The document summarizes the development of the heart and associated vessels in the embryo. It discusses the formation of the primitive heart tube and the divisions that form the four chambers. It describes the development of internal structures like the atrioventricular canal and septa. It also covers the formation of the aortic arches and branching arteries as well as the umbilical and cardinal veins. The development occurs through the fusion, division and remodeling of early heart structures in the embryo.


![=DEVELOPMENT OF HEART (cardiac loop):-
[ 1 ]=External features of cardiac loop.
1*development of primitive heart tube.
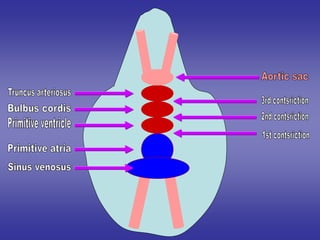
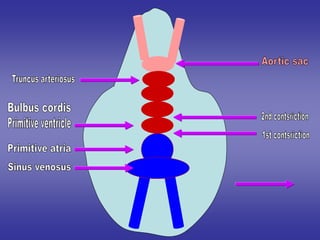
2*development of cardiac contstrictions.
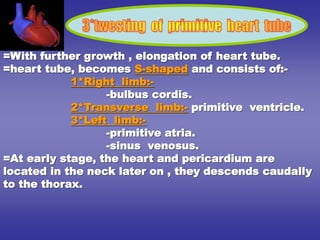
3*twesting of primitive heart tube.
[ 2 ]=Internal features of cardiac loop:-
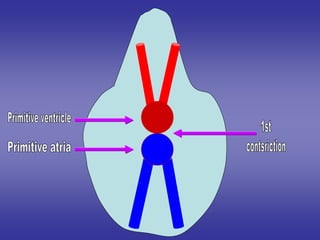
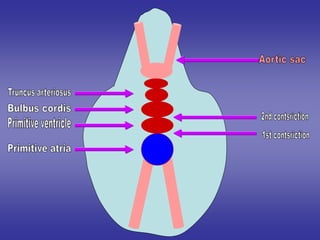
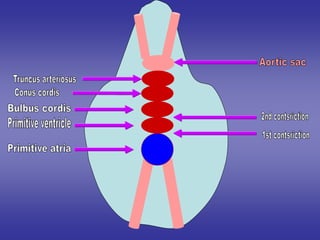
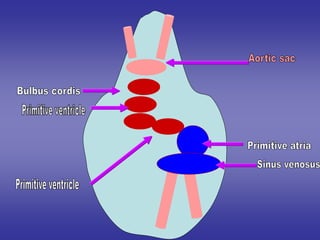
1*Development sinus venosus.
2*Division of atrio-ventricular canal.
3*Development of primitive atria.
4*Development of primitive ventricle.
5*Development of bulbus cordis.
6*Development of truncus arteriosus.
[ 3 ]=Fetal circulation.
[ 4 ]=Congenital anomalies of heart.
=DEVELOPMENT OF ARTERIES:-
Development of aortic arches
DEVELOPMENT OF VEINS:-
1.UMBILICAL VEINS.
2.VETILLINE VEINS.
3.CARDINAL VEINS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-6-320.jpg)

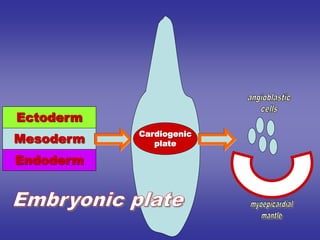
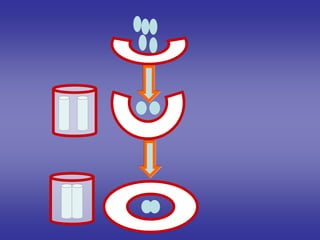
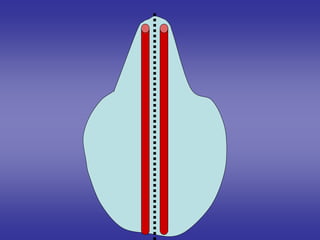
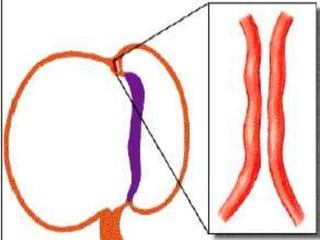

