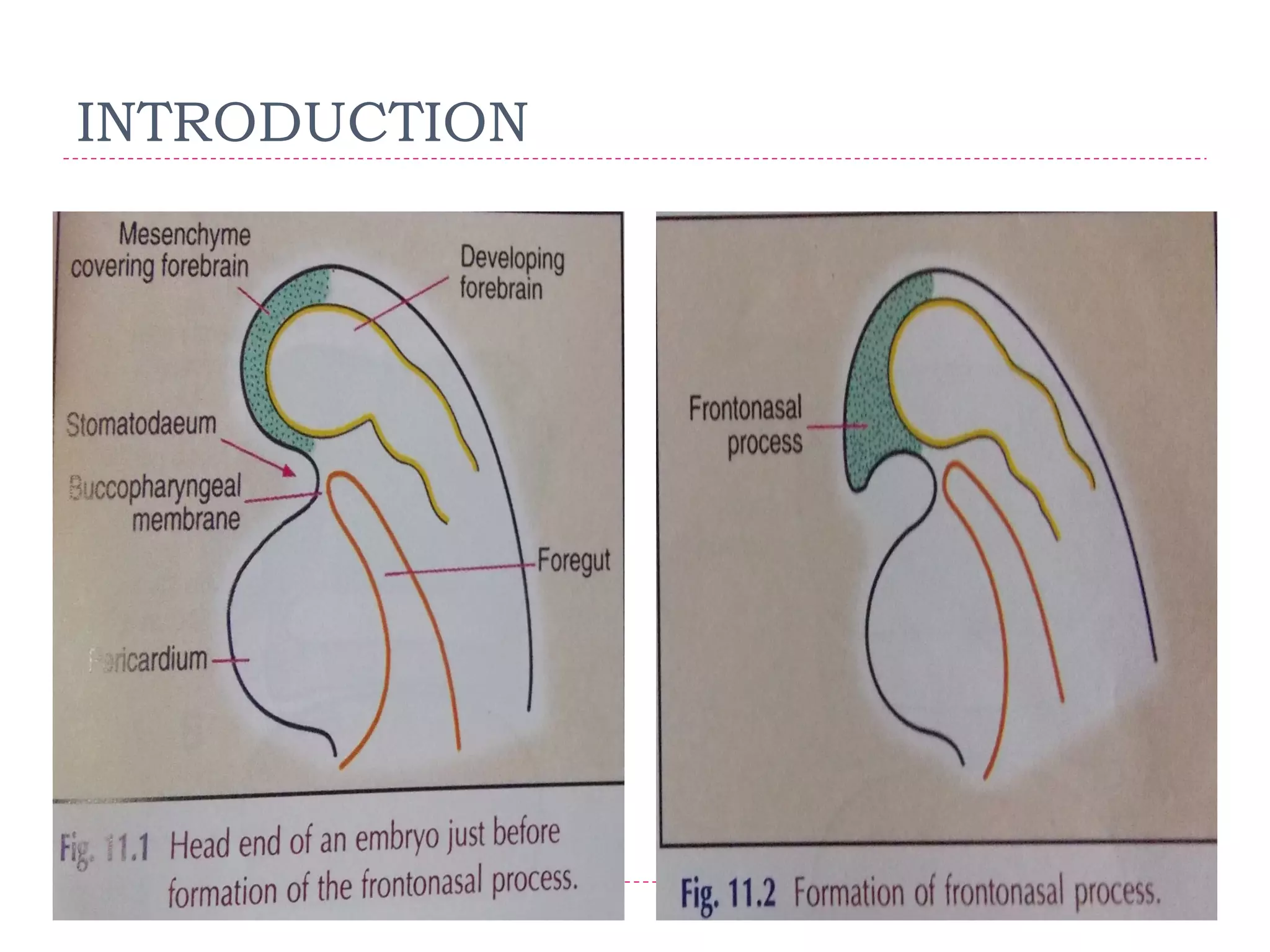
