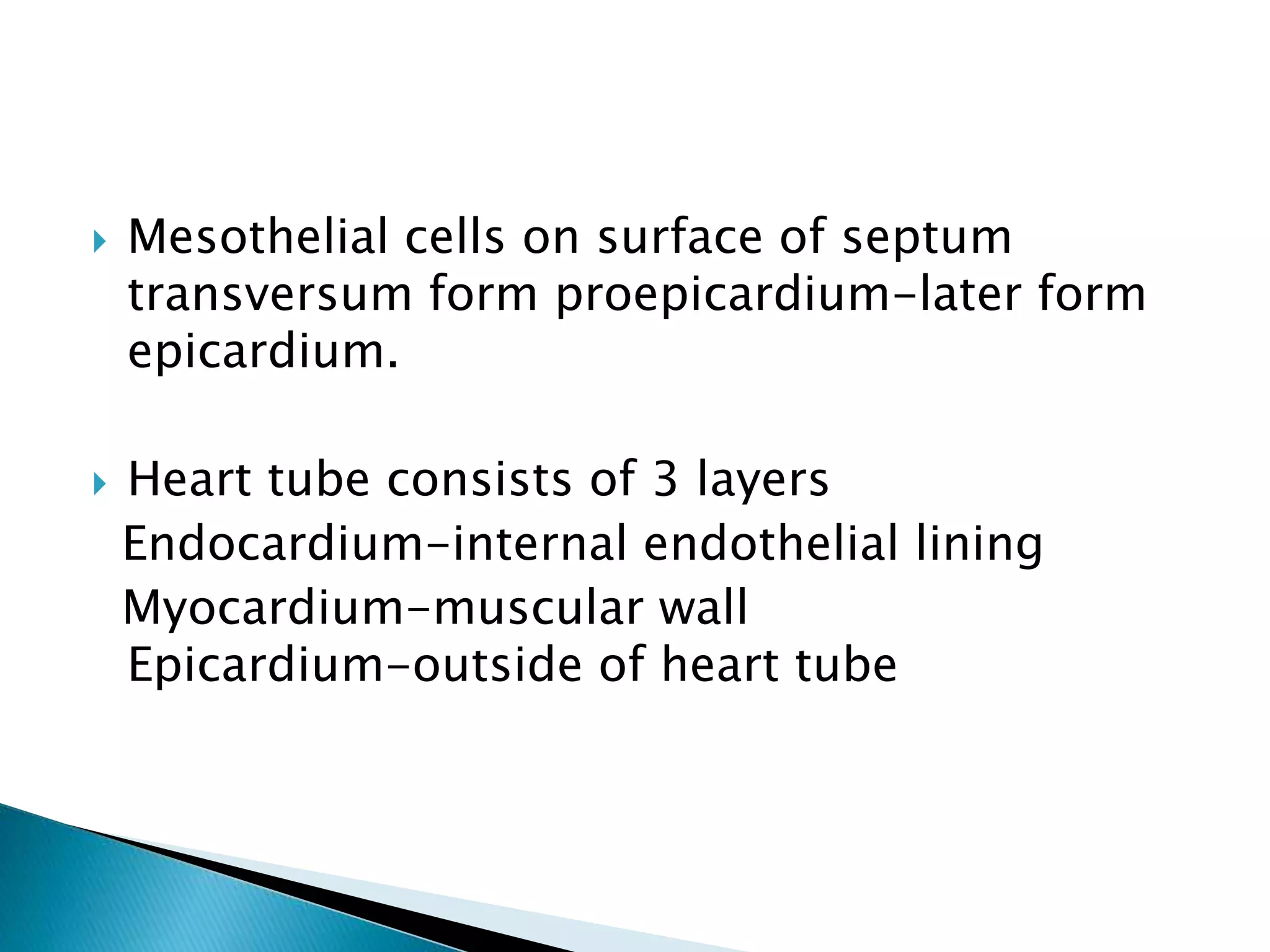
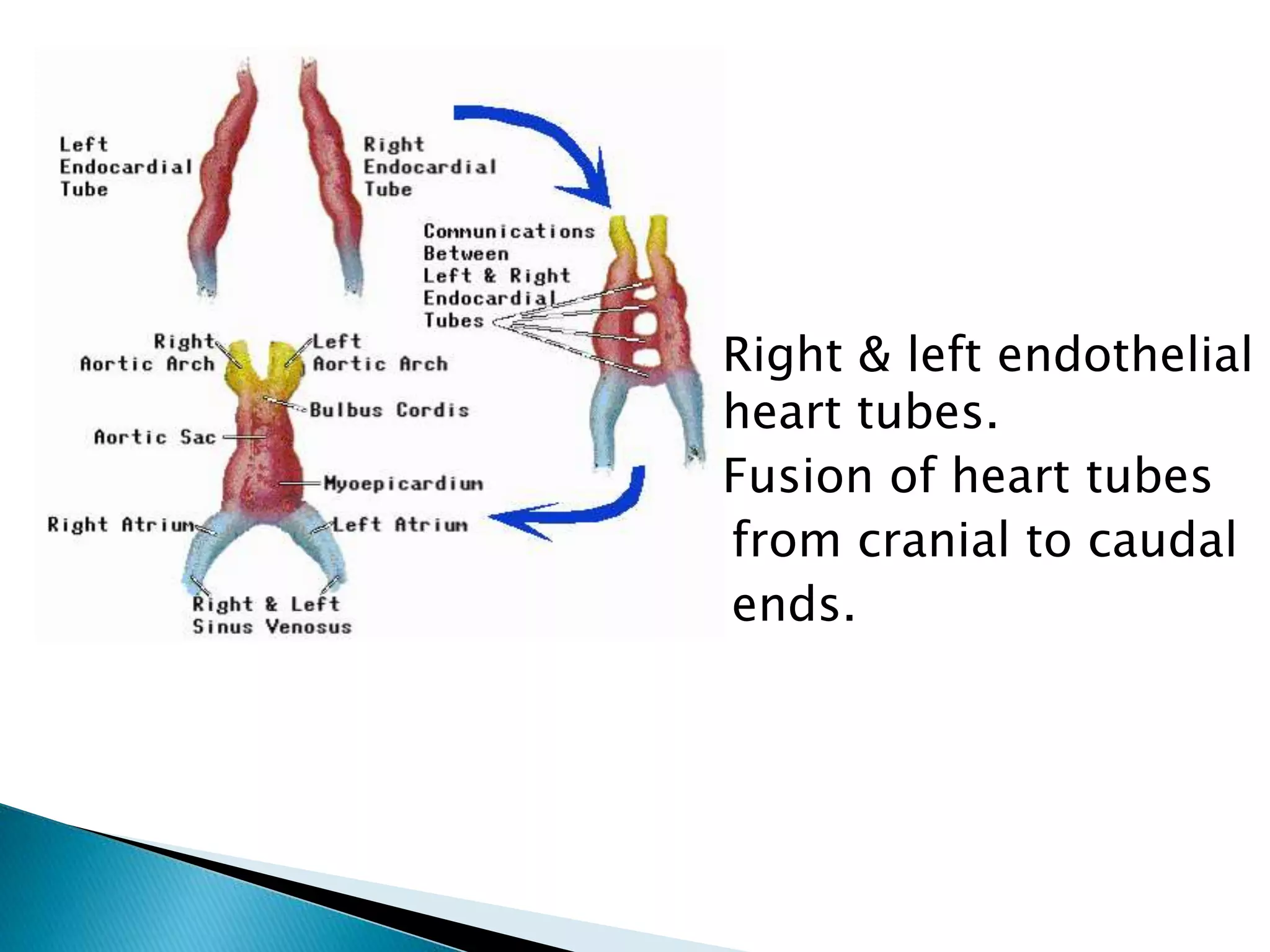
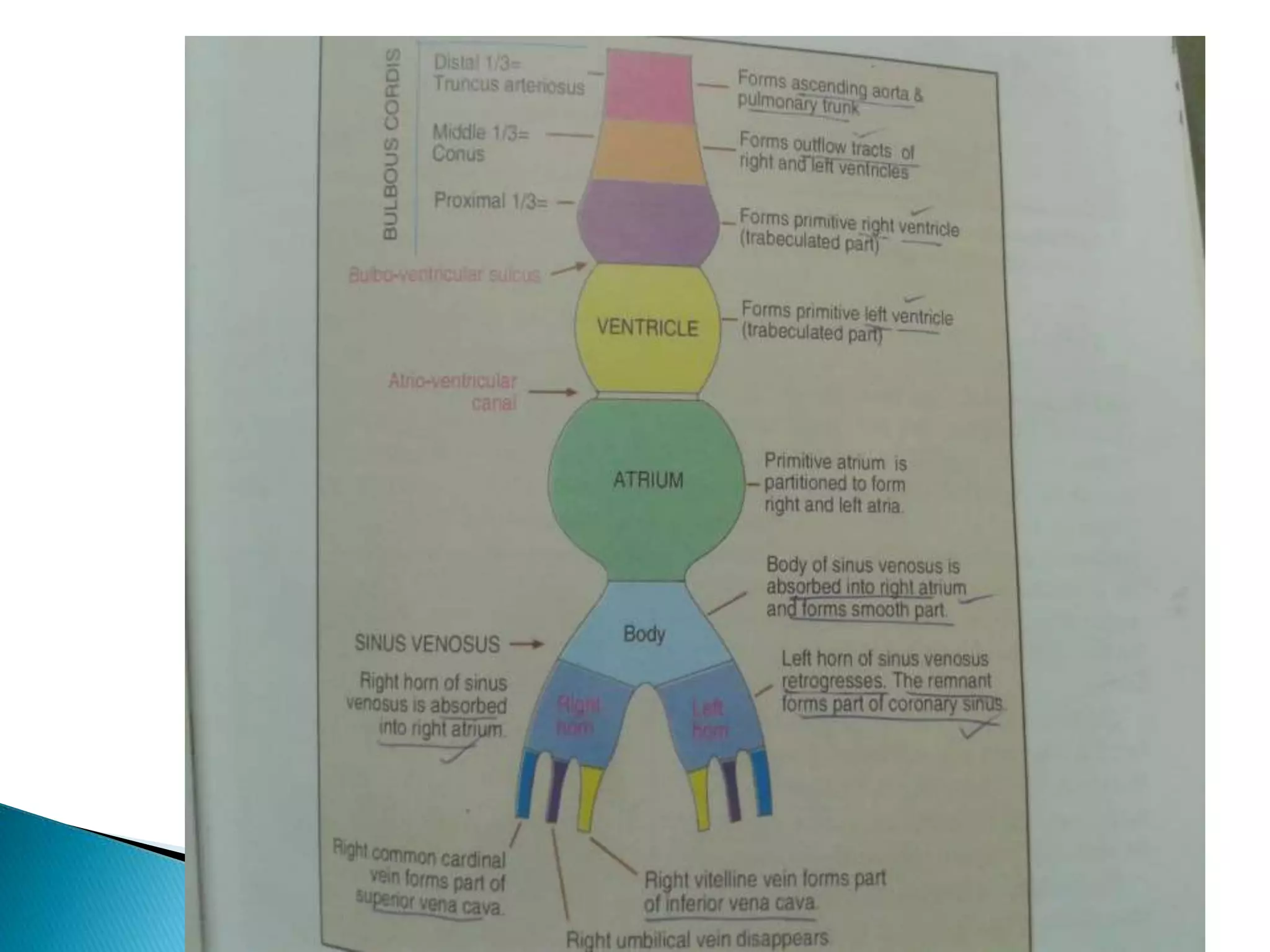
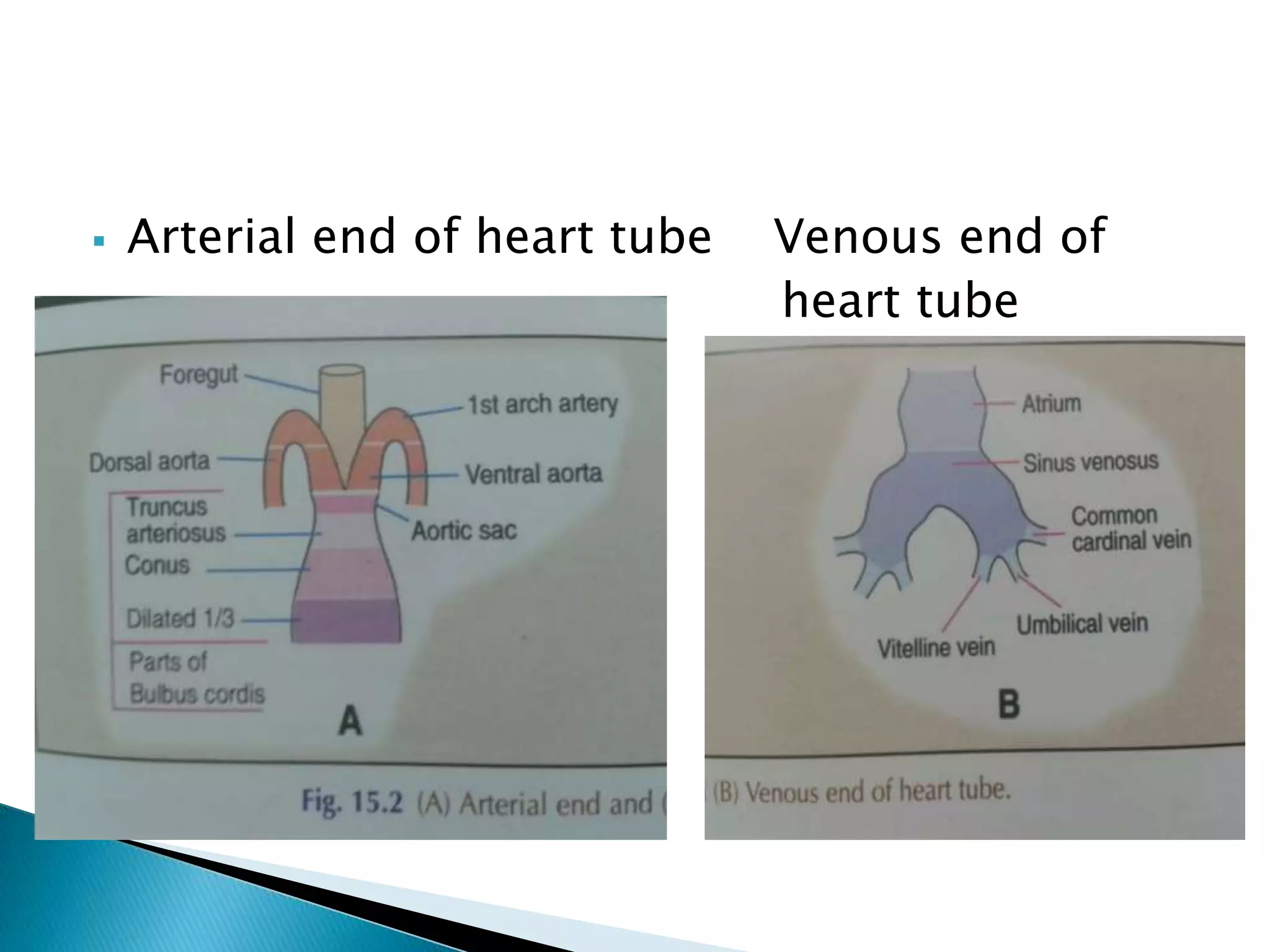
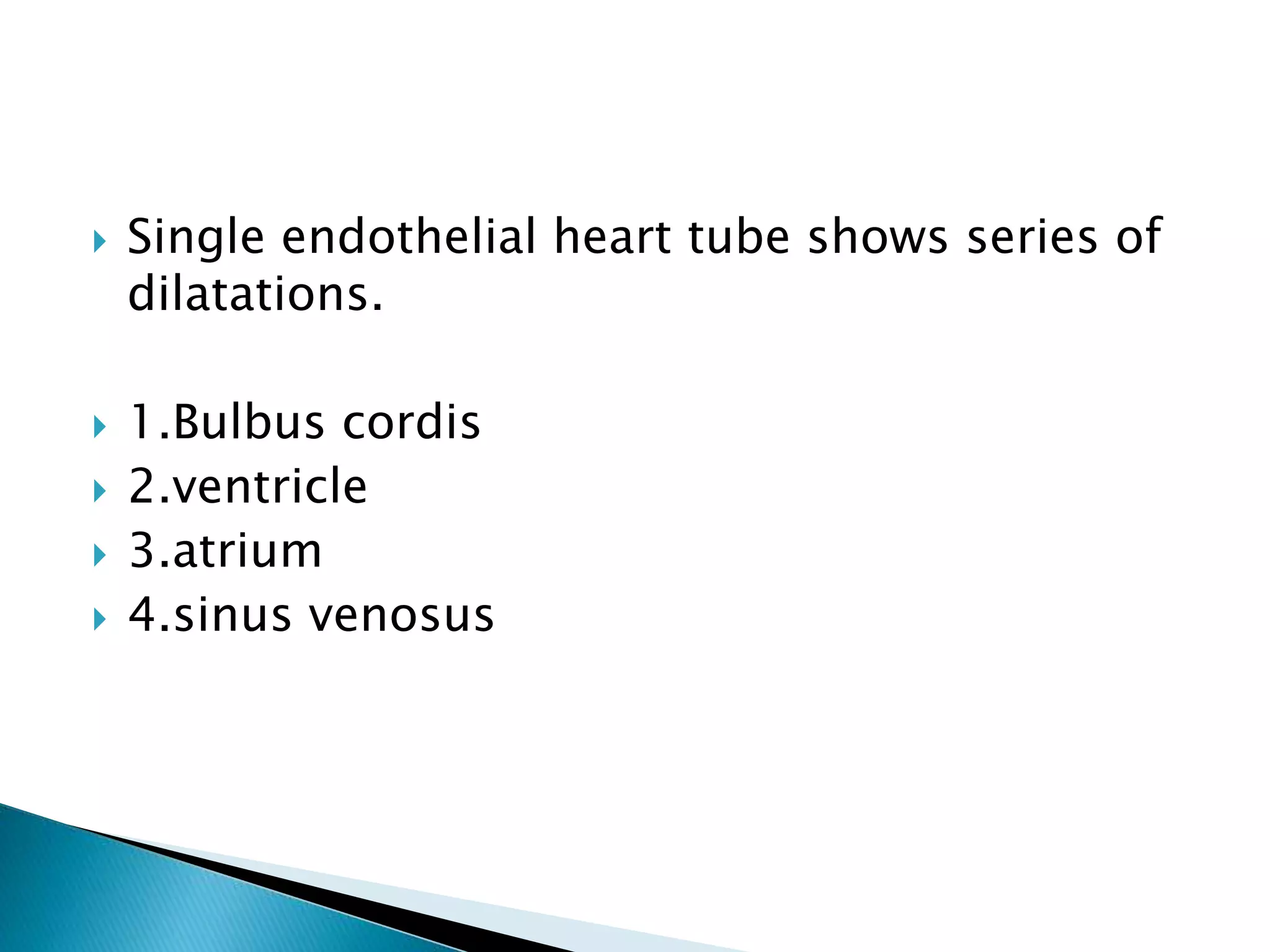
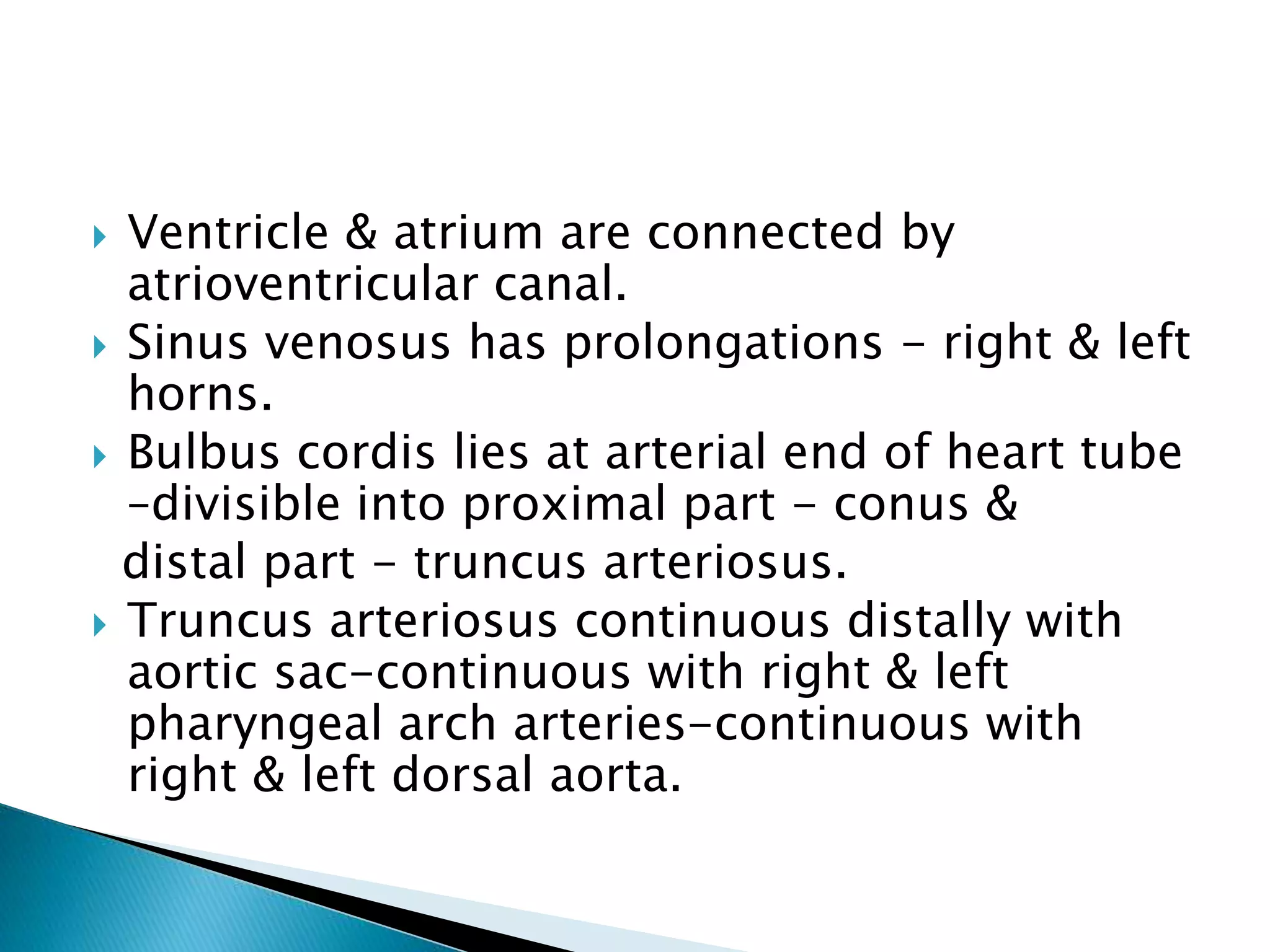
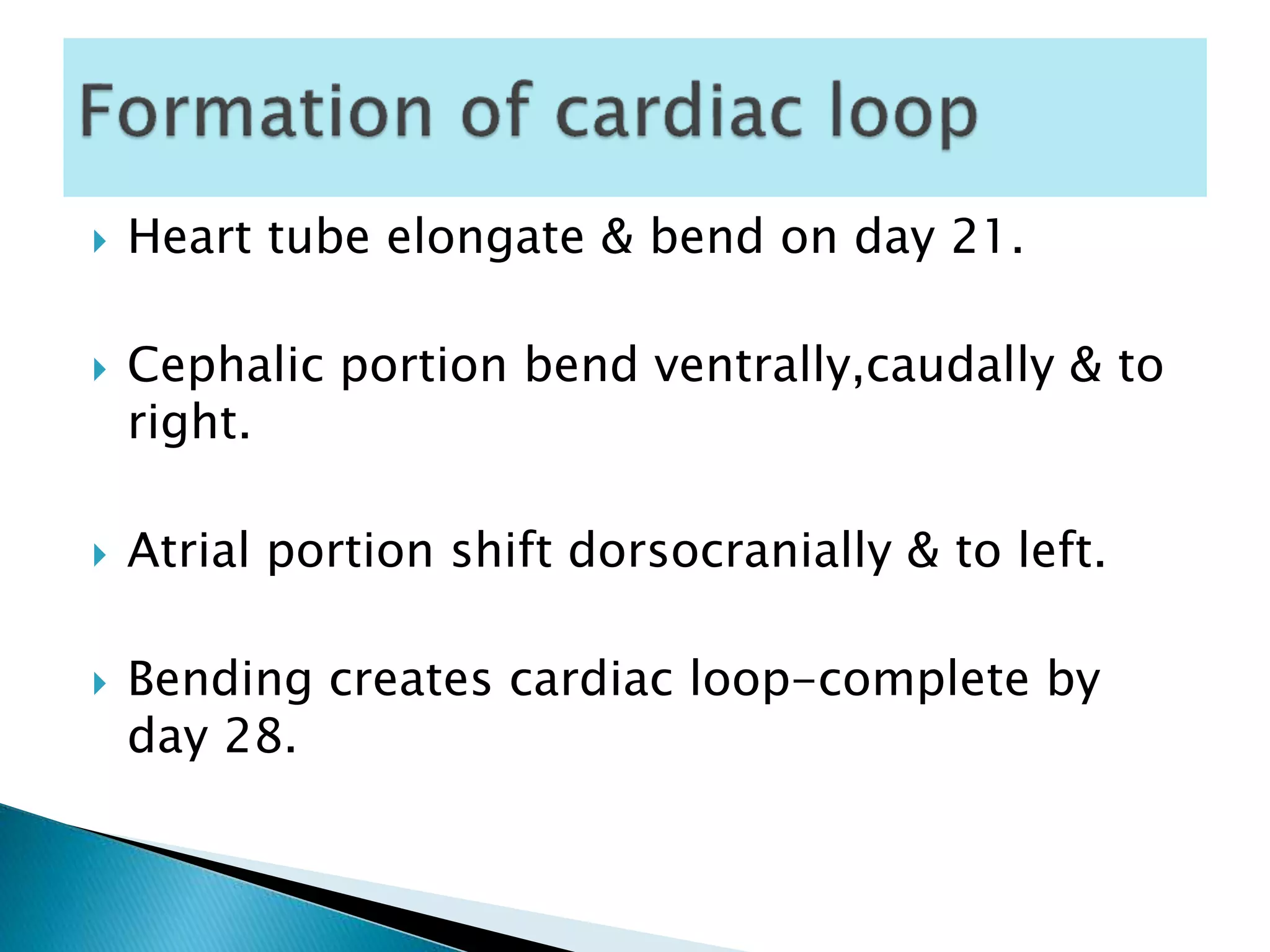