![[ 1 ]=External features
of cardiac loop.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-16-320.jpg)


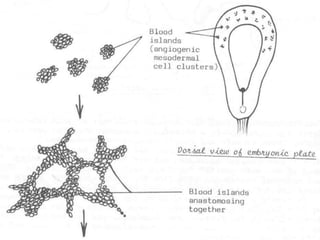
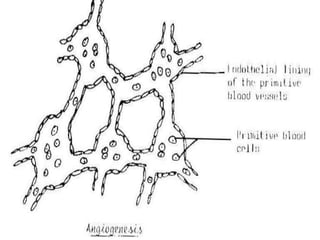
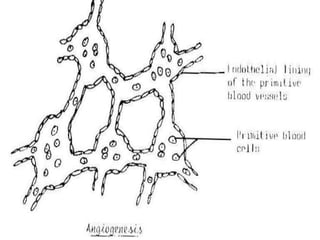
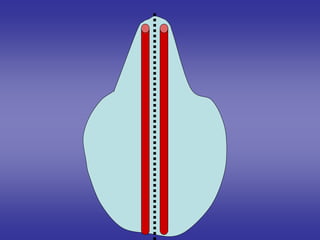
![1]=One will form of a pair of primitive heart tubes.
arranged in the parasagittal plane.
2]=Others will growe, elongate & branch.
to form network of blood vessels.
one end of this network:-
-where the blood leaves the network.
-will form veins.
the other end of this network:-
-where the blood enters the network.
-will form arteries.
the network in between the ends will form the
blood capillarie
These blood vessels in two types](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-23-320.jpg)
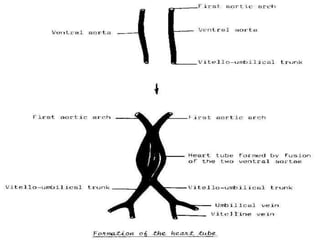
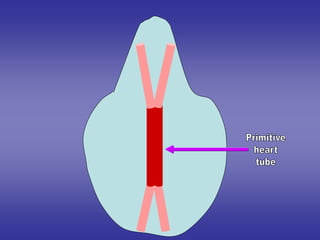
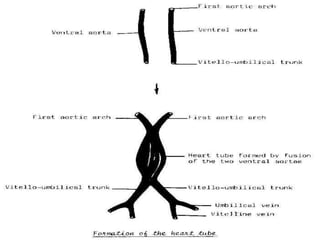
![=The two heart tubes will fuse with
each other giving single primitive
heart tube.
=One end of the tube is arterial
[for exit of blood]
=Other end of tube is venous
[for entering of blood]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-26-320.jpg)




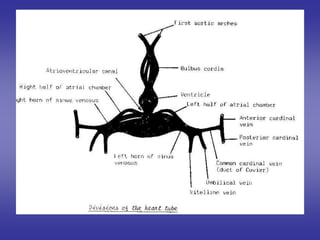
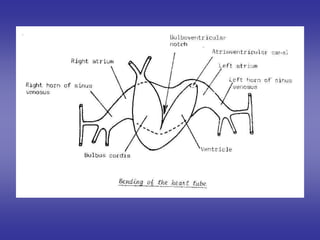
![[ 2 ]=Internal features
of cardiac loop.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-49-320.jpg)


