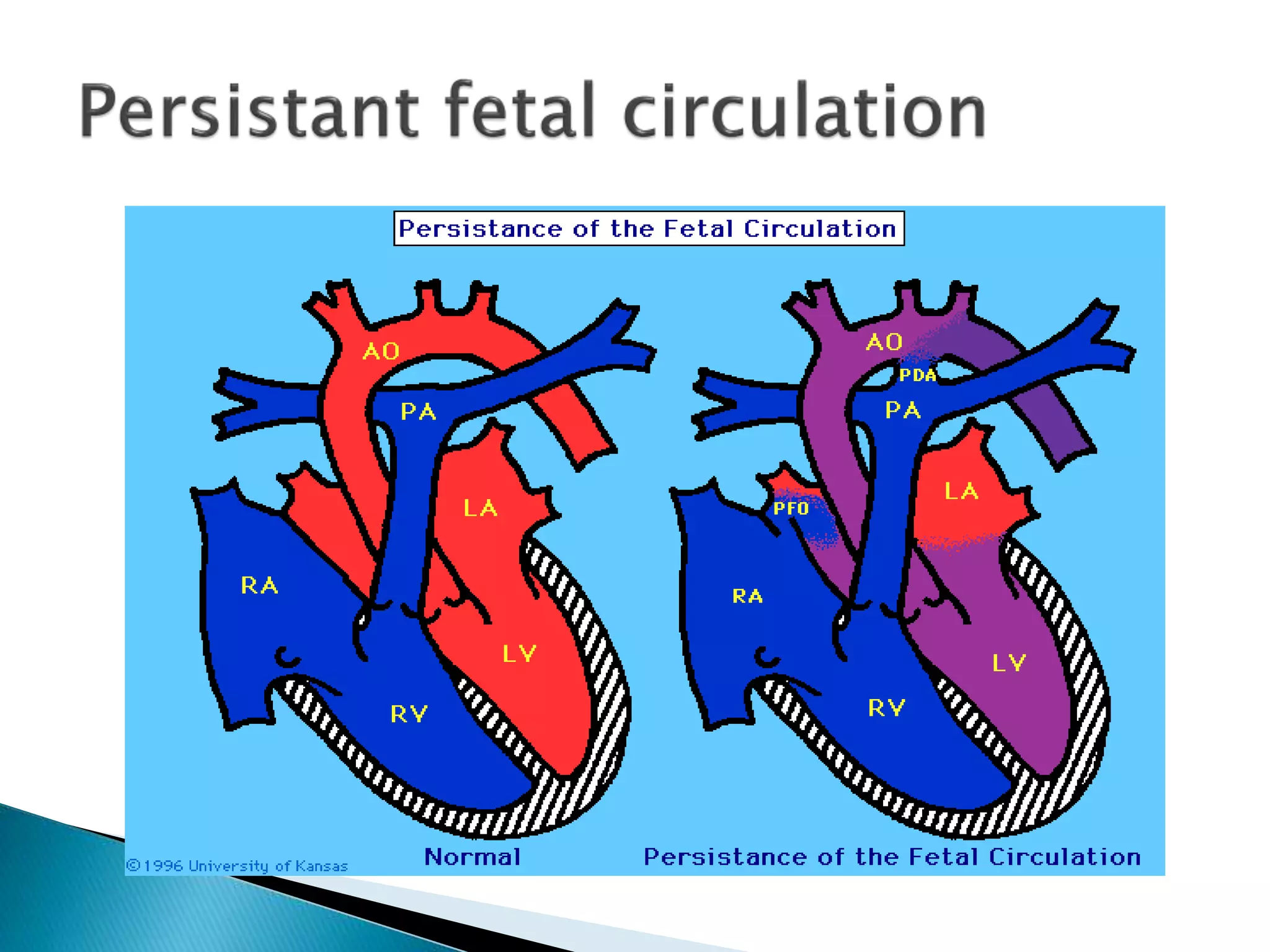
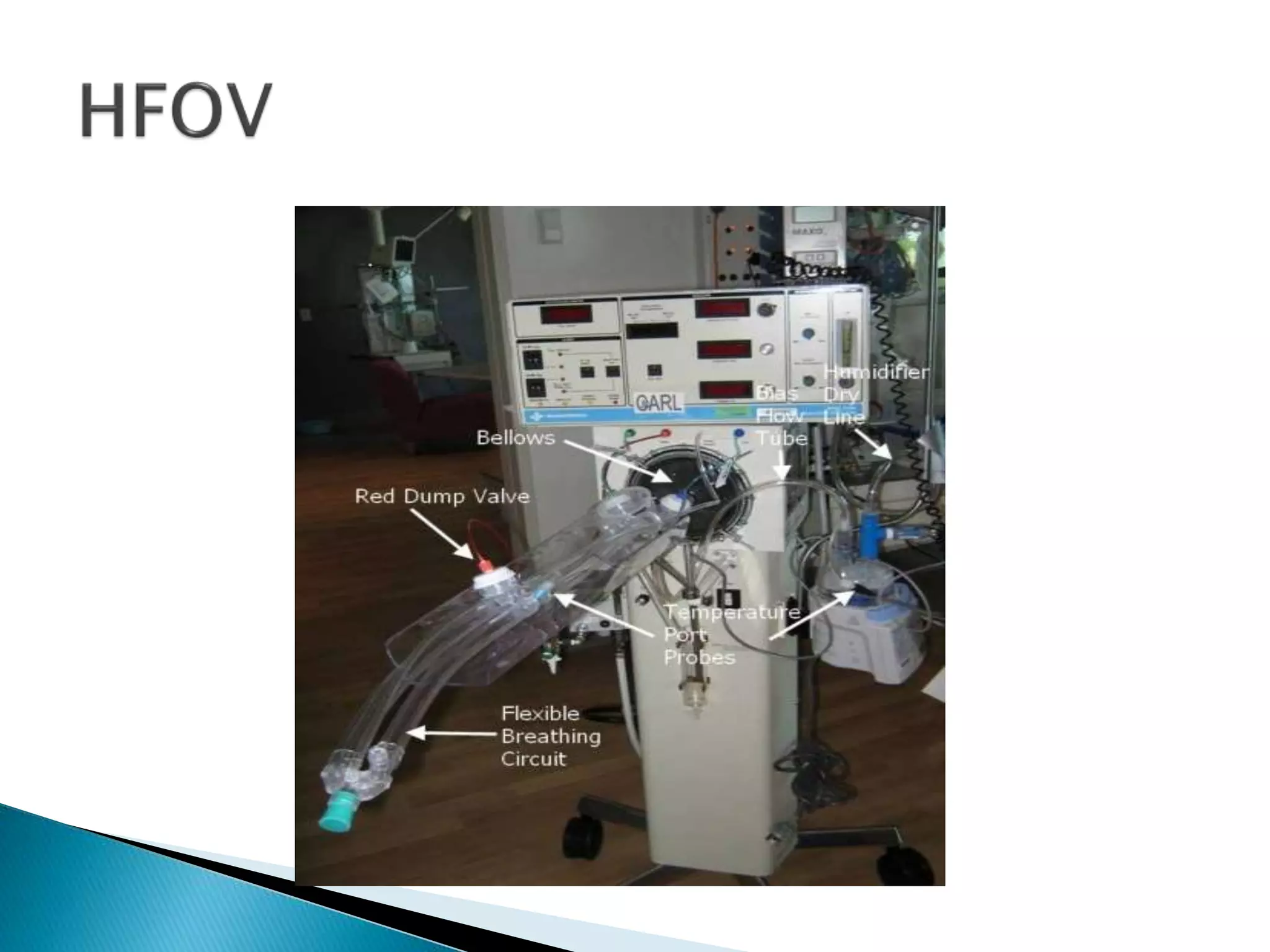
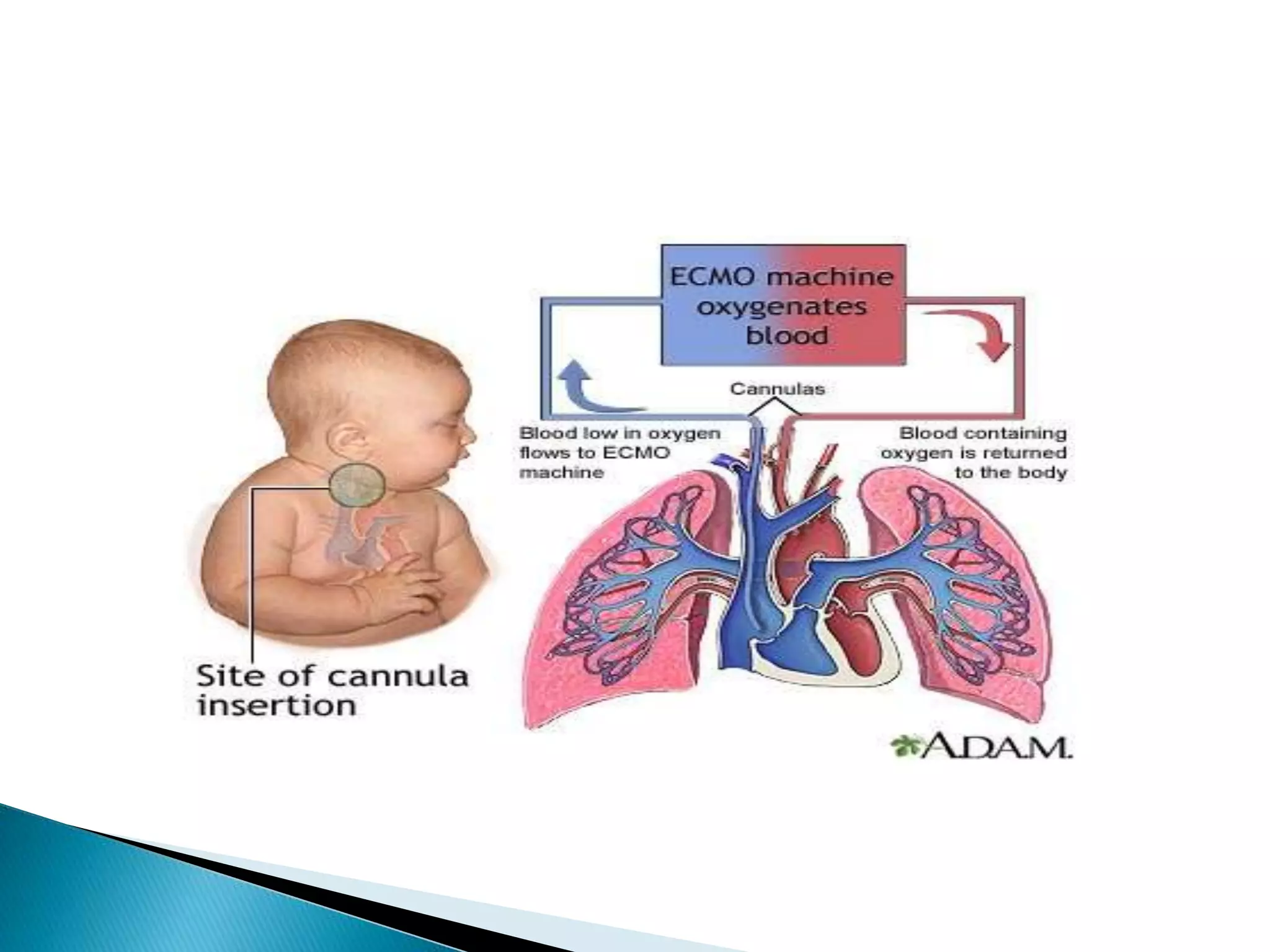
This document discusses persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN). It defines PPHN as sustained elevation of pulmonary vascular resistance, disrupting normal circulatory transition after birth. PPHN carries risks of chronic lung disease and neurodevelopmental issues. Treatment aims to reverse hypoxemia through respiratory support, pulmonary vasodilation (e.g. inhaled nitric oxide), and hemodynamic support (e.g. medications, ECMO). The prognosis of PPHN depends on the underlying cause and response to treatment.