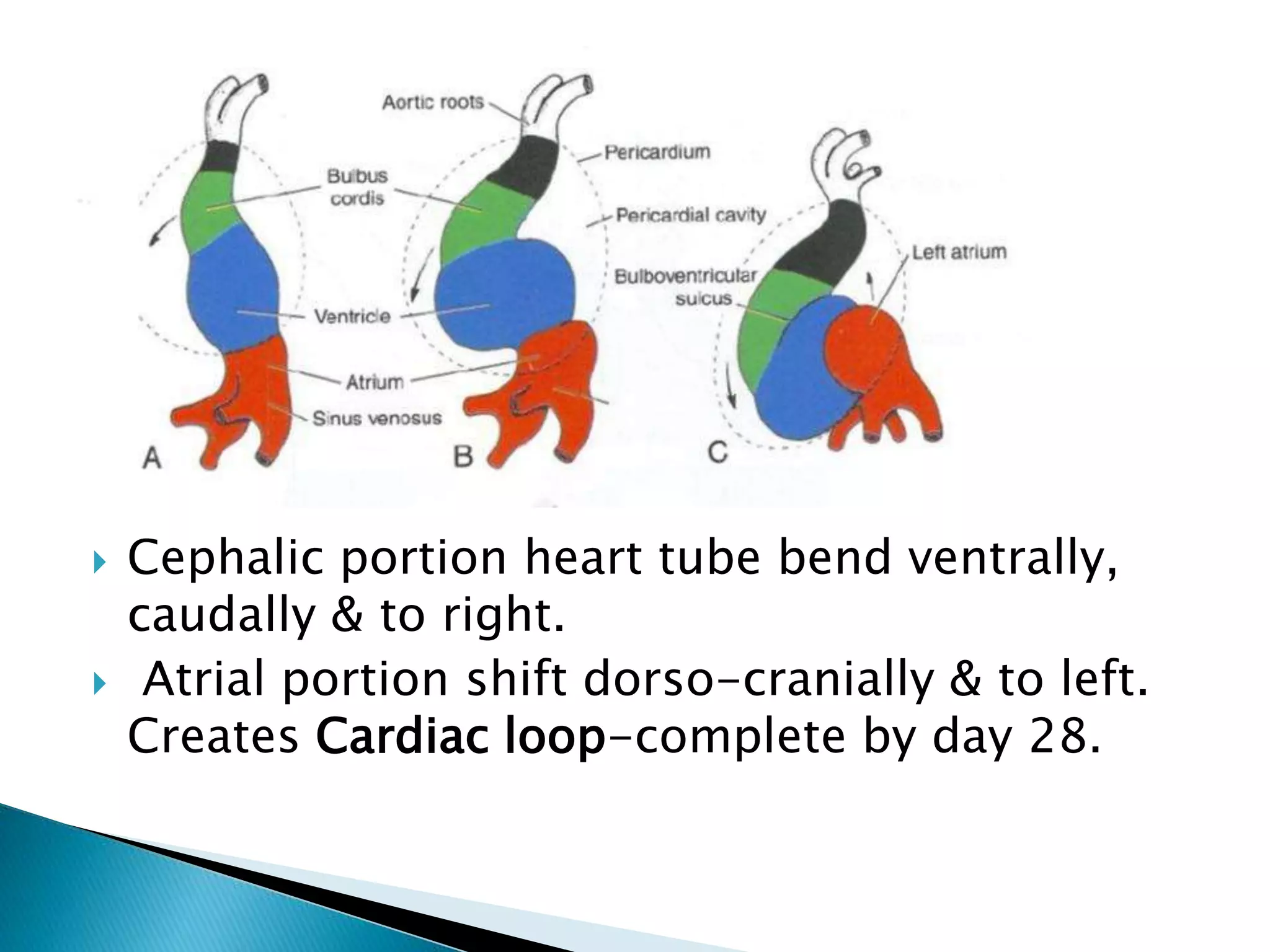
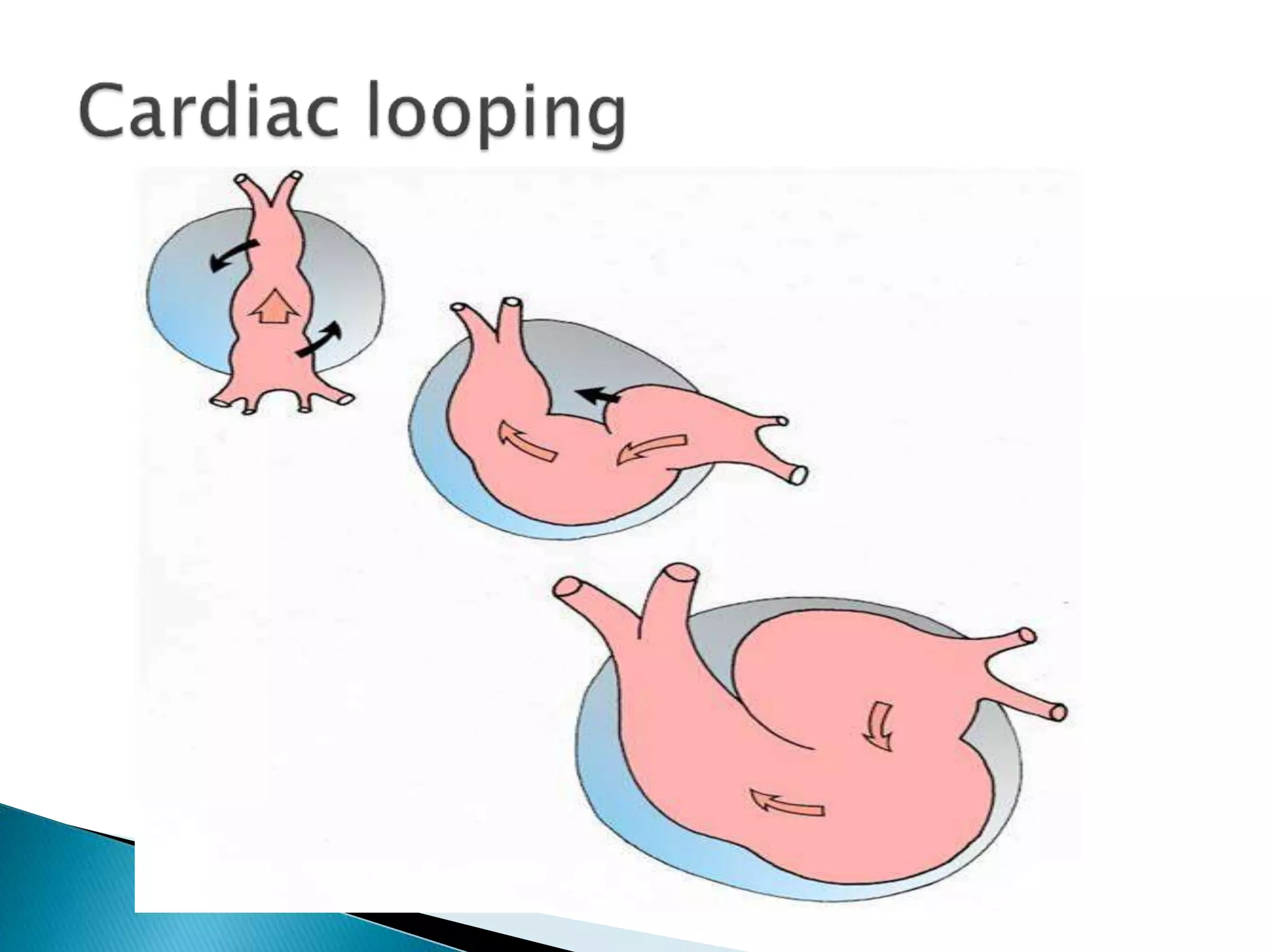
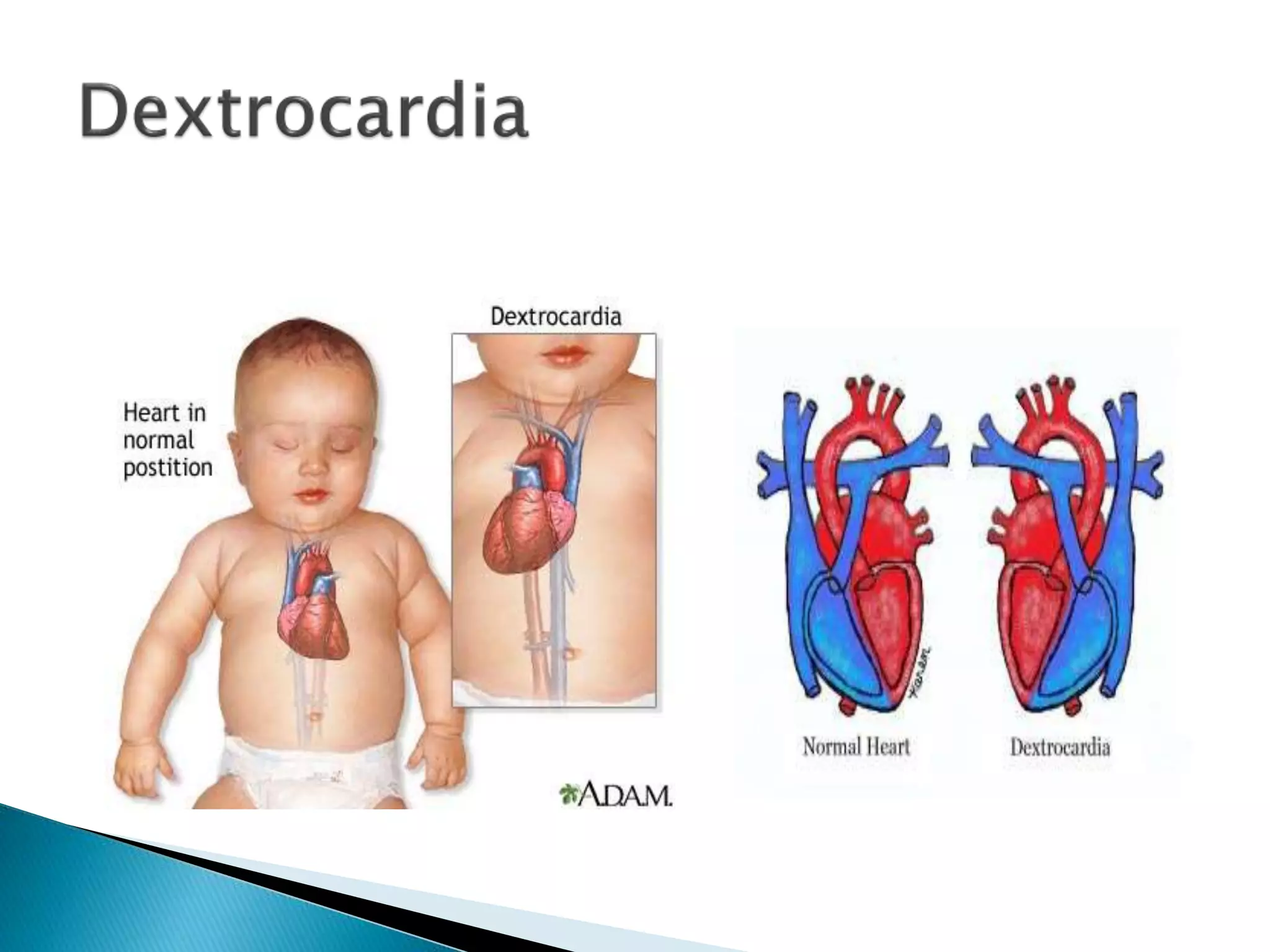
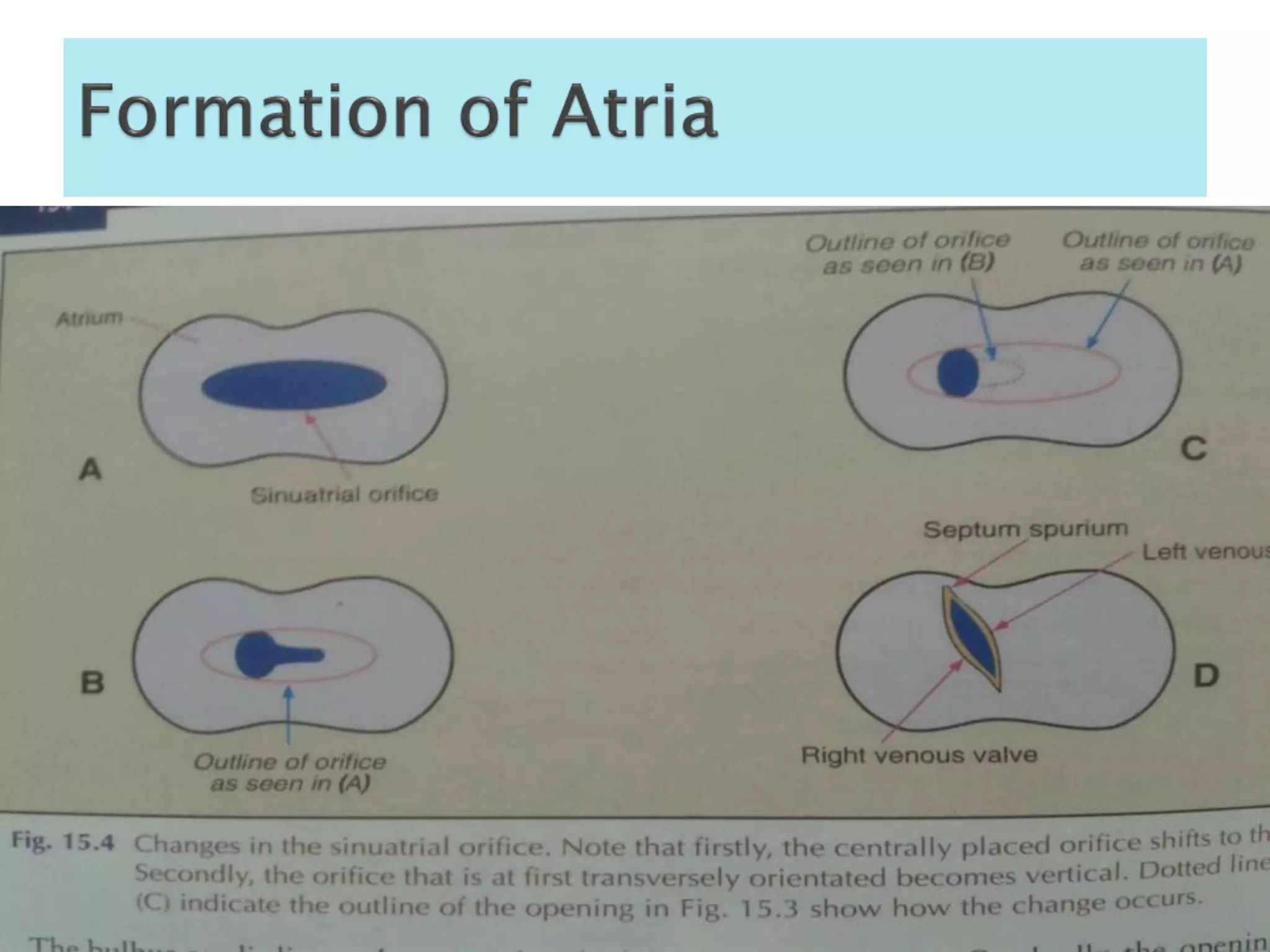
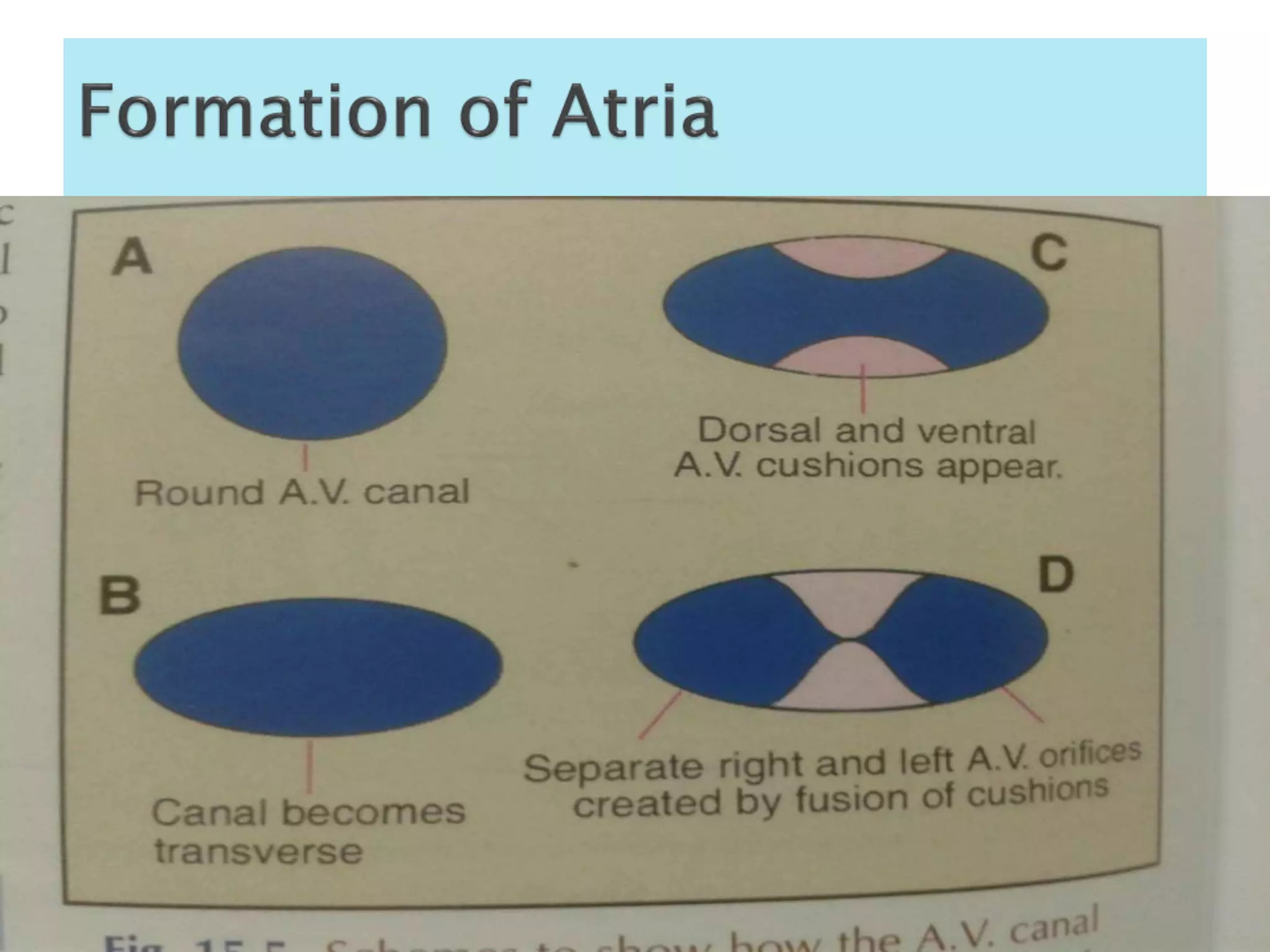
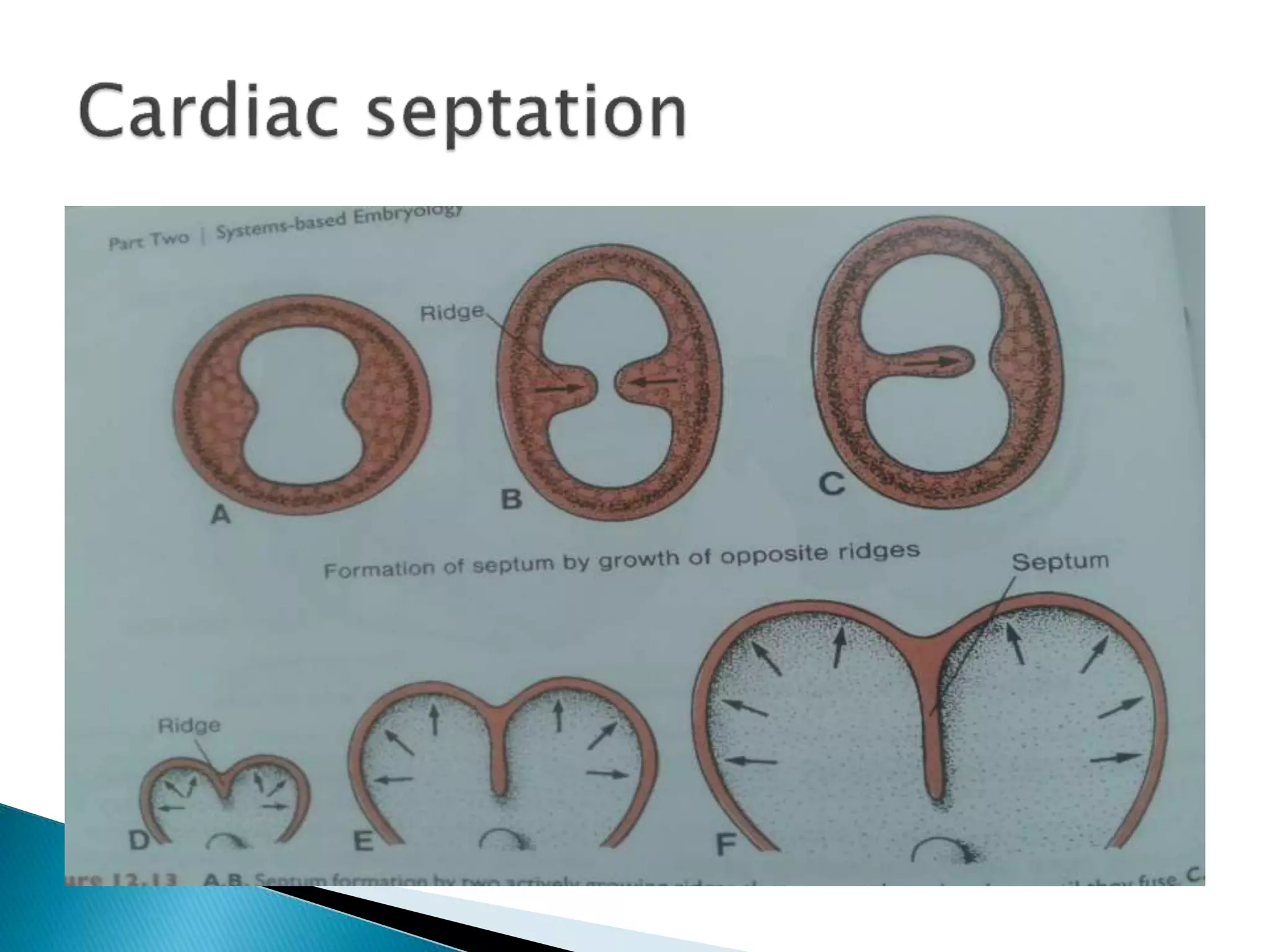
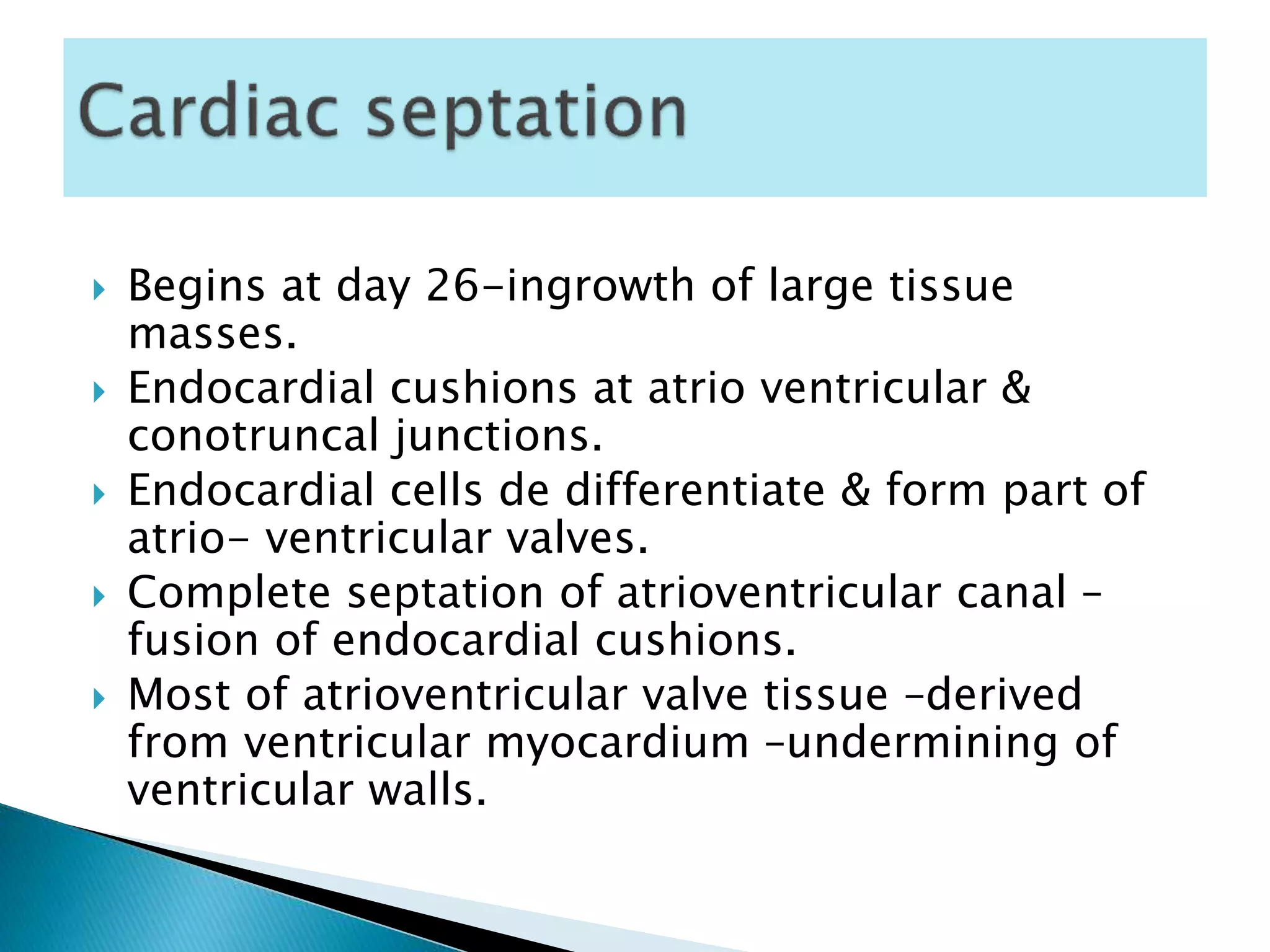