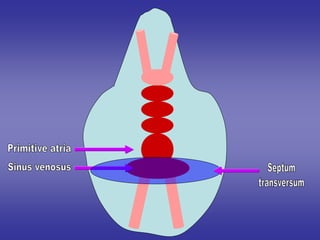
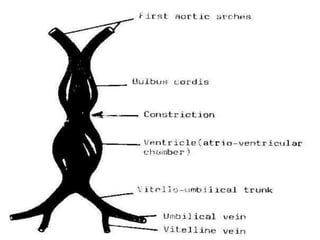
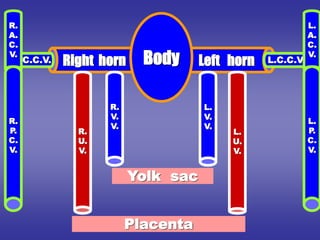
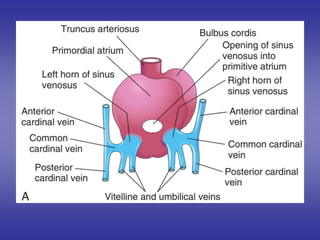
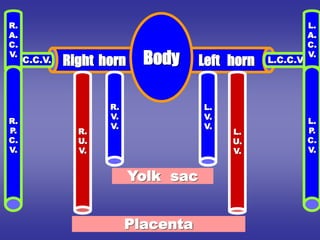
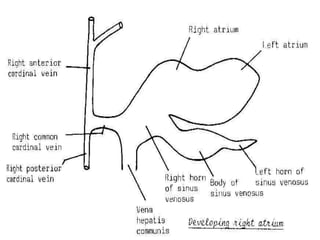
![*SHAPE
[in early stage of development]
1=BODY [CENTRAL PART]:-
-opens into posterior wall of primitive atria by sino-atrial orifice.
2=TWO HORNS [RIGHT & LEFT]:-Each one receives the following:-
Vitelline vein:-
*medial.
*carries unoxygenated blood from yolk sac.
Umbilical vein:-
*lateral.
*carries oxygenated blood from placenta.
Common cardinal vein:-
*the most lateral.
*carries unoxygenated blood from body wall.
*it is formed by union of :- anterior & posterior cardinal veins.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-53-320.jpg)
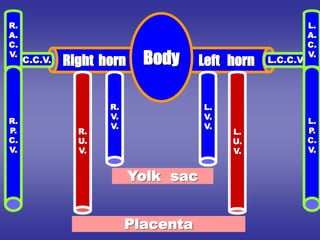
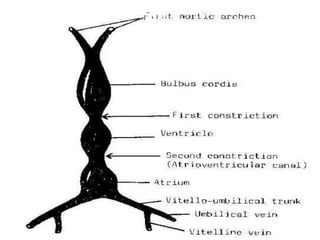
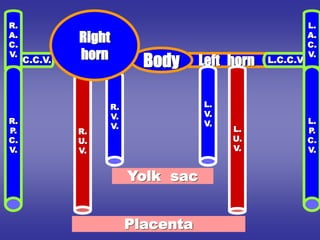
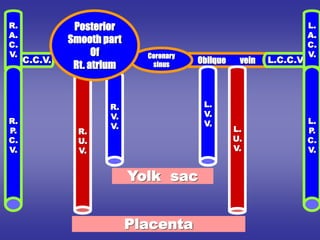
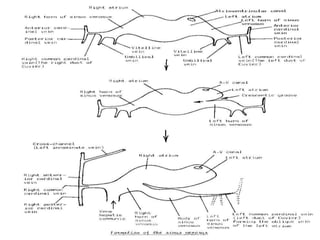
![=Blood reaches right horn exceeds that of left horn
due to:-
1-development of liver on right side.
2-presence of anastmoses between left and right
cardinal veins shifting blood from left to right.
=Resulting in:-
1-Body :- reduced in size.
2-Right horn:- increases in size on expense of body.
3-Left horn :- reduced in size.
4-Sino-atrial orifice :-
=at first :- lies transversely.
=then :- vertical
=guarded by two valves :- right & left.
PROCESS OF DEVELOPMENT
[in late stages of development]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-55-320.jpg)
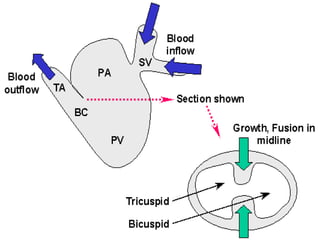