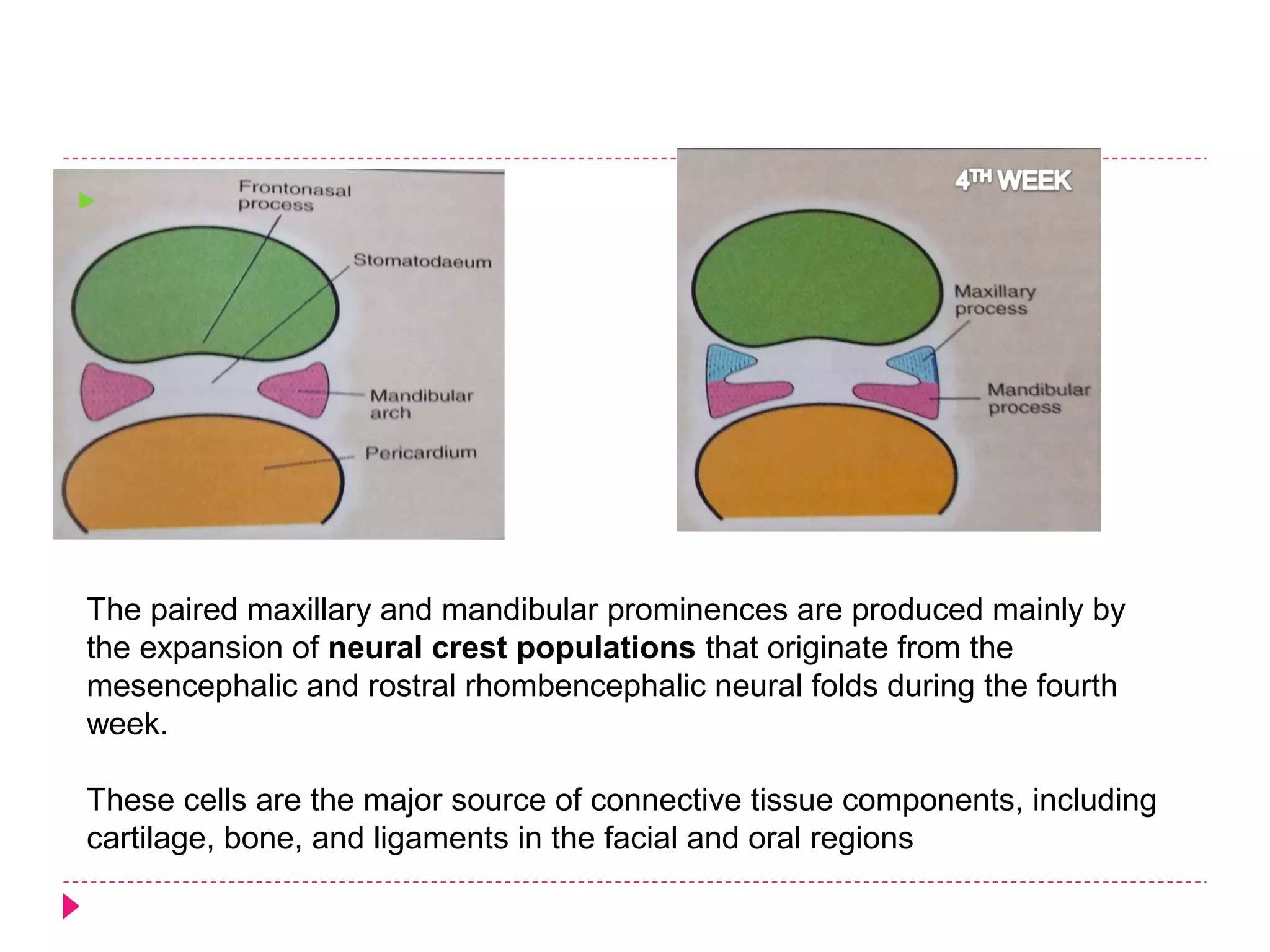