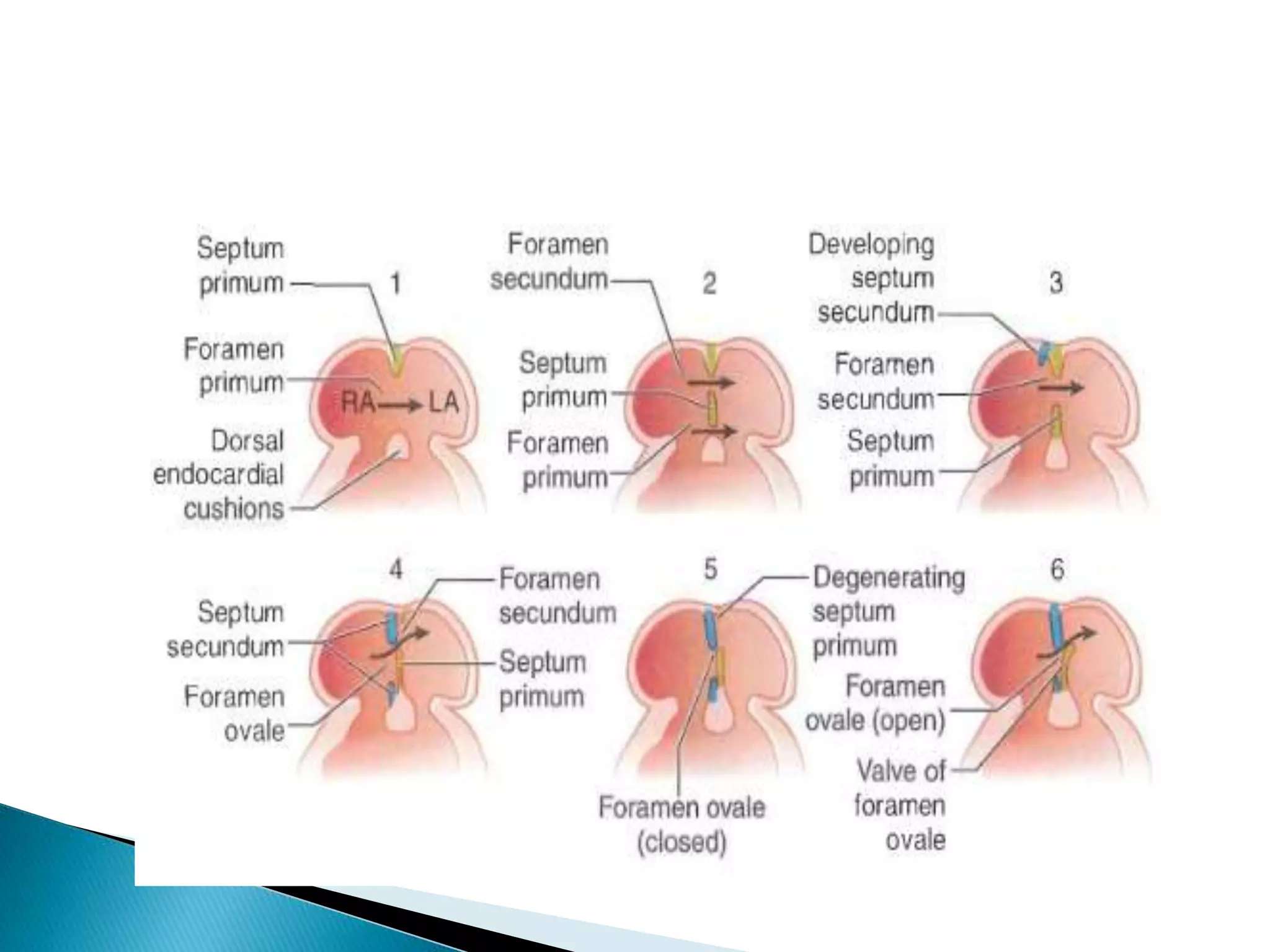
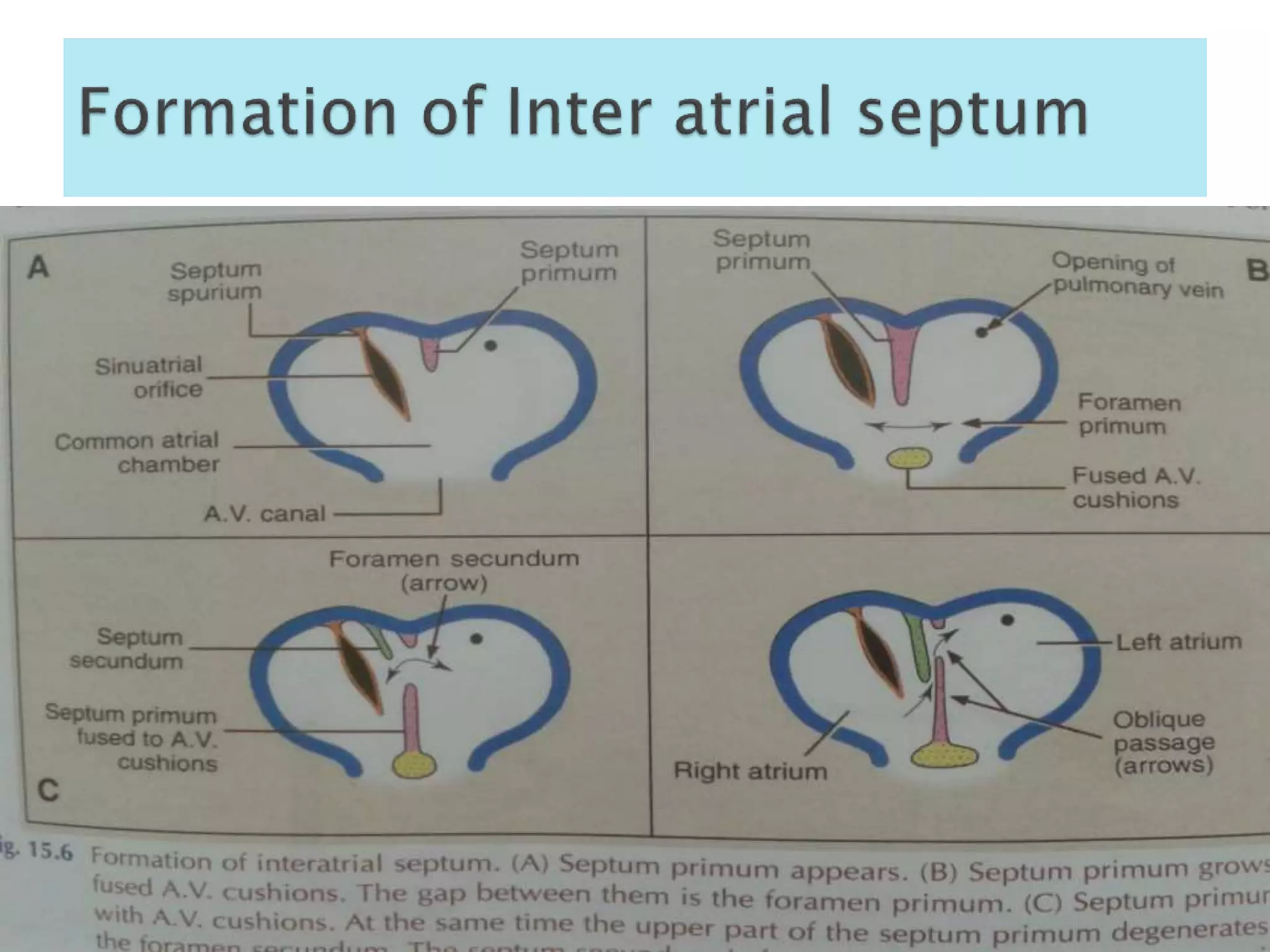
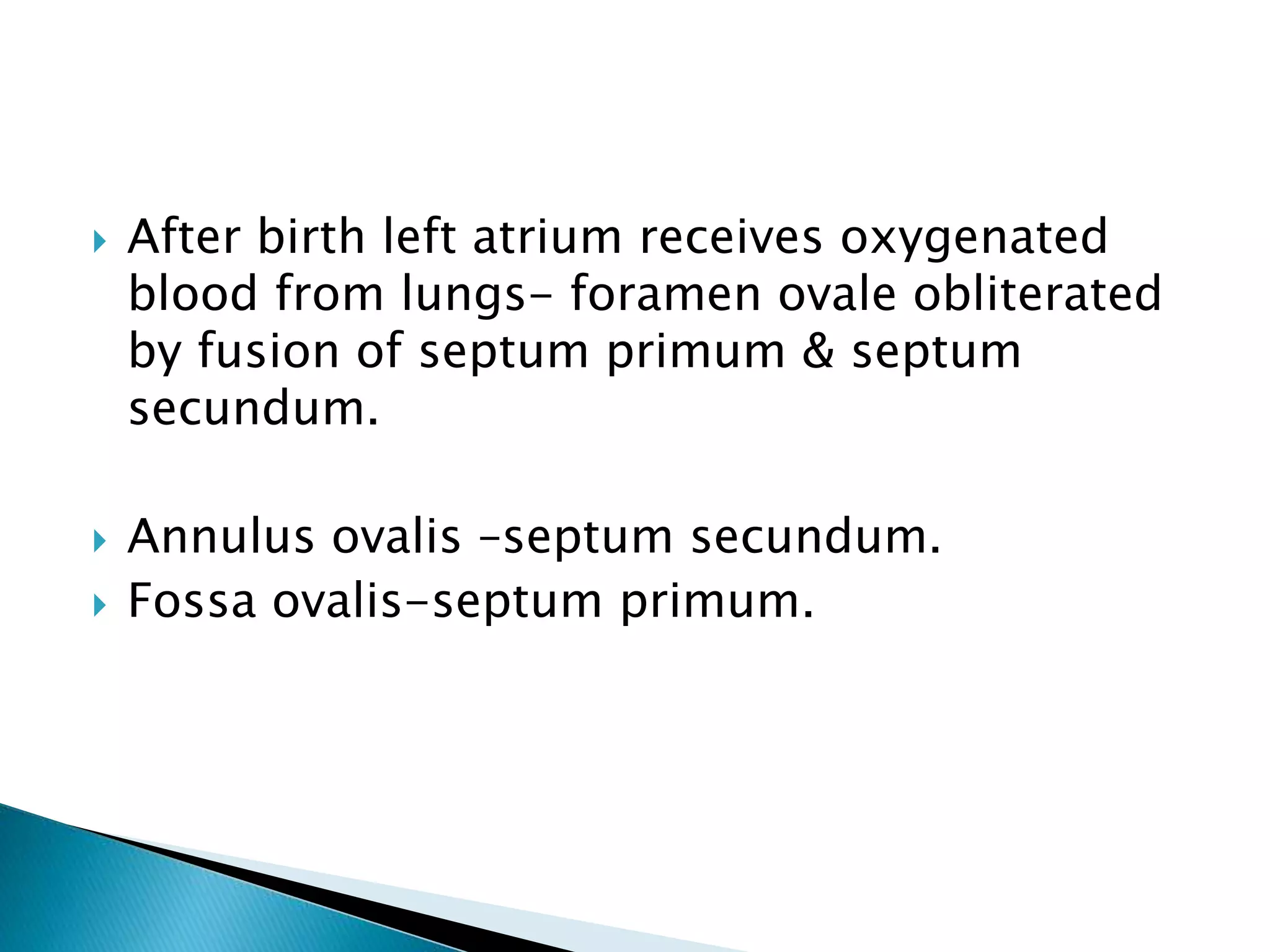
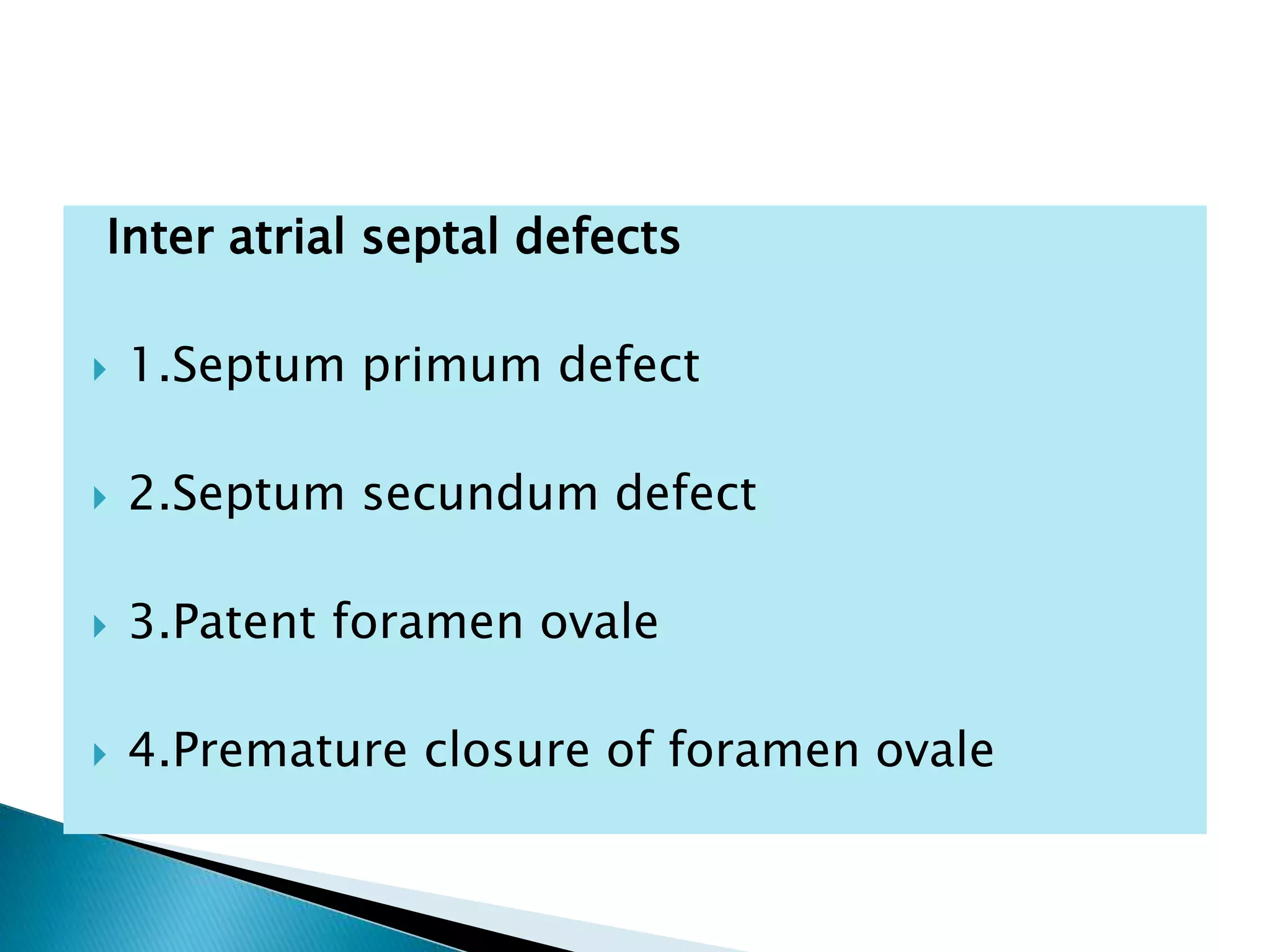
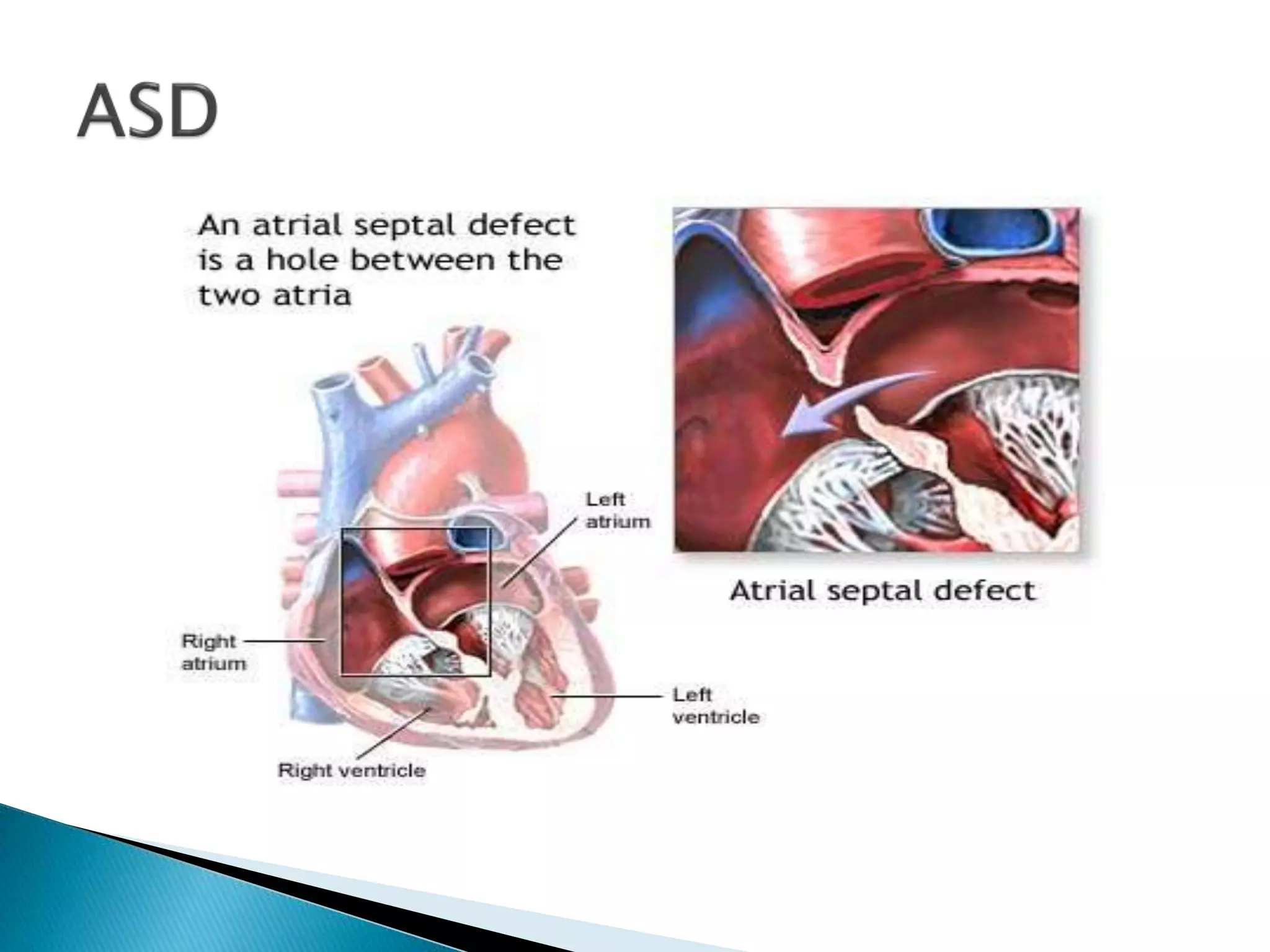
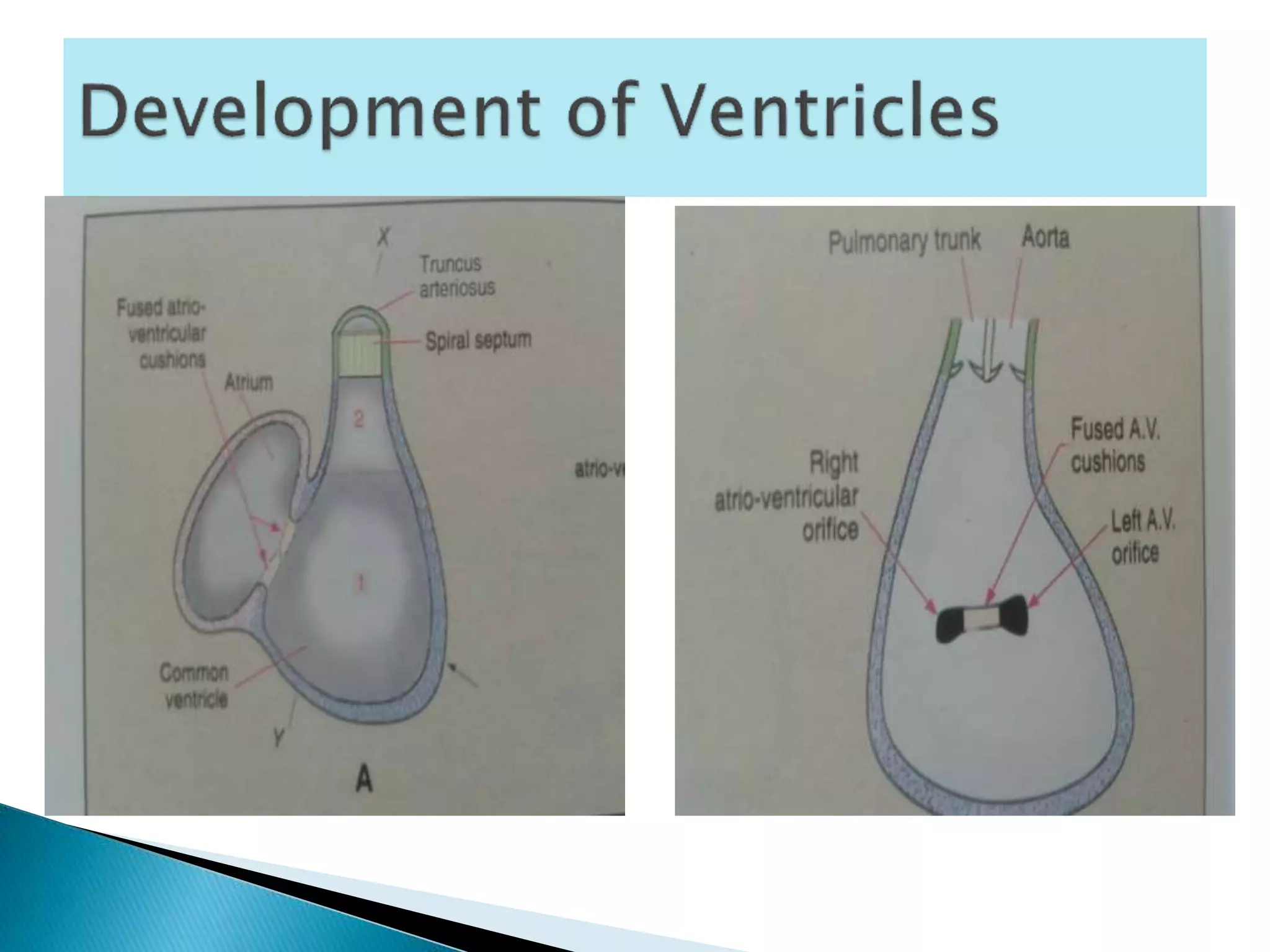
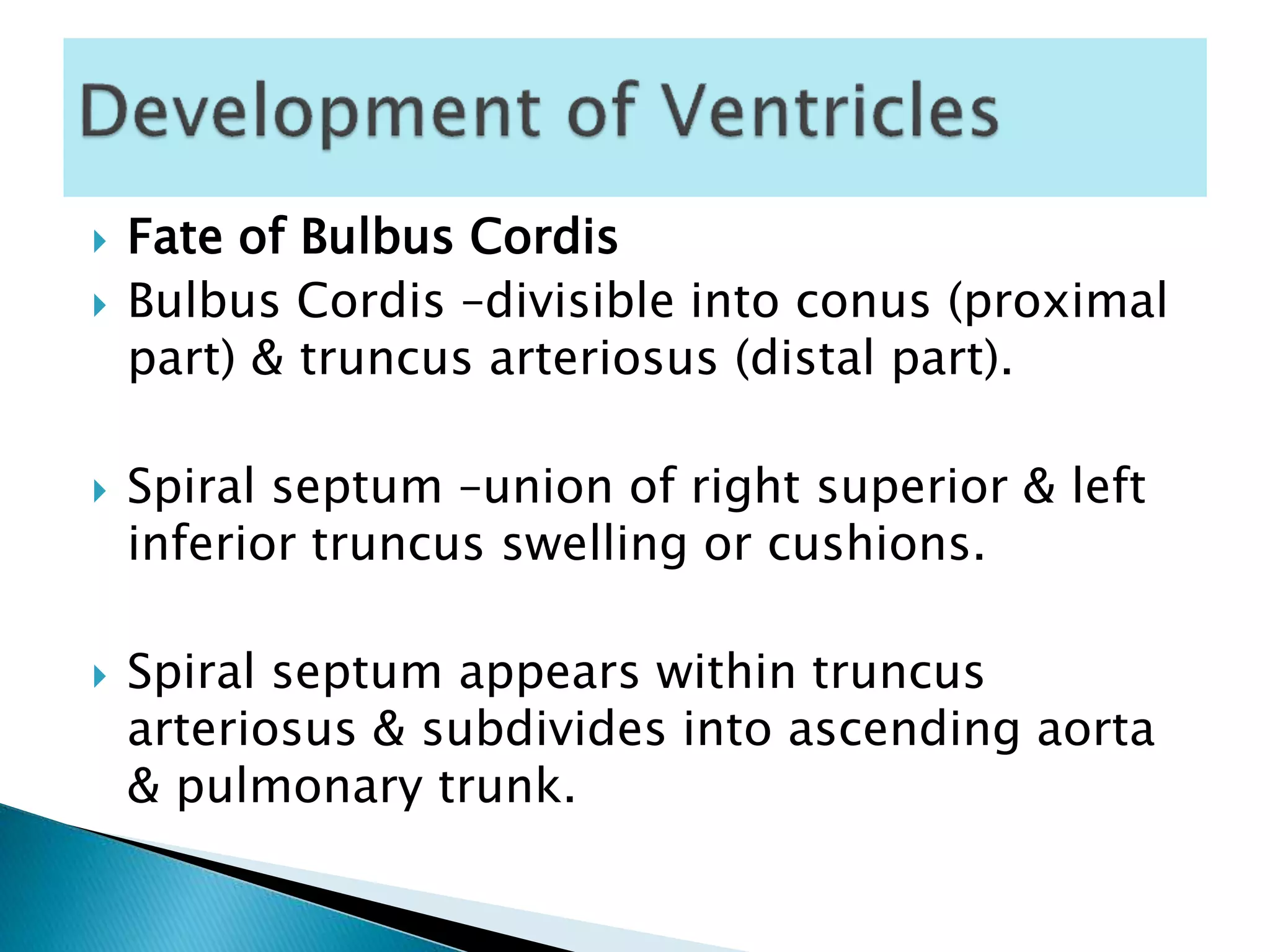
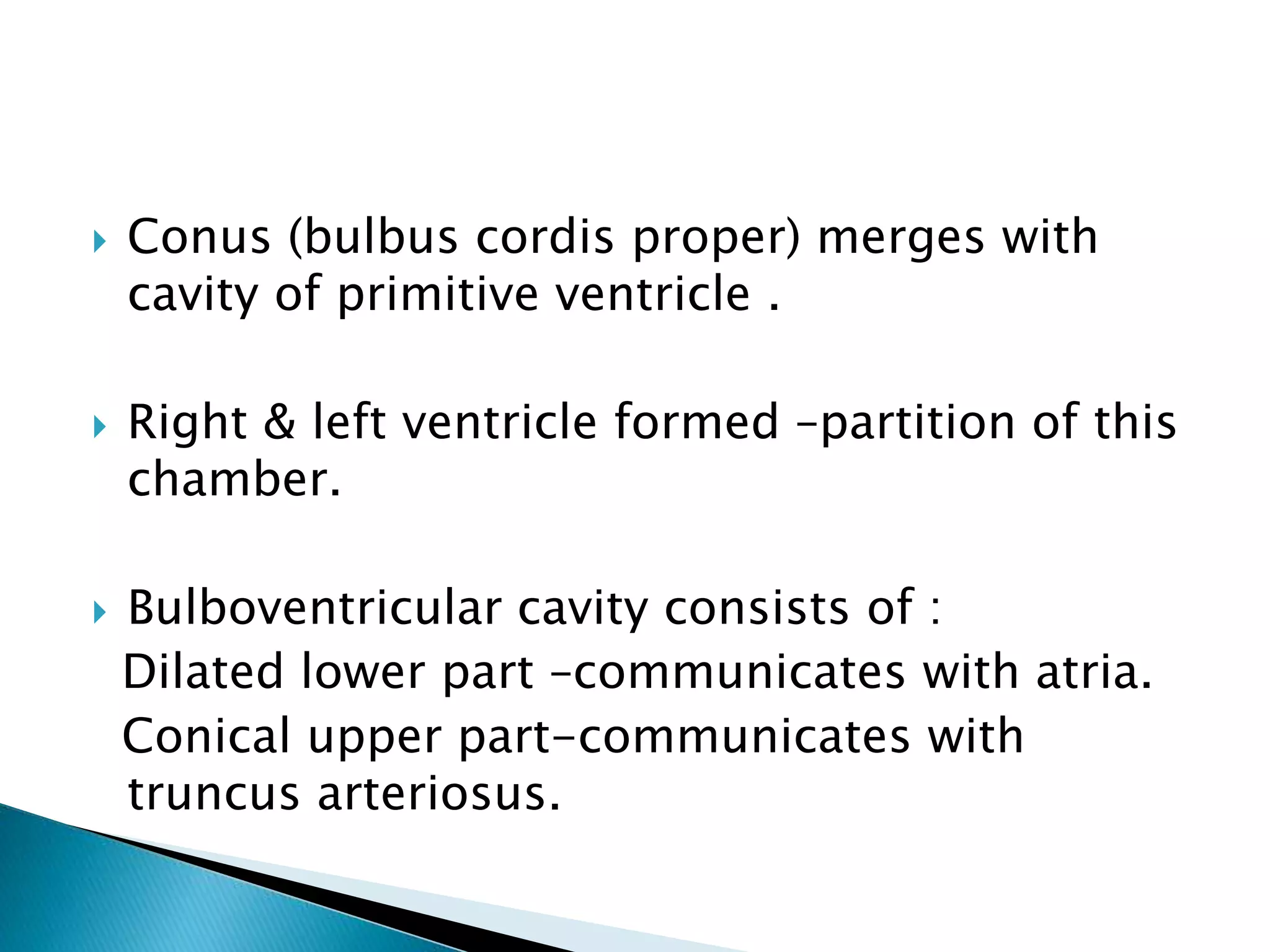