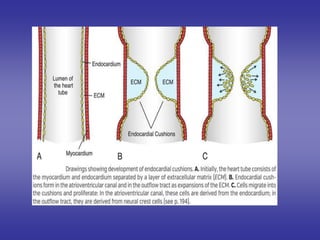
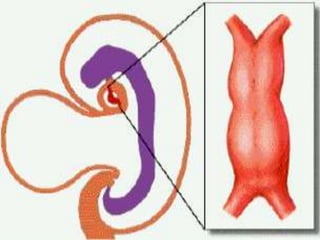
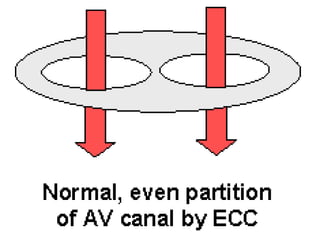
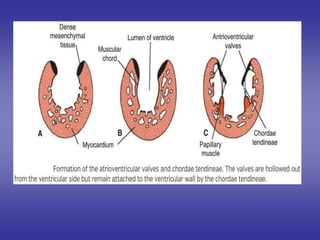
![*PROCESS OF DEVELOPMENT:-
=is divided into two canals right & left by:-
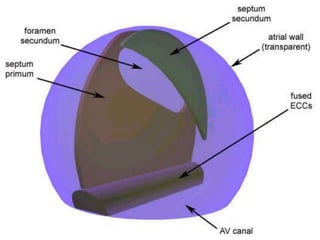
Dorsal A-V E.C.C.:- from dorsal wall of the canal.
Ventral A-V E.C.C.:-from ventral wall of the canal.
=Two cushions grow towards each others & fuses to form:-
septum intermedium.
*FATE & DERIVATIVES:-
1-Upper part of both halves:
absorbed into the corresponding atrium. [right & left]
2-Lower part of both halves:
absorbed into the corresponding ventricles. [right & left]
3-Septum intermedium:-
shares in formation of interatrial & interventricular septa
[SEE NEXT]
Is the canal connects the primitive atrium & primitive ventricle.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-70-320.jpg)
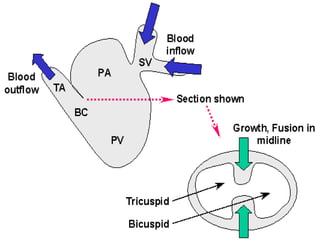
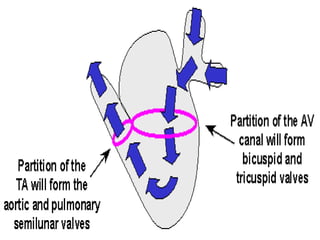


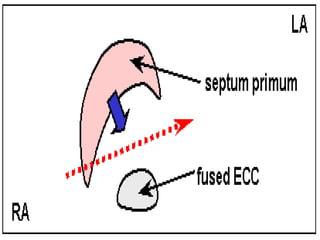
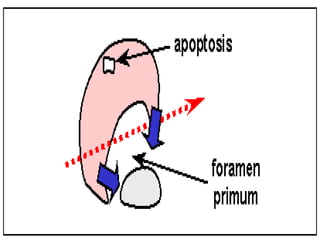
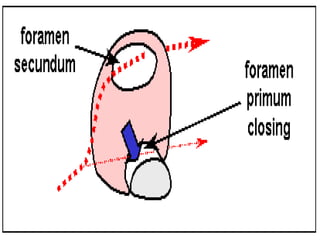
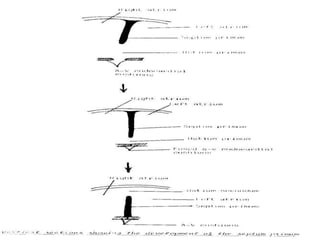
![**By inter-atrial septum:-
**developed by the following order:-
development of septum premium:-
=It arises from the roof of primitive atrium.
=arises as a sickle shaped septum.
=that grows towards septum intermedium.
=Its lower rim is separated from septum intermedium by
foramen premium.
=Finally, the septum premium fuses with septum intermedium
closing foramen premium.
=As soon as, the fusion occurs , the cranial end of septum
premium is rupture [break down ] forming foramen secondum.
=foramen secondum:-
*present between the cranial border of septum premium and
the roof of primitive atria.
*allows free passage of blood.
1*Partitioning of primitive atria](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-77-320.jpg)