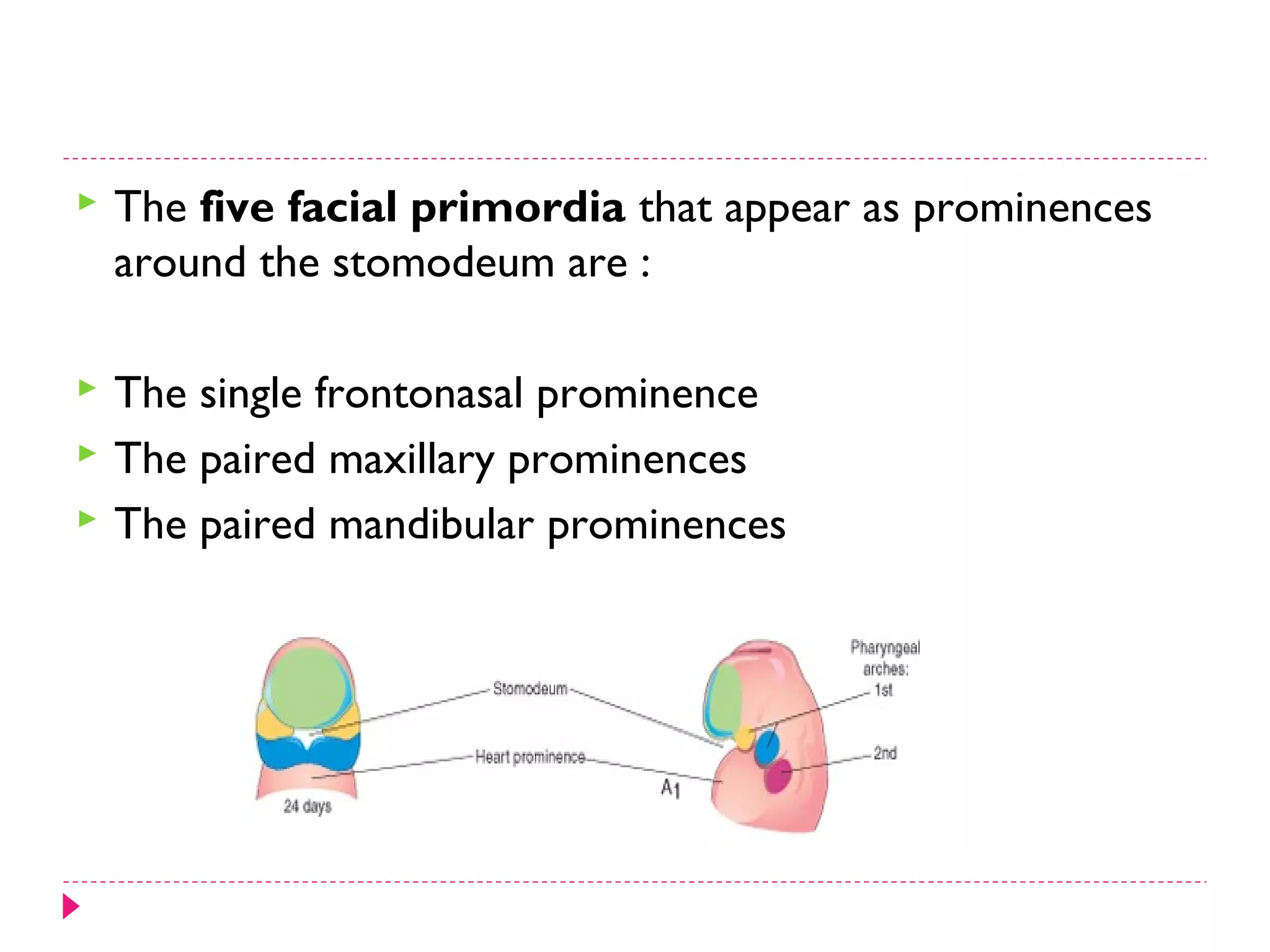