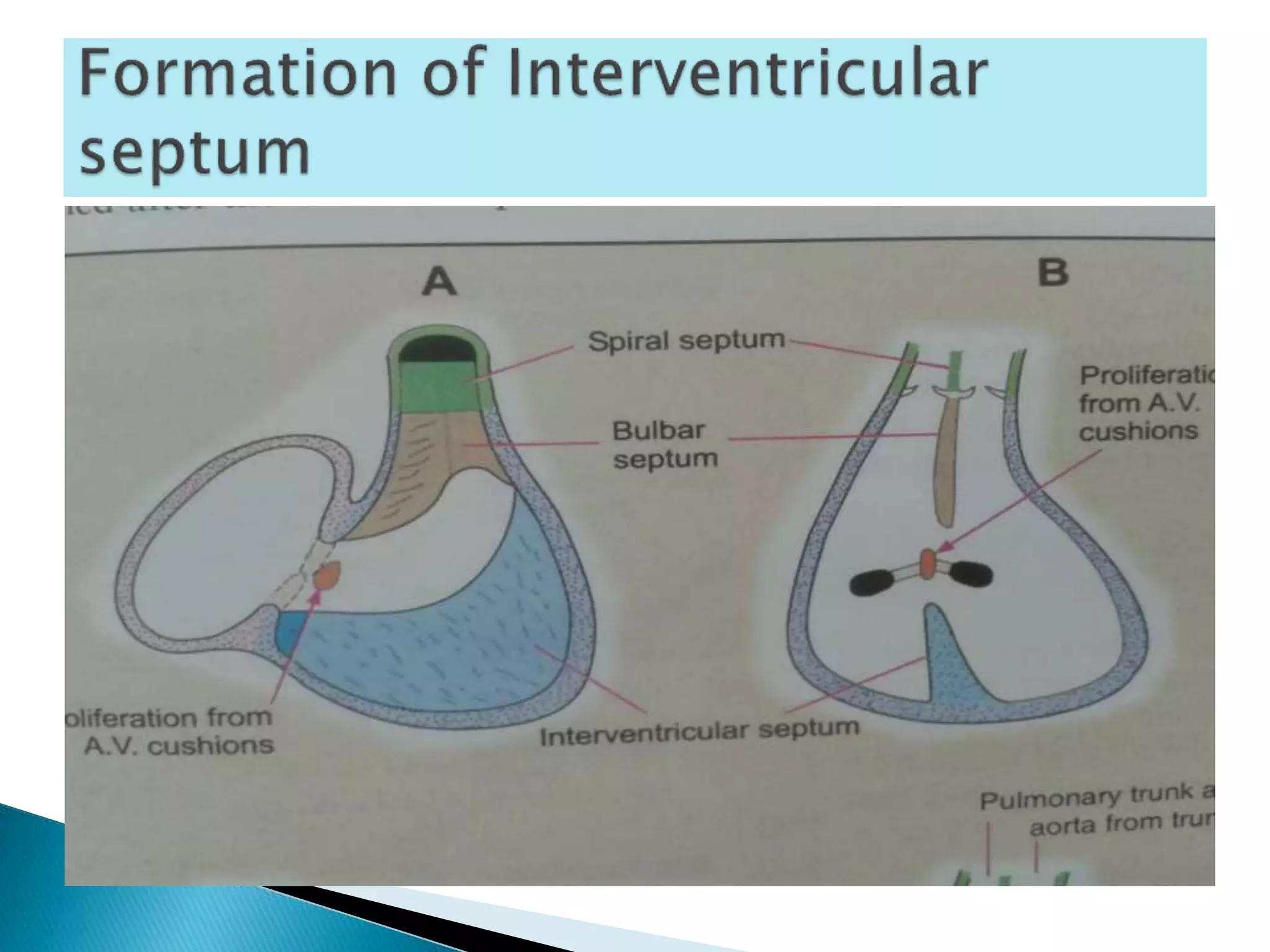
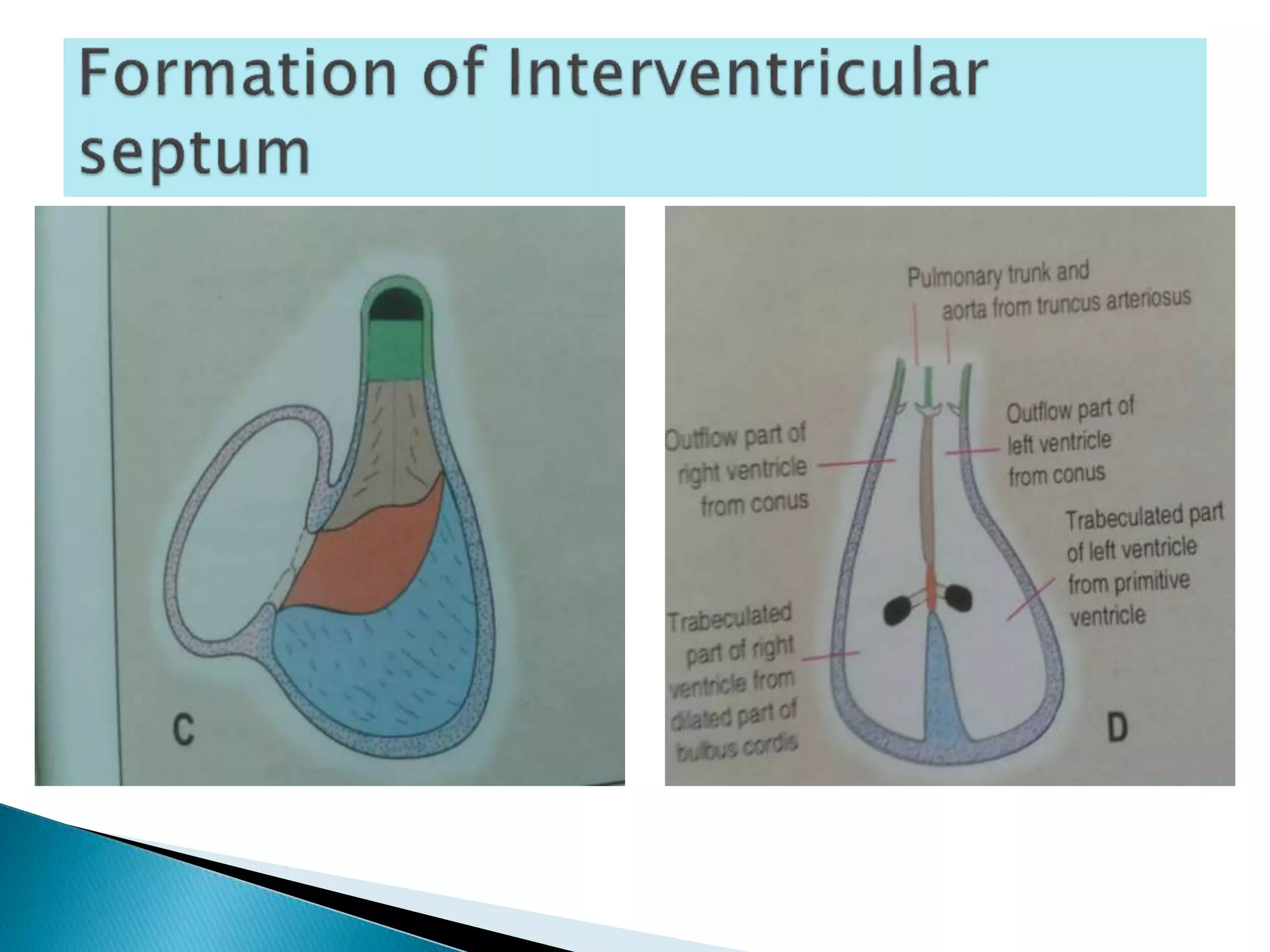
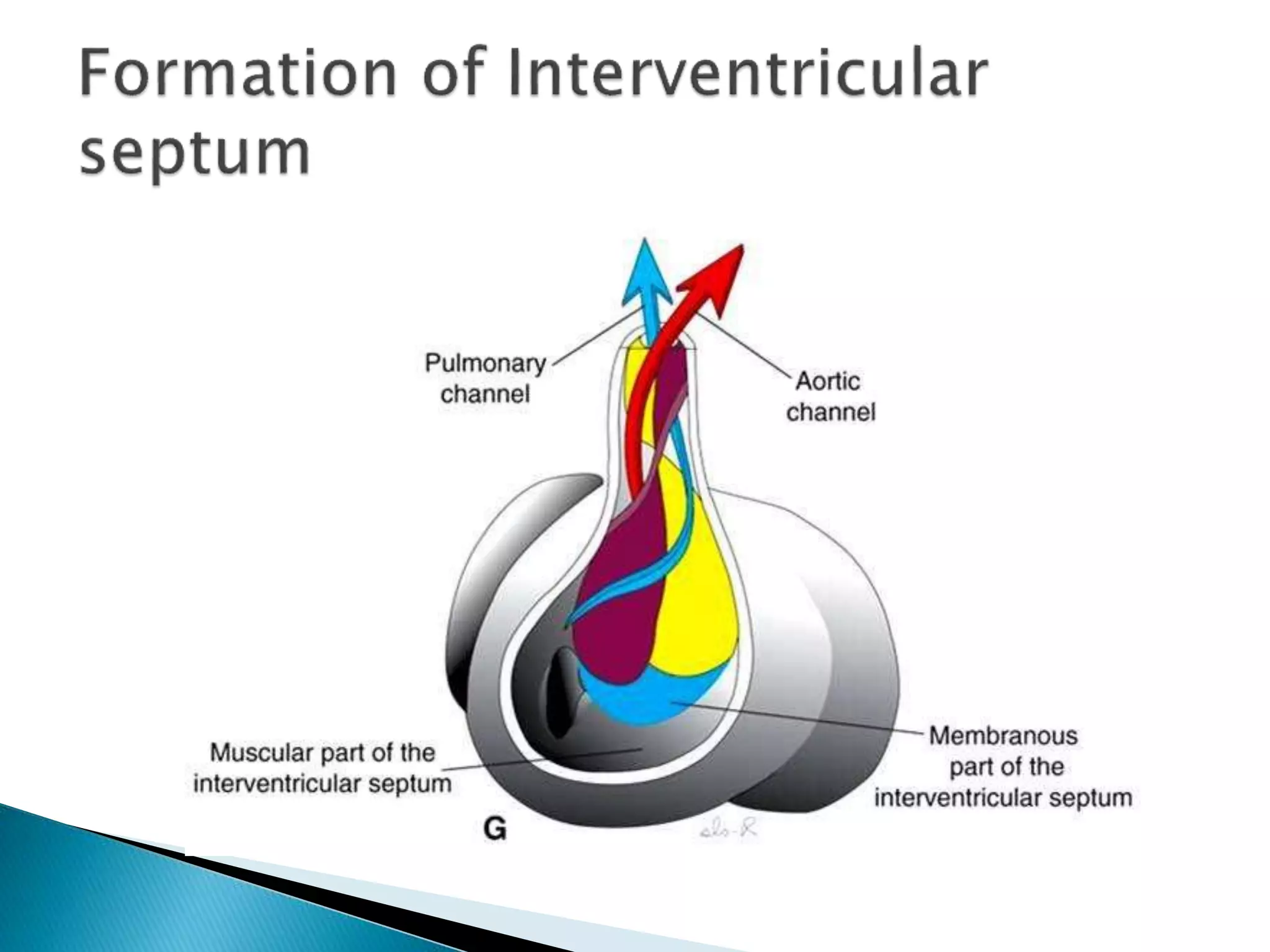
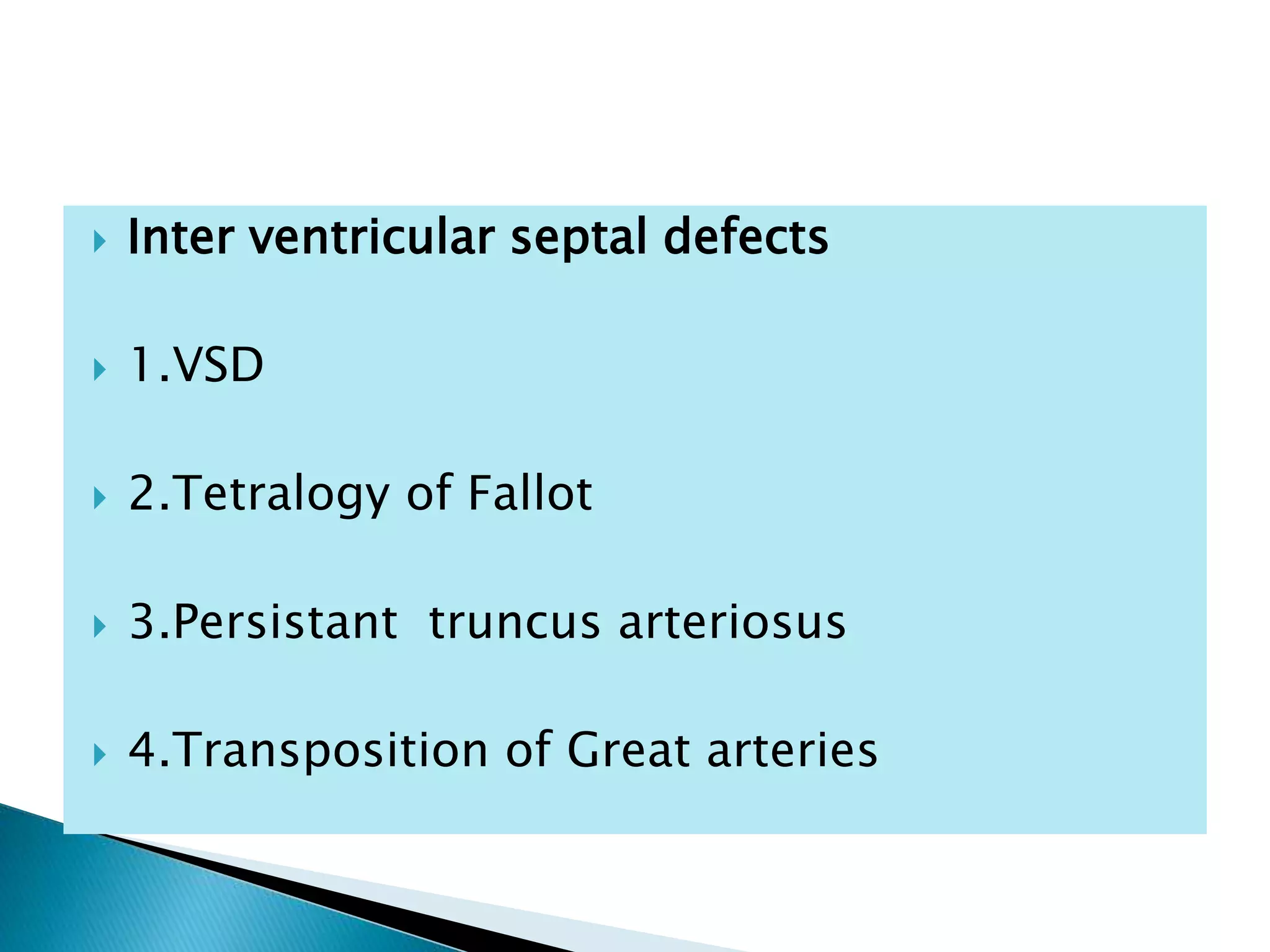
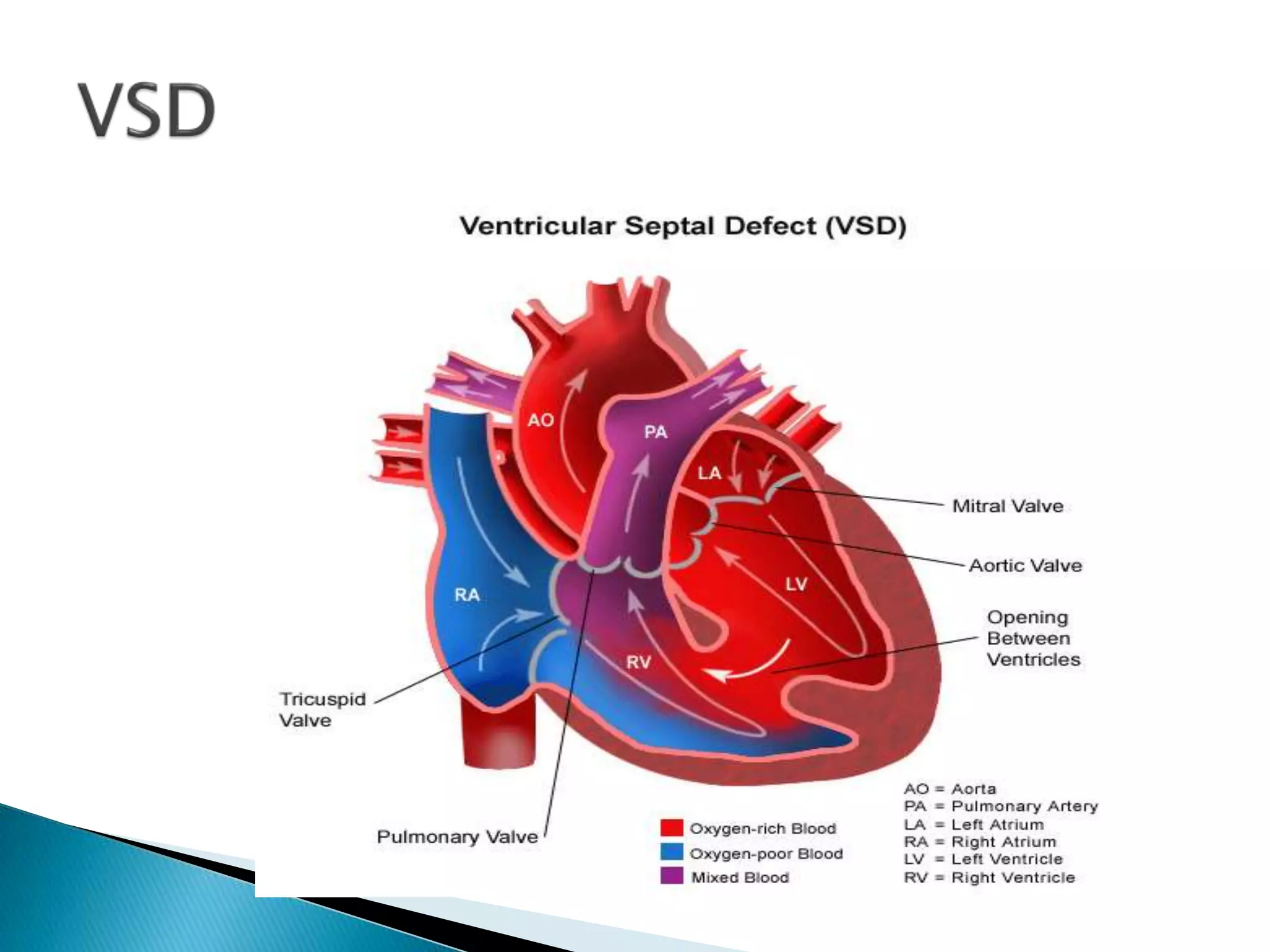
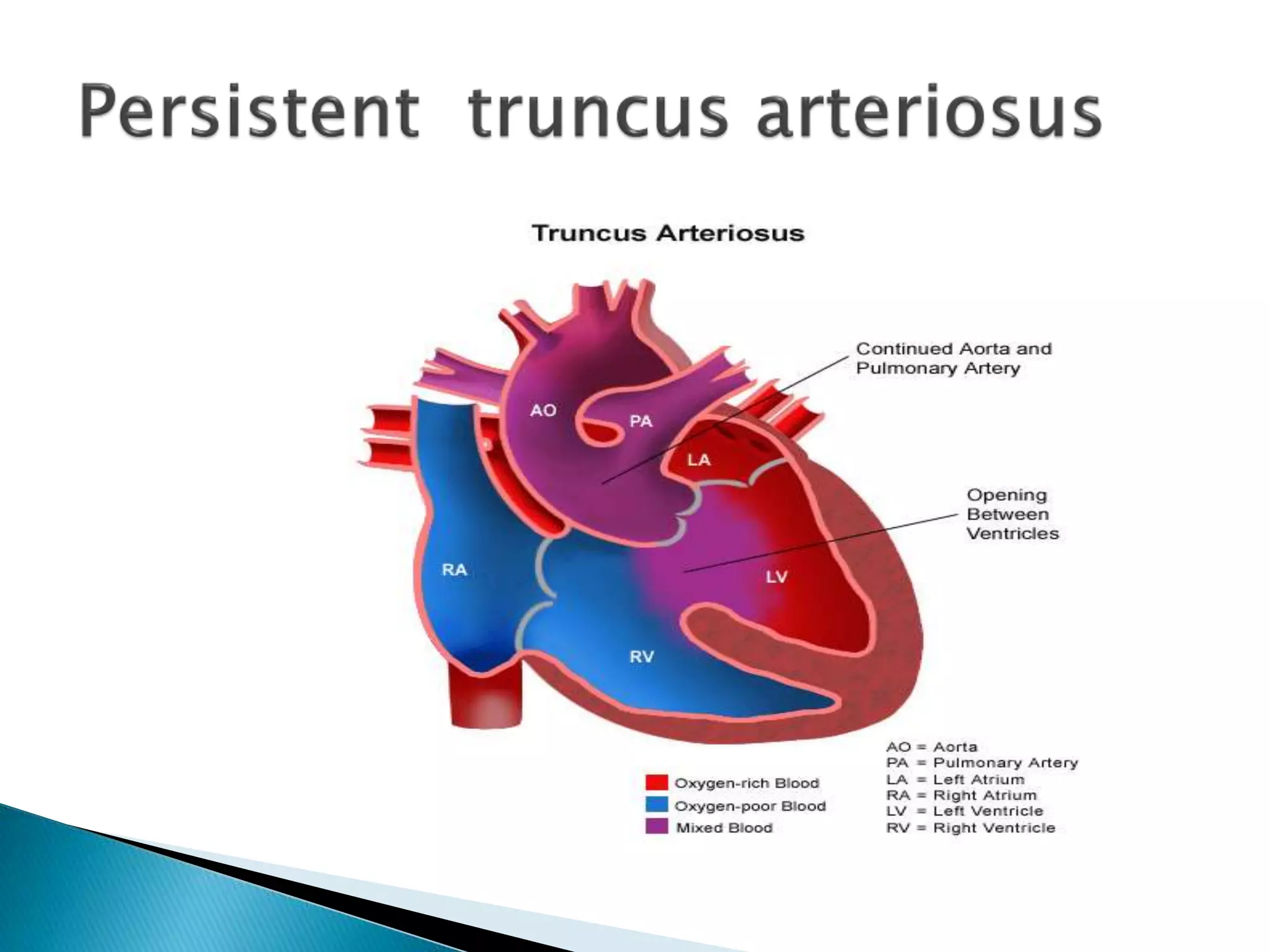
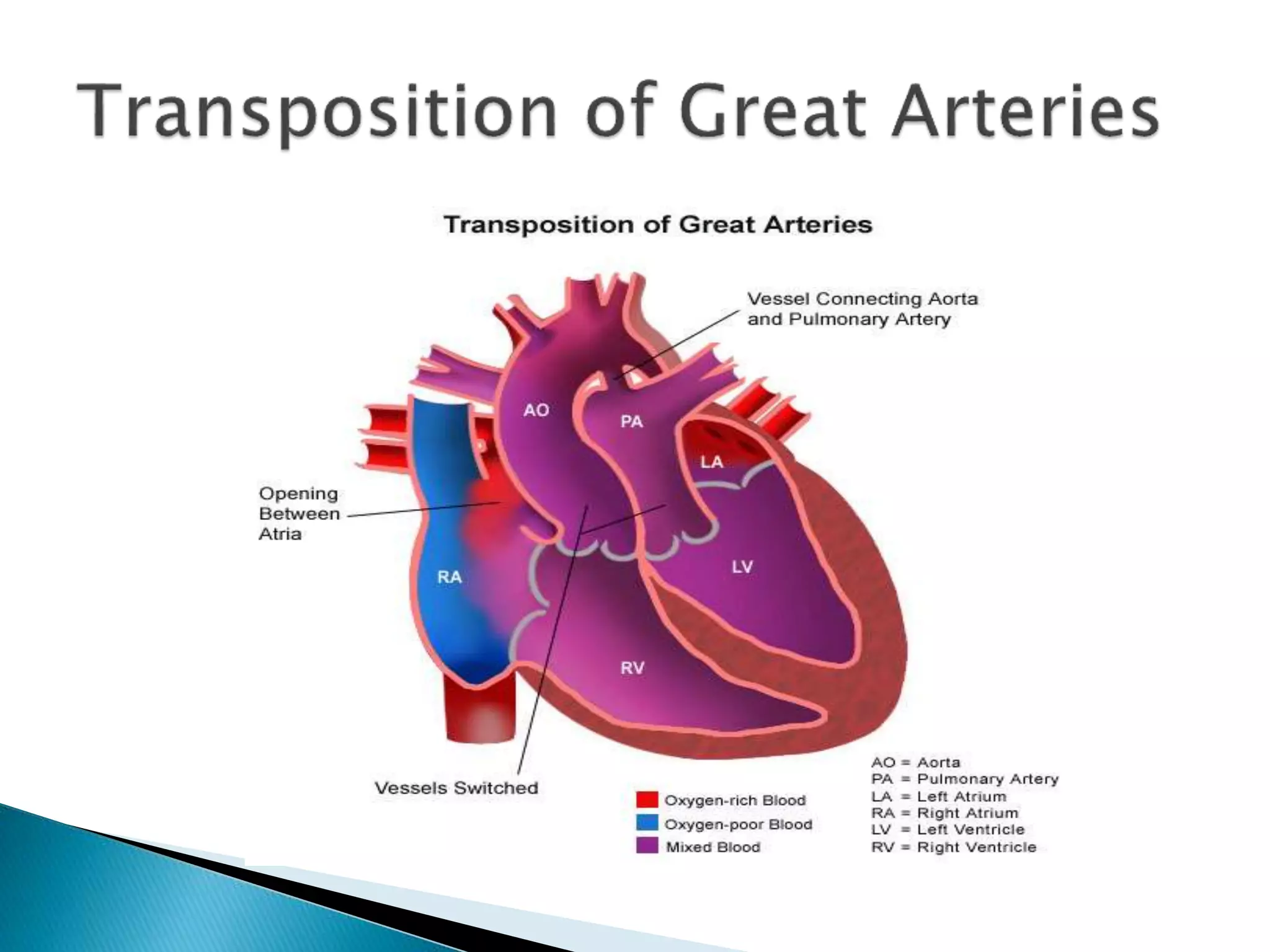