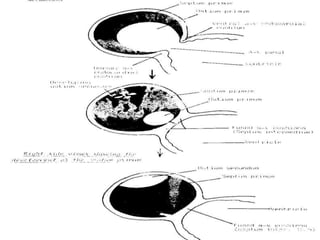
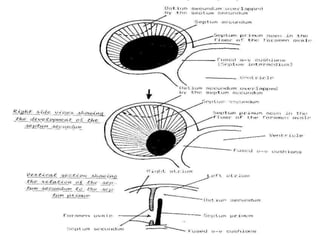
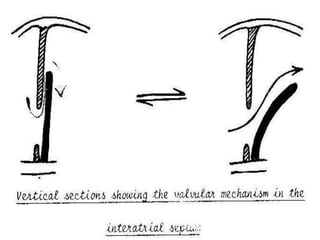

![1-septum premium.
2-septum secondum.
3-septum intermedium.
4-left valve of sino-atrial orifice.
5-neural crest. [some cells]
Inter-atrial septum develops from](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-89-320.jpg)

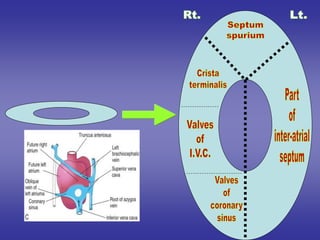
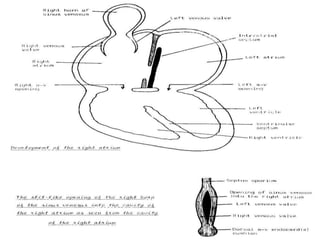
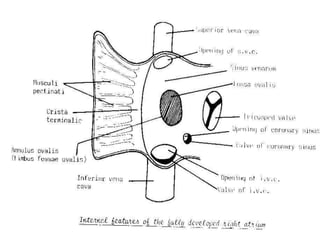
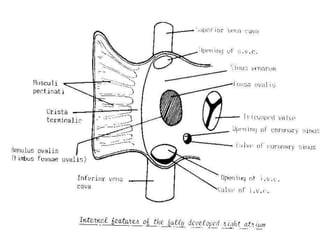
![1-Rt. half of primitive atria :-rough anterior part.
2-Rt. horn of sinus venosus :- smooth posterior part.
3-Right half of atrio-ventricular canal [its upper part]
4-Interior of right atrium:-
1-fossa ovalis:-from septum premium.
2-annulus ovalis:- from septum secondum.
3-crista terminalis:- from upper 1/3 of Rt. sino-atrial v.
4-valve for I.V.C.:- from middle 1/3 of """"""""""""""".
5-valve of coronary sinus:-from lower 1/3 of """"""".
2*Development of right atrium](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-91-320.jpg)
![1-Lt. ½ of primitive atria:- rough anterior part.
2-Lt. ½ of atrio-ventricular canal [its upper part]
3-Pulmonary vein [root and 1st division ] :-
[its posterior smooth]
resulting in four separate openings for the
pulmonary veins.
3*Development of left atrium](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-94-320.jpg)