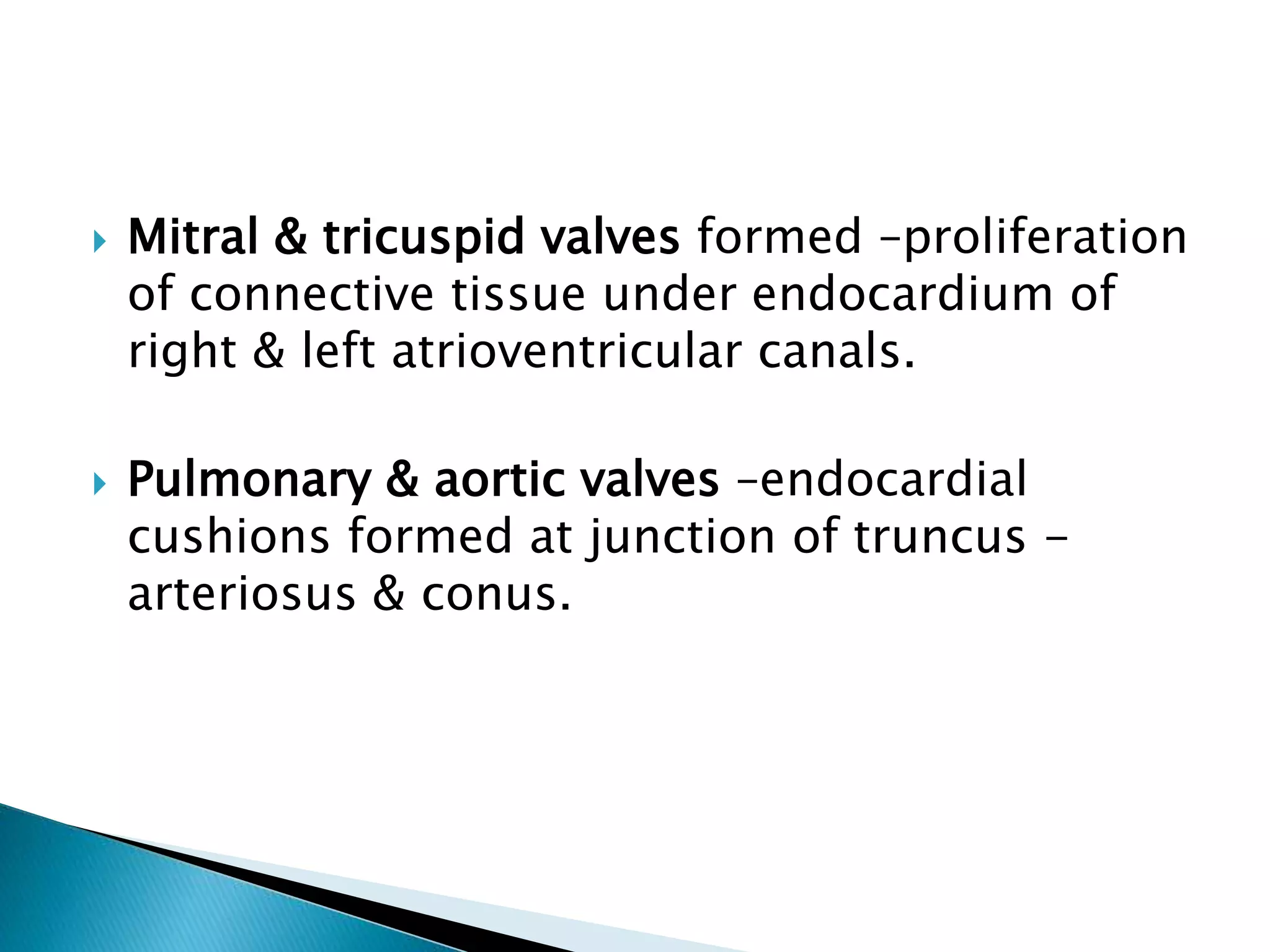
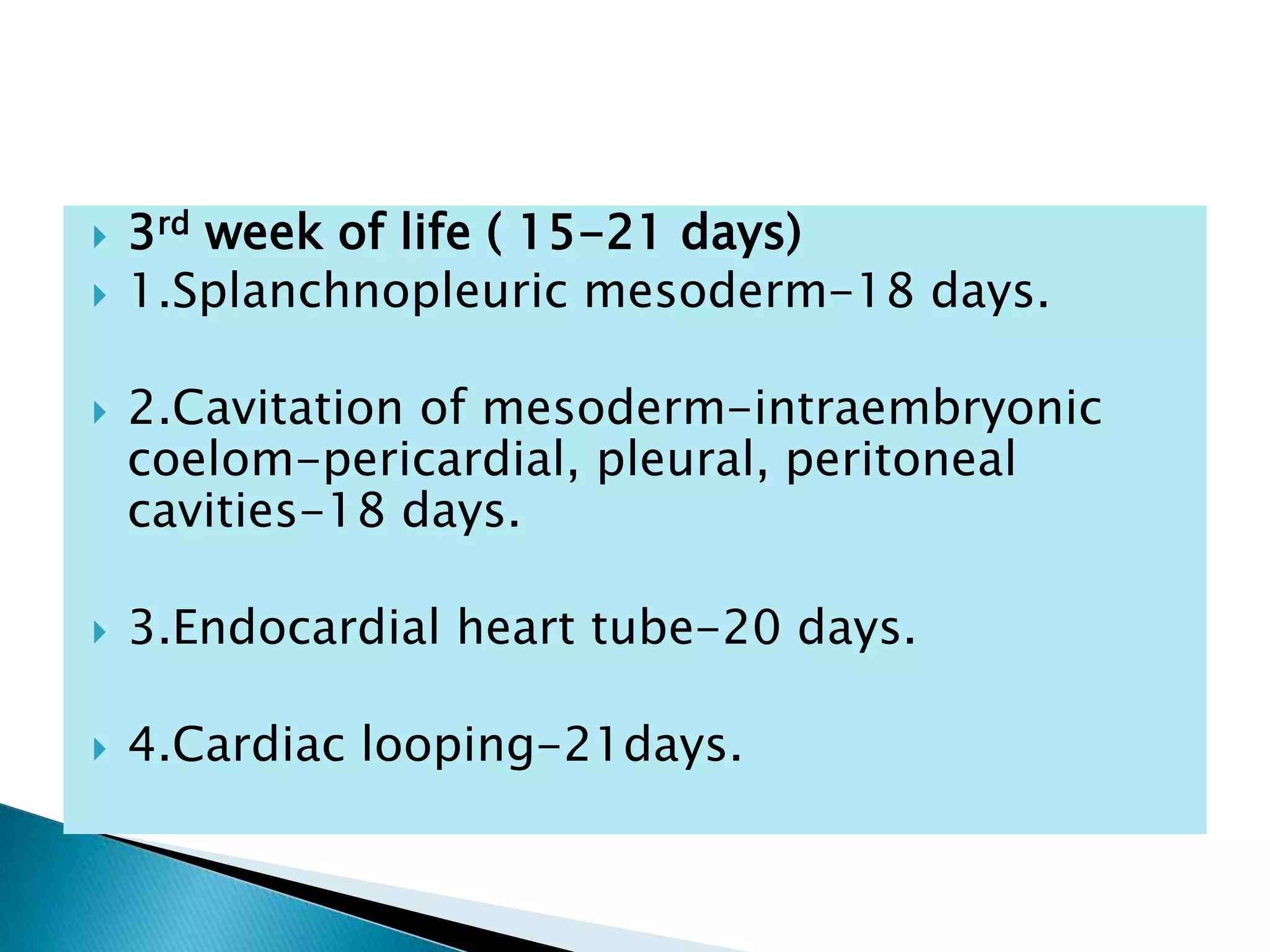
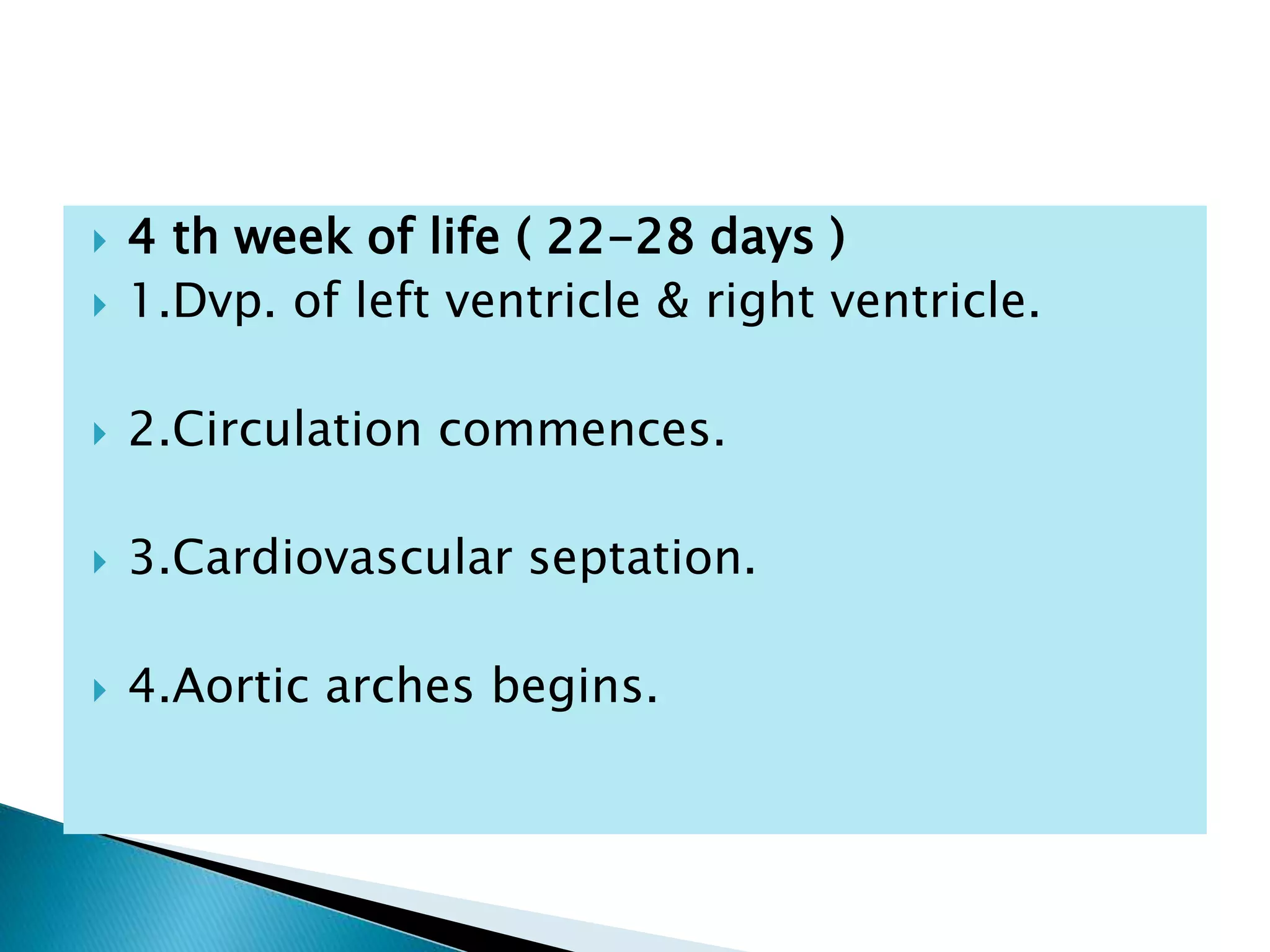
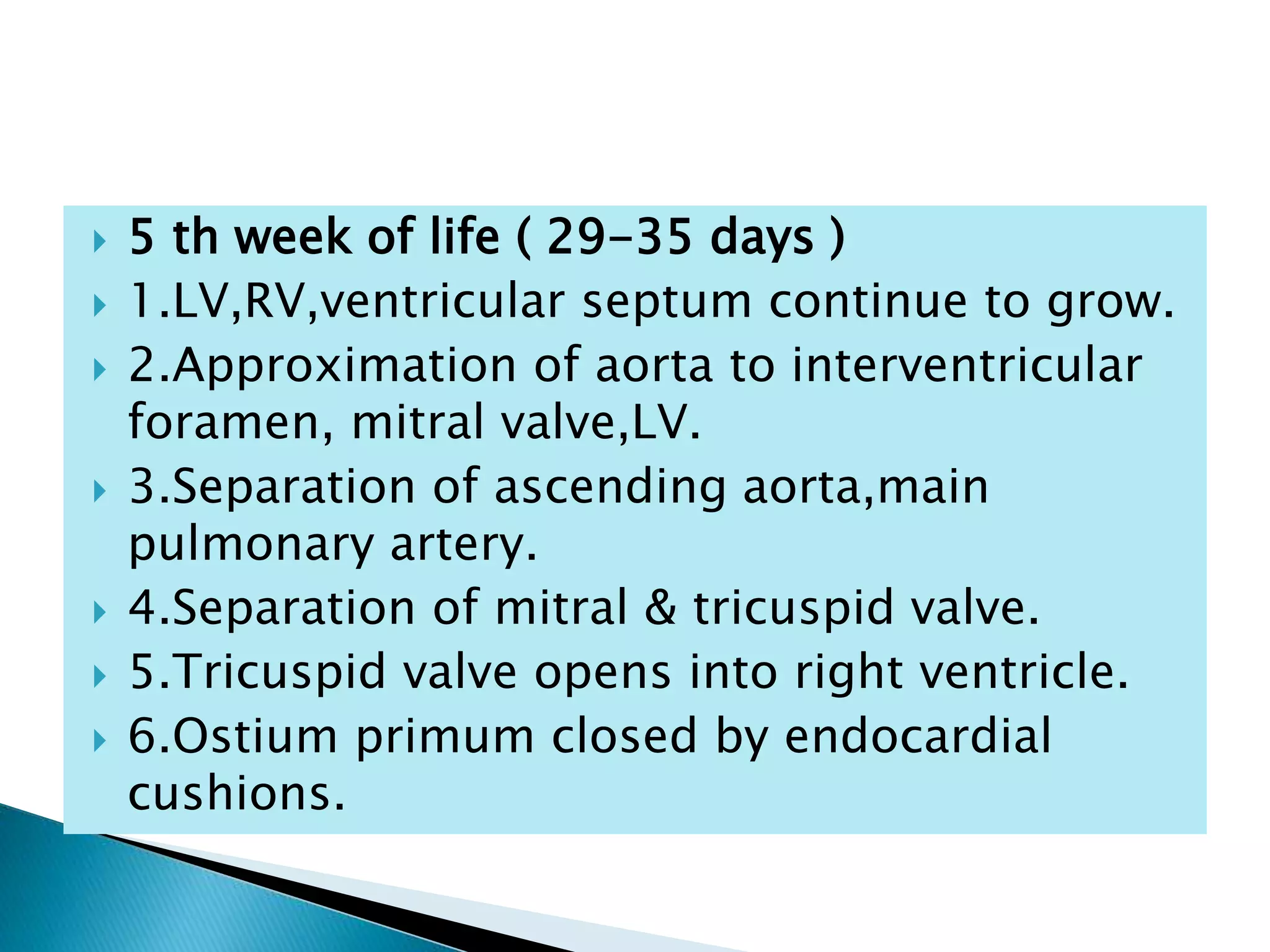
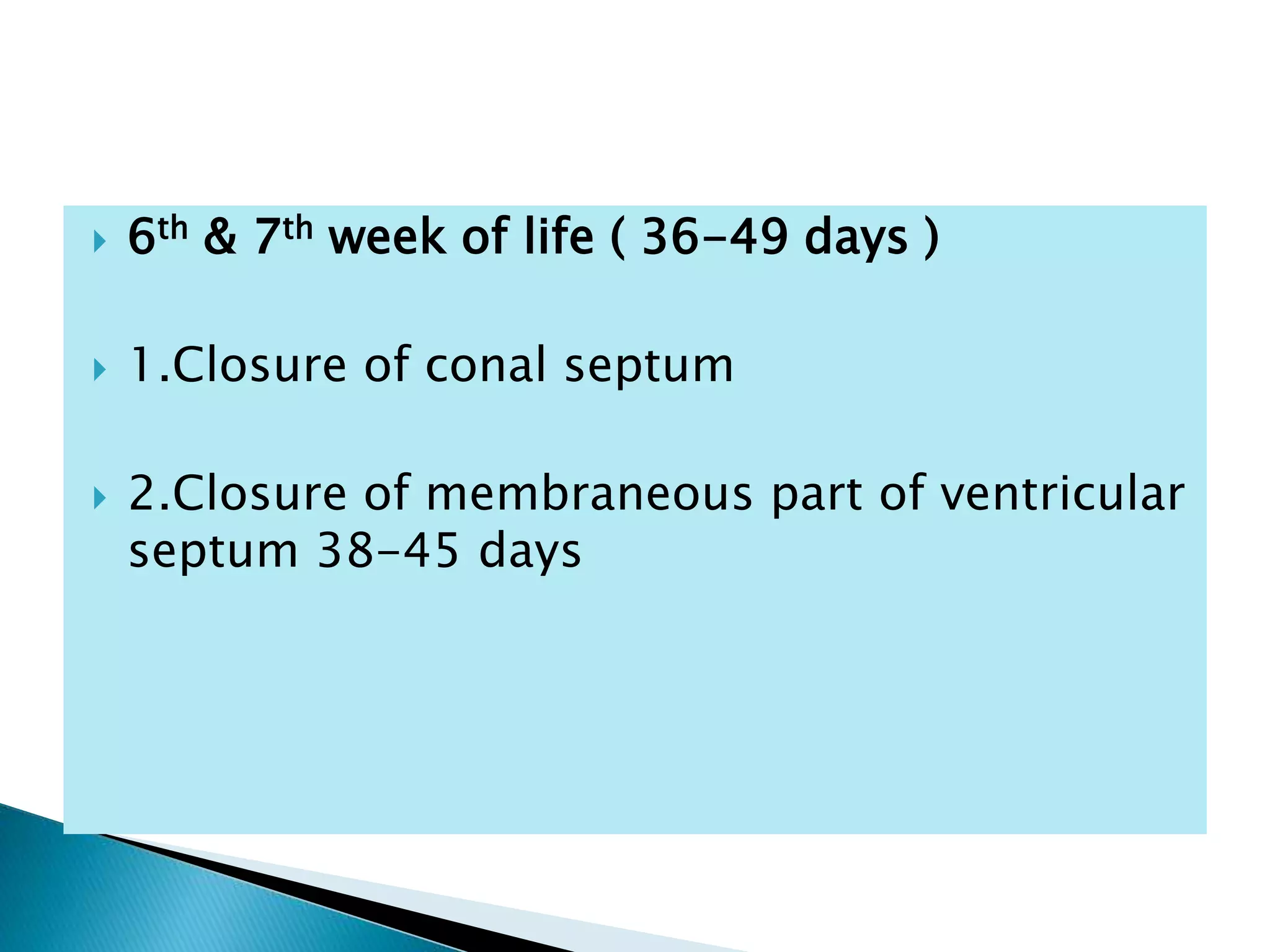
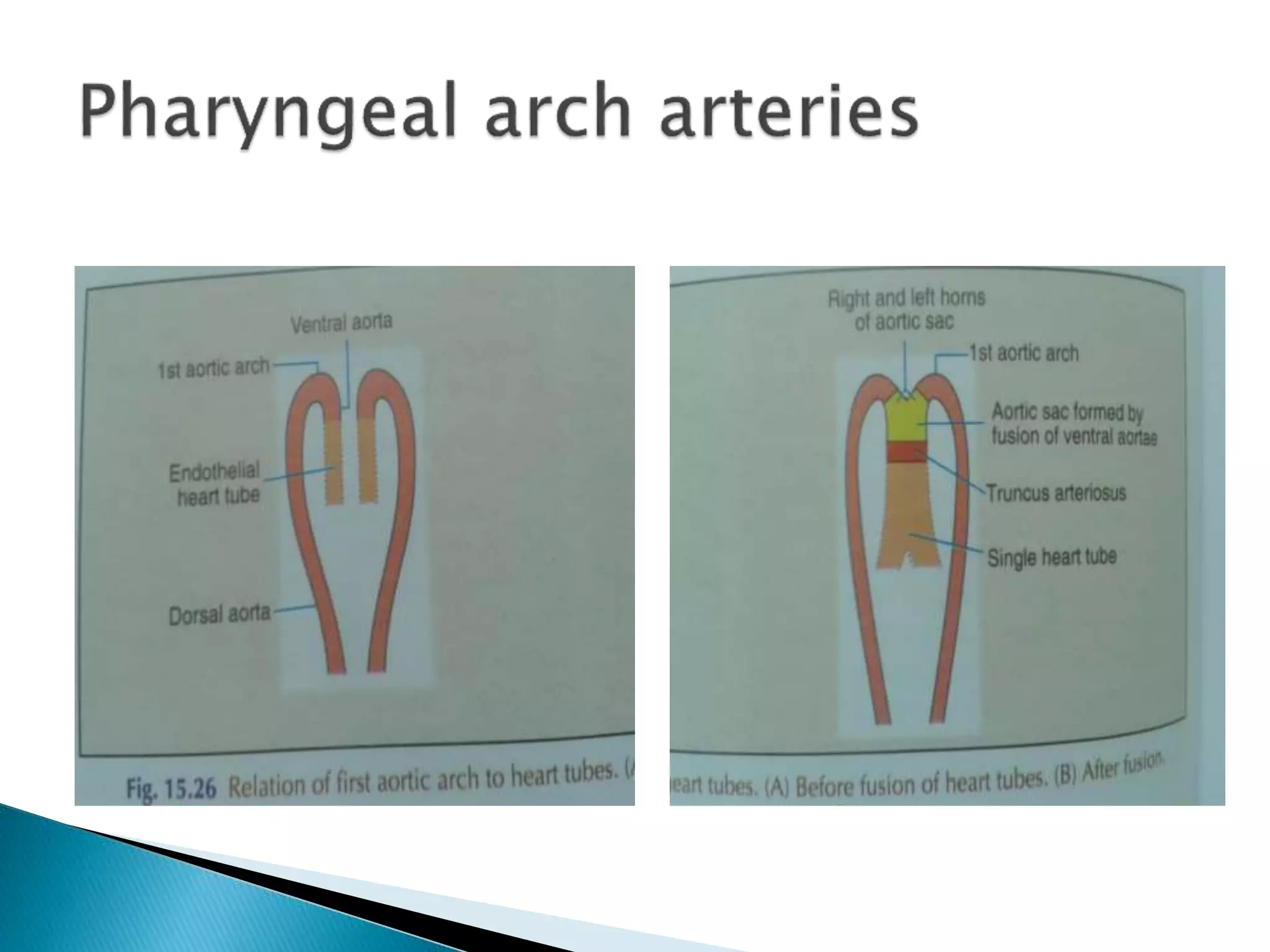
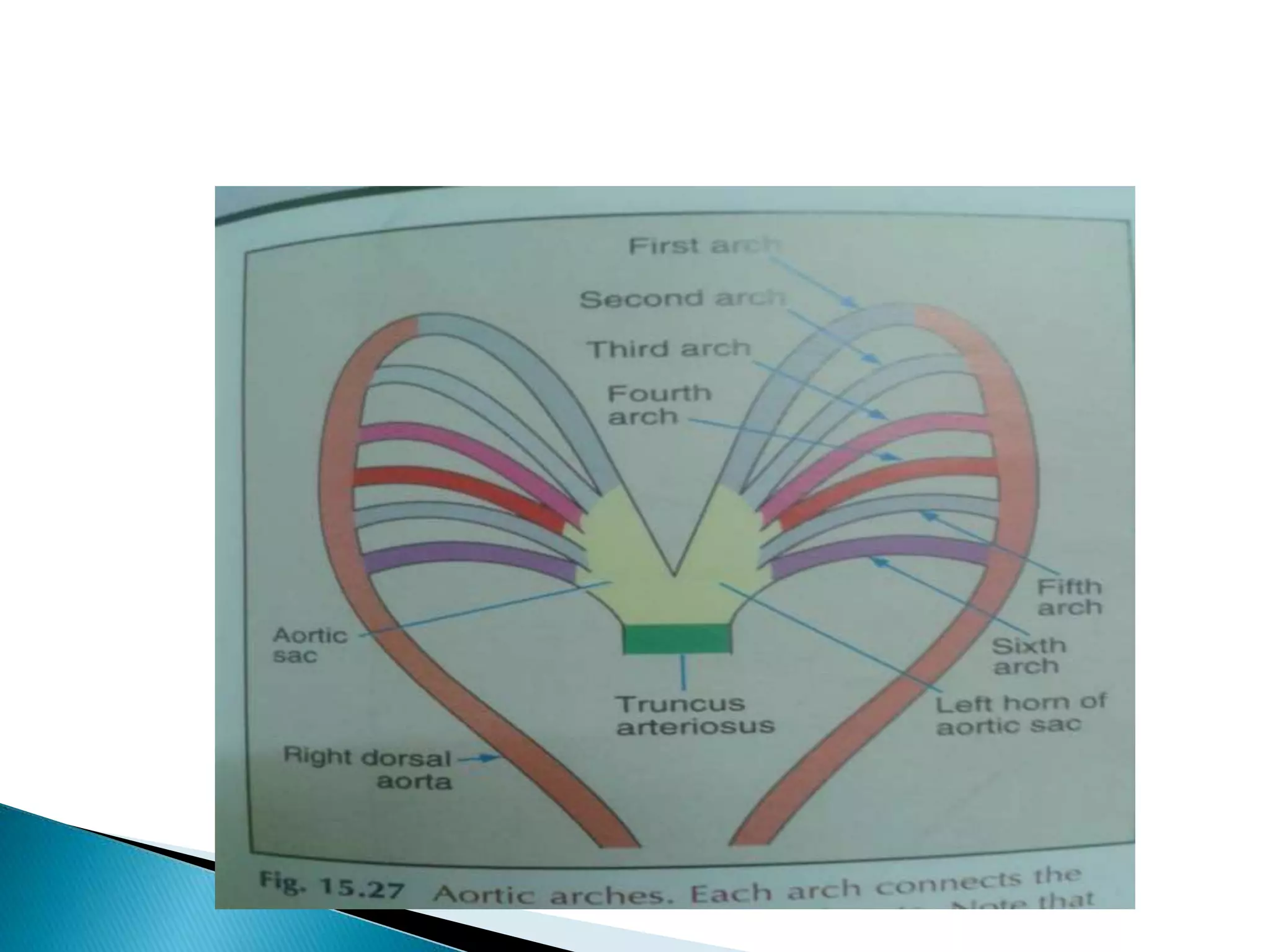
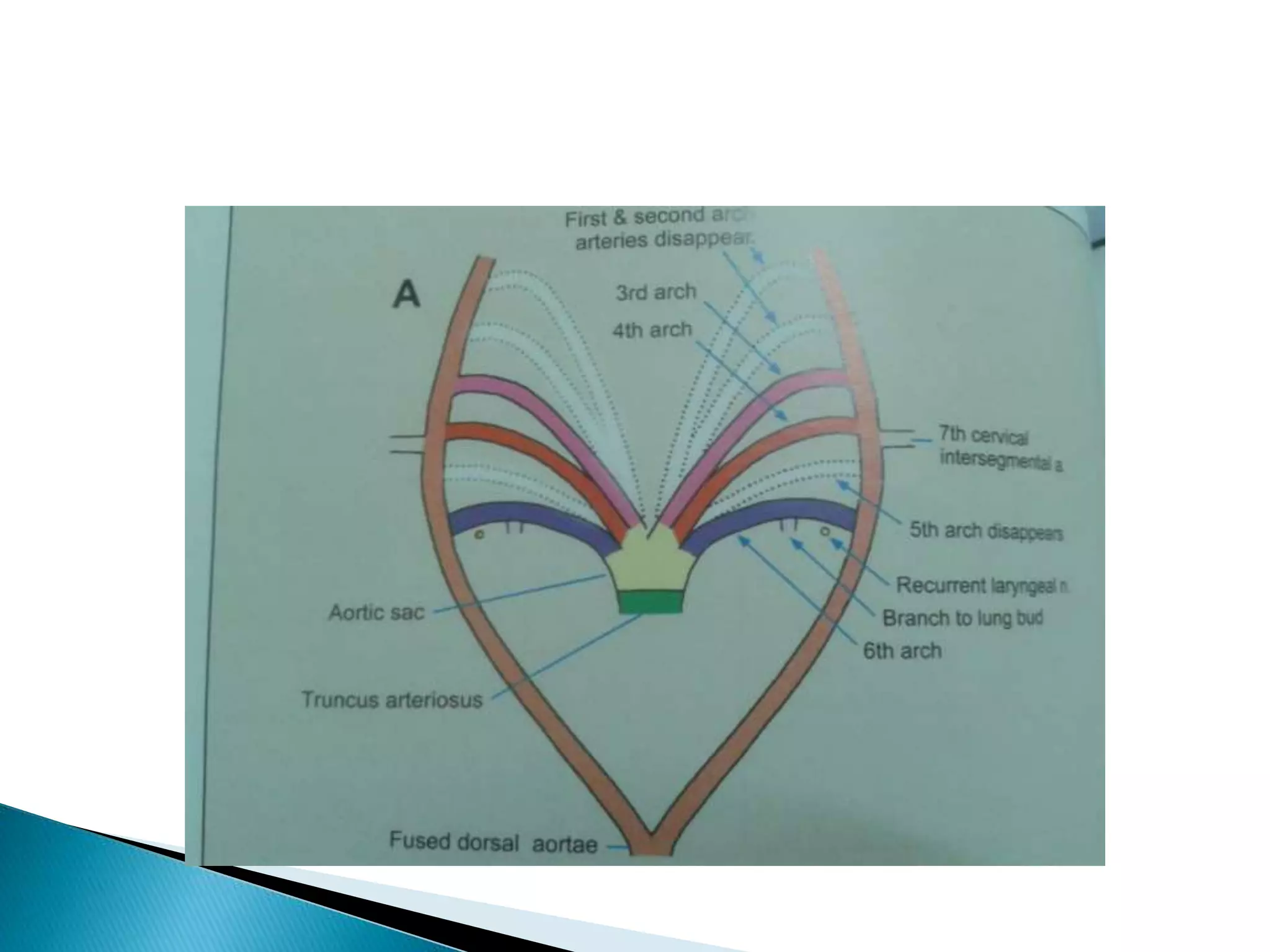
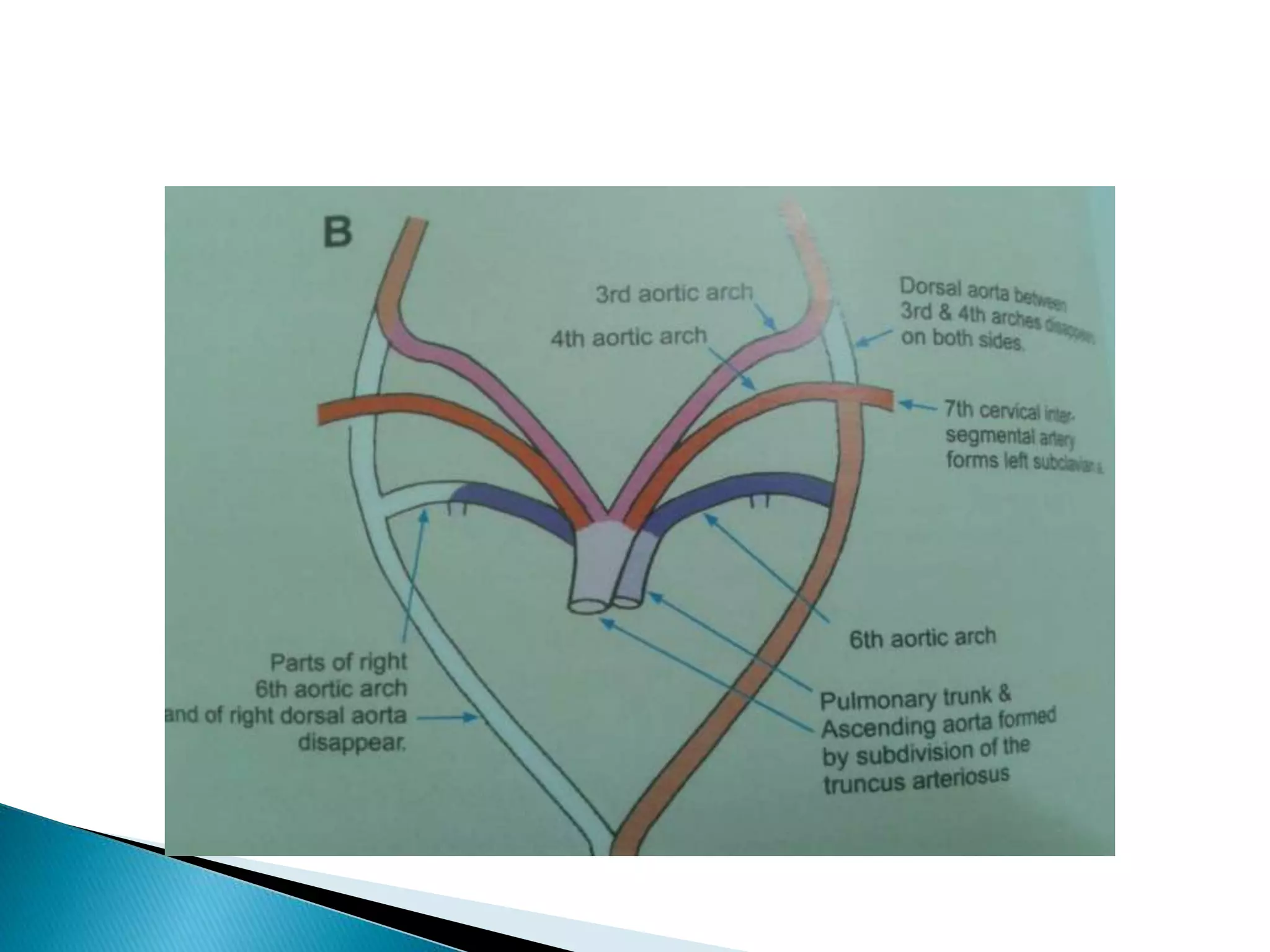
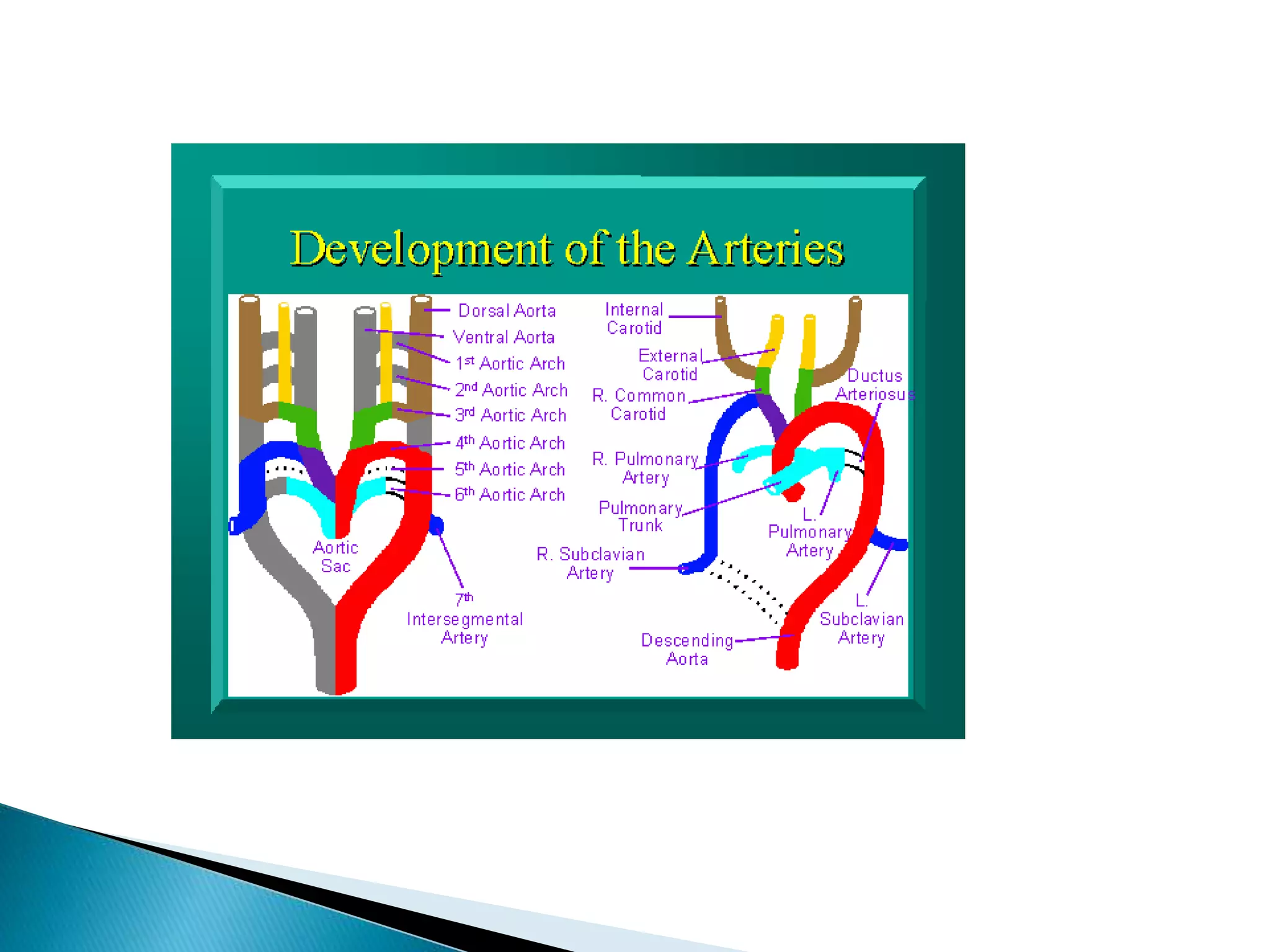
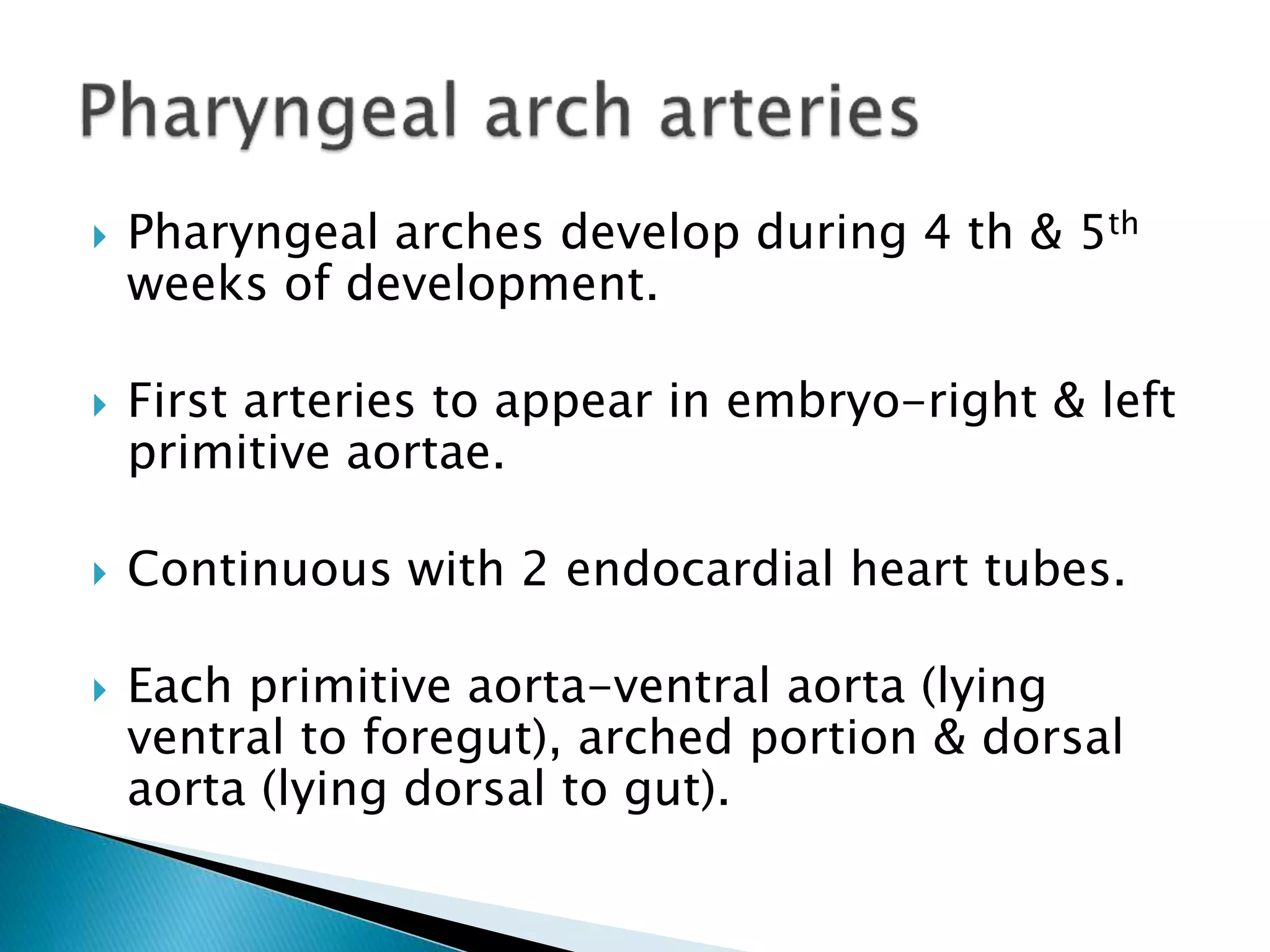
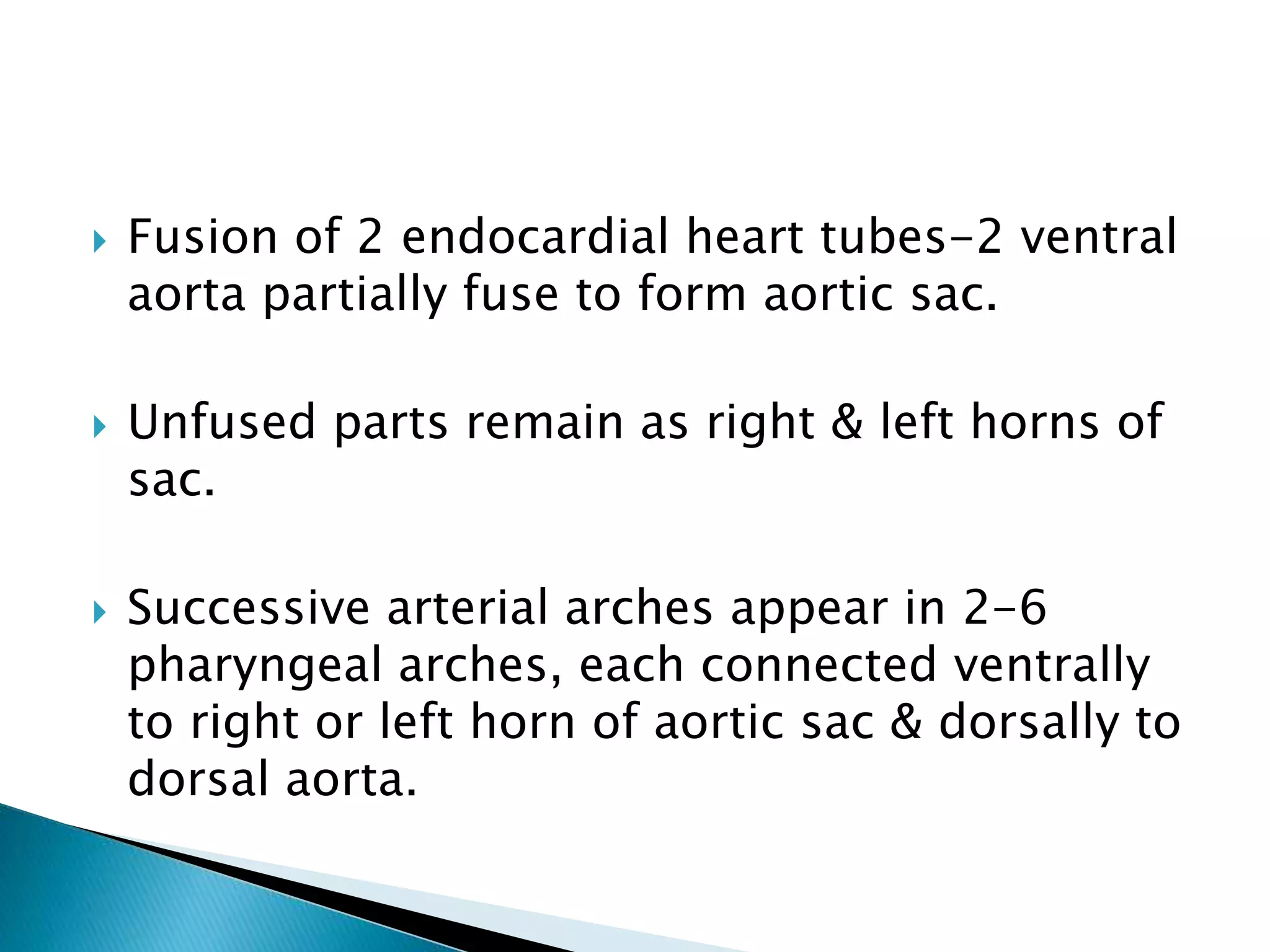
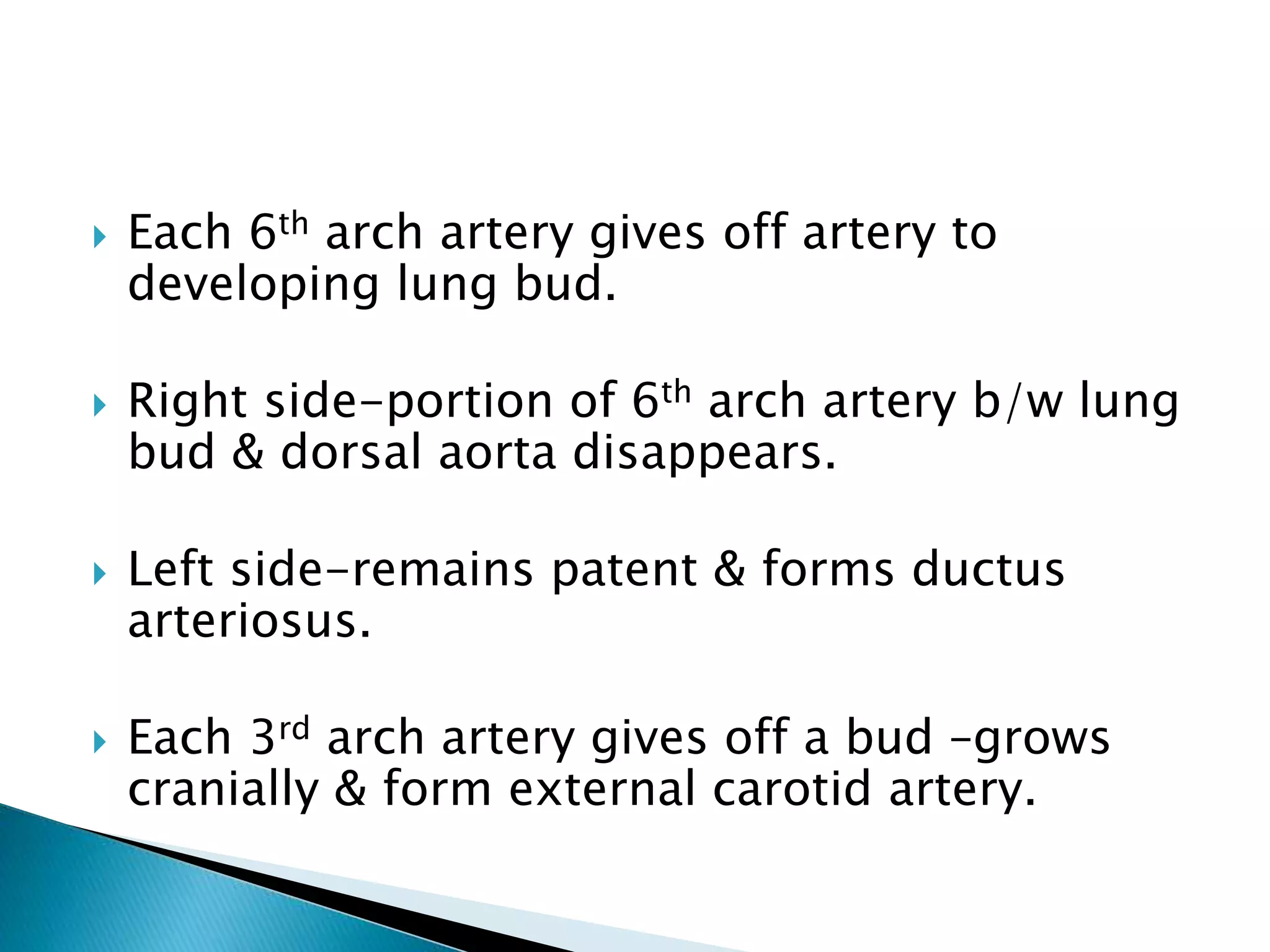
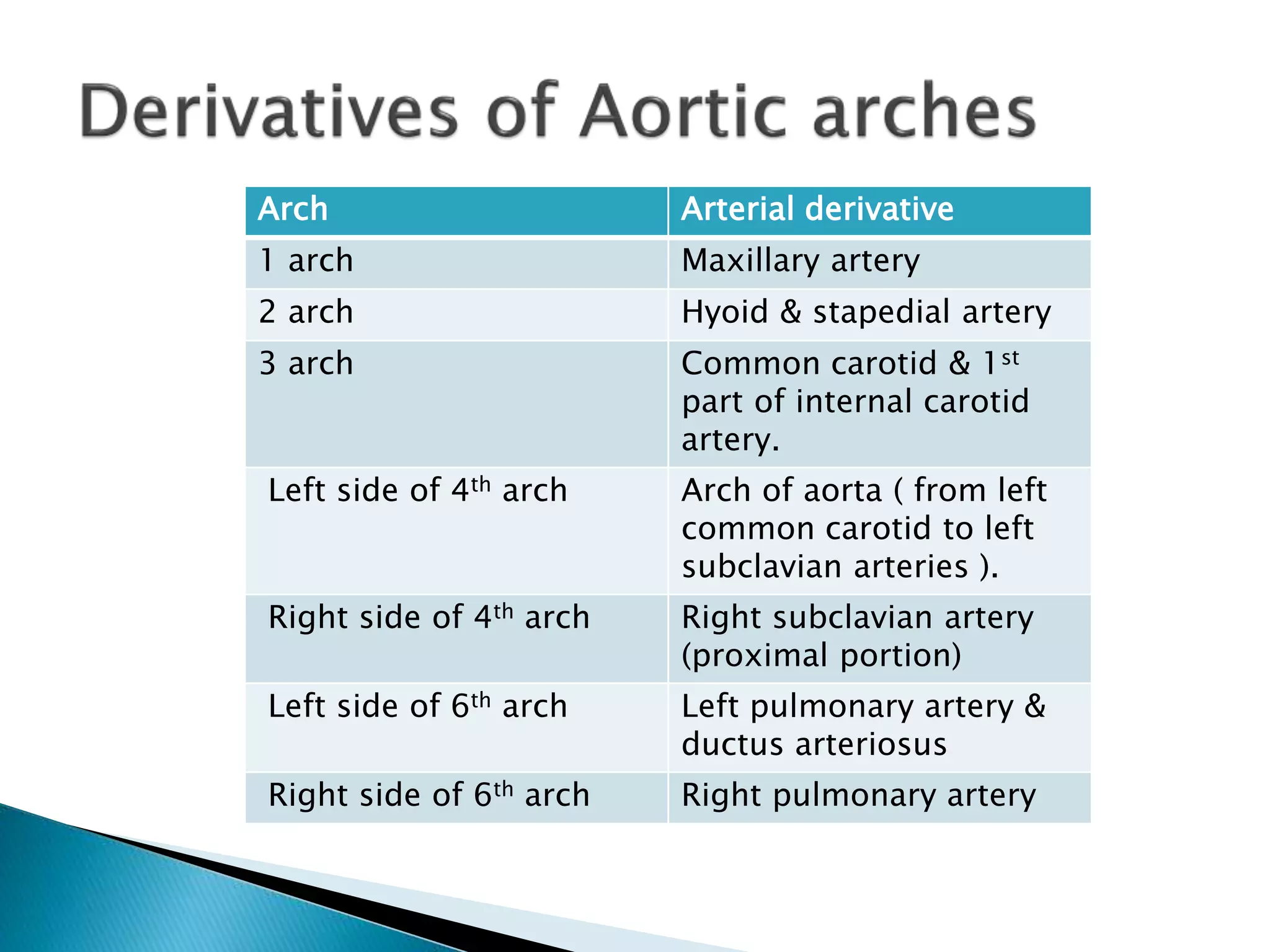