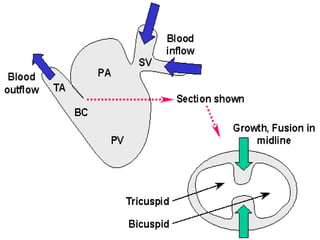
![**By inter-ventricular septum:-
**developed by the following order:
development of muscular part :-
=It is a larger antero-inferior part.
=arises as a sickle shaped septum.
=it arises from endocardium of the floor of primitive ventricle.
=it grows towards septum intermedium.
=Its upper rim is separated from septum intermedium by inter-
ventricular f.
development of membranous part:-
=It is derived from:-
dorsal A-V E.C.C..
ventral A-V E.C.C..
bulbar ridges [right & left]
=It will close the interventricular foramen.
1*Partitioning of primitive ventricle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-98-320.jpg)
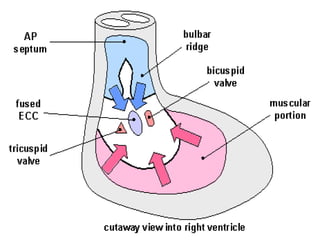
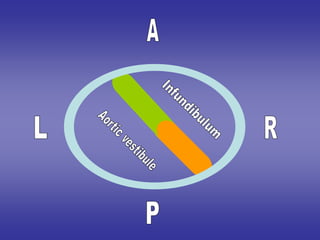
![=The infundibulum [smooth part]:-
*from antero-lateral portion of bulbus cordis.
=The rough part [papillary muscles, chorda tendinae,
trabecular carnae]
*right half of primitive ventricle.
2*Development of right ventricle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-101-320.jpg)
![=The aortic vestibule. [smooth part]:-
*from postero-medial portion of bulbus cordis.
=The rough part [papillary muscles , chorda tendinae
, trabecular carnae]
*left half of primitive ventricle.
3*Development of left ventricle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-102-320.jpg)




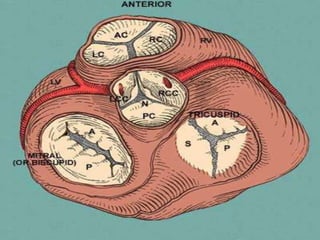
![1]=Four endocardial cushions:-
1-anterior.
2-posterior.
3-right .
4-left.
2]=Develop from the walls of
cephalic part of bulbus cordis at its
junction with truncus arteriosus.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-112-320.jpg)

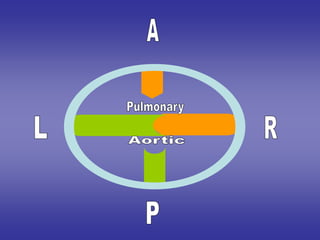
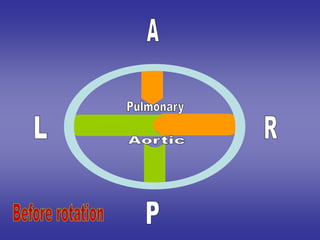
![1*right & left cushions fuse with each
others to divide the orifice into:-
1-anterior [pulmonary] orifice.
2-posterior [aortic] orifice.
2*anterior & posterior cushions remain
separated.
3*each aortic & pulmonary orifices has
three cushions:-
FATE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-114-320.jpg)

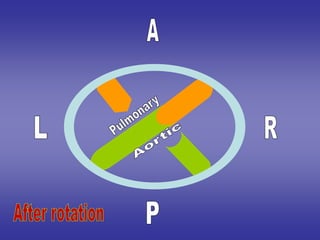

![FATE
AT THE CRANIAL
PART OF TRUNCUS
ARTERIOSUS
AT THE MIDDLE
PART OF TRUNCUS
ARTERIOSUS
AT THE CAUDAL
PART OF TRUNCUS
ARTERIOSUS
1-septum lies
transversely.
2-It is divided into:-
a]=anterior part :-
ascending aorta.
b]=posterior part:-
pulmonary trunk.
1-septum lies
anteroposterior.
2-It is divided into:-
a]=right part :-
ascending aorta.
b]=left part:-
pulmonary trunk.
1-septum lies
transversely.
2-It is divided into:-
a]=posterior part :-
ascending aorta.
b]=anterior part:-
pulmonary trunk.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-121-320.jpg)