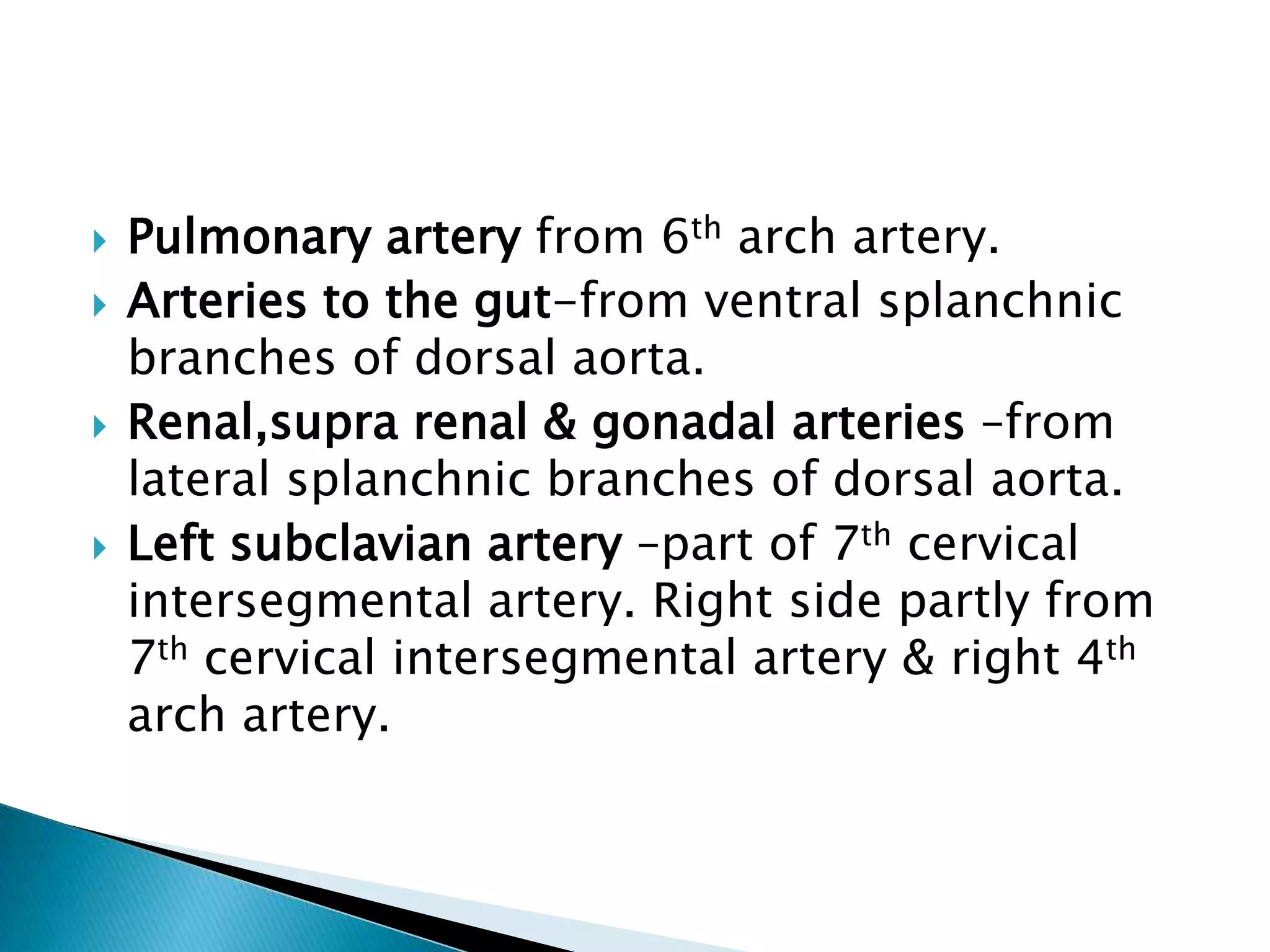
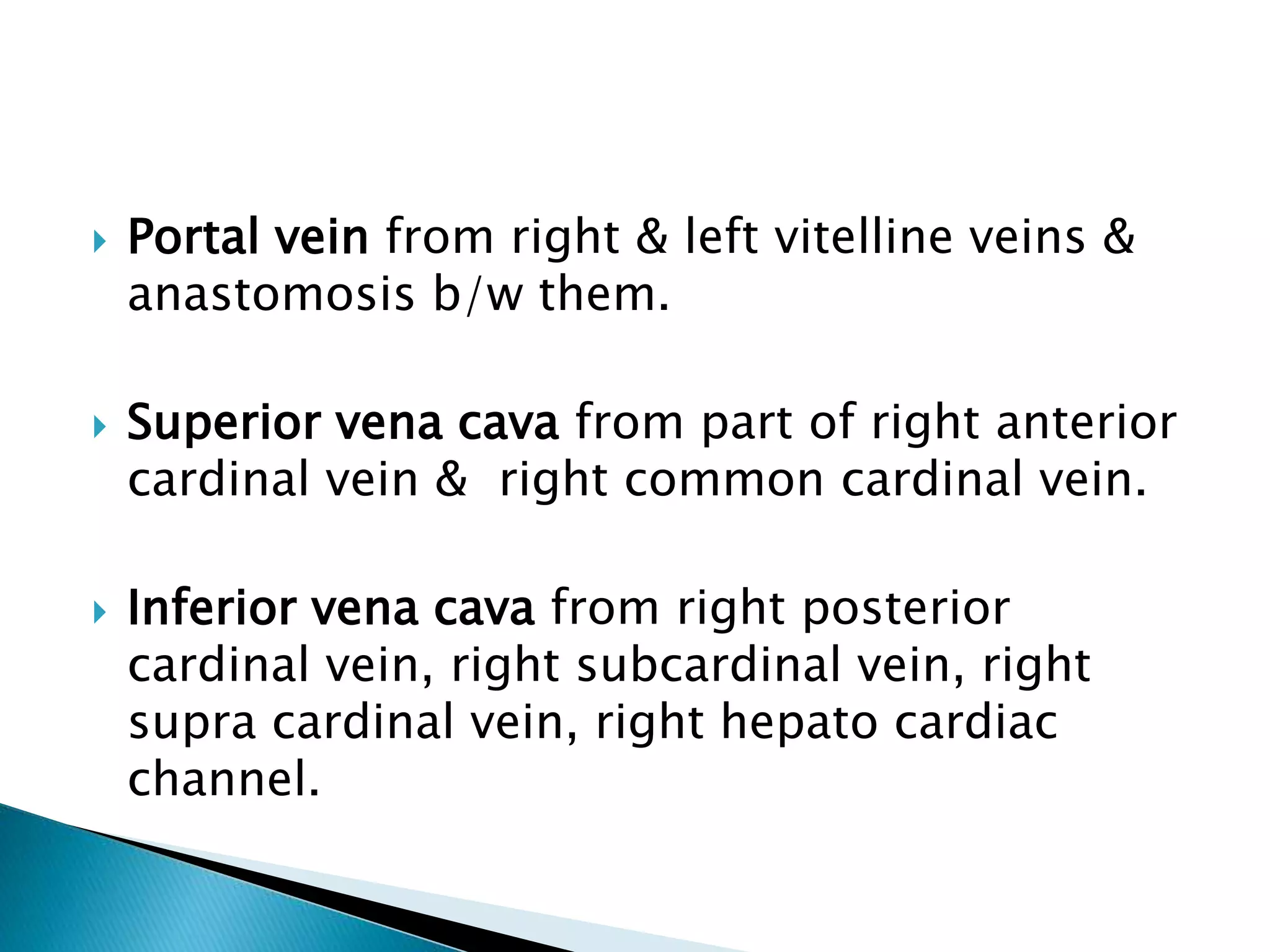
The heart develops from cardiac progenitor cells that migrate to the cardiogenic field and form blood islands that fuse to create the endothelial heart tube. The heart tube undergoes cardiac looping and septation to form the four-chambered heart. During septation, the atria, ventricles, and great arteries are partitioned. The aortic arches give rise to major blood vessels of the head and neck. By the end of the 7th week, septation is largely complete and the heart has transformed into a functional four-chambered pump.