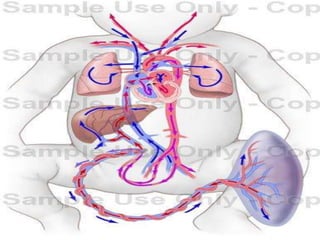
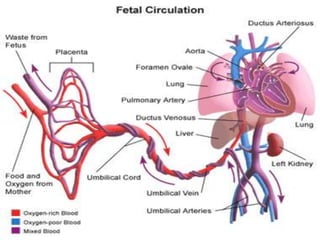
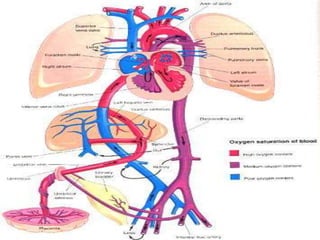
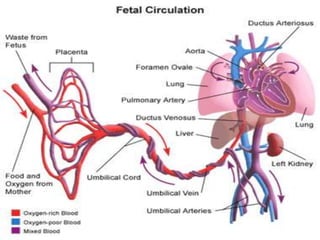
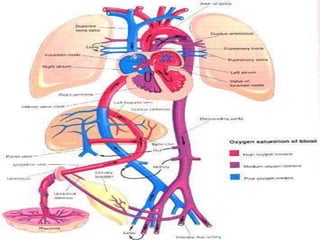
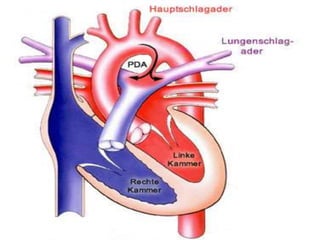
![CONTENTS OF UMBILICAL CORD:-
FETAL CIRCULATION BEFORE BIRTH
*Early in embryonic life:
Two umbilical arteries:-[right & left]
-carry un-oxygenated blood.
-from fetus to placenta.
Two umbilical veins:-[right & left]
-carry oxygenated blood .
-from placenta to fetus.
*Later in embryonic life:-
Two umbilical arteries:-[right & left]
One umbilical veins:-
Which is left umbilical vein , the right one disappears.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-127-320.jpg)
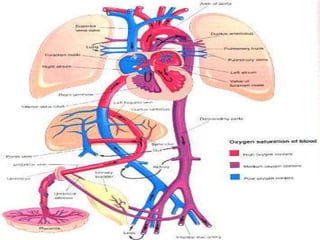

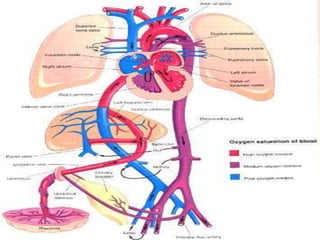

![1]=Ligature of umbilical cord.
2]=Exposure to cold.
*CAUSES OF THESE CHANGES:-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-139-320.jpg)
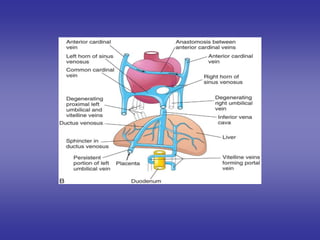
![The two umbilical arteries:-
=It will give the following derivatives:-
(1)-The proximal portion:-remains patent superior vesical artery.
(2)-The distal portion:- will form lateral umbilical ligaments.
The umbilical veinligamentum teres of liver.
Ductus venosus:ligamentum venosum of liver.
Foramen ovale:
=occluded due to:-
1]-increased pressure of Lt. atrium.
2]-decreased pressure of Rt. atrium due to decreased blood from I.V.C.
=It will give the following derivatives:-
*Fossa ovalis :-from septum premium.
*Annulus fossa ovalis:- from septum secondum.
1]=Ligature of umbilical cord](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-140-320.jpg)
![1-respiration is stimulated.
2-lungs become functioning.
3-decrease in resistence of lungs.
4-blood shifted from pulmonary trunk to lungs for
oxygenation.
5-It returns to Lt. atrium through pulmonary veins
leads to increase Lt. atrium pressure inside.
6-closure of ductus arteriosus will give:-
ligamentum arteriosum.
2]=Exposure to cold:-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embryologyheart-230508191331-cc41d237/85/Embryology-heart-ppt-141-320.jpg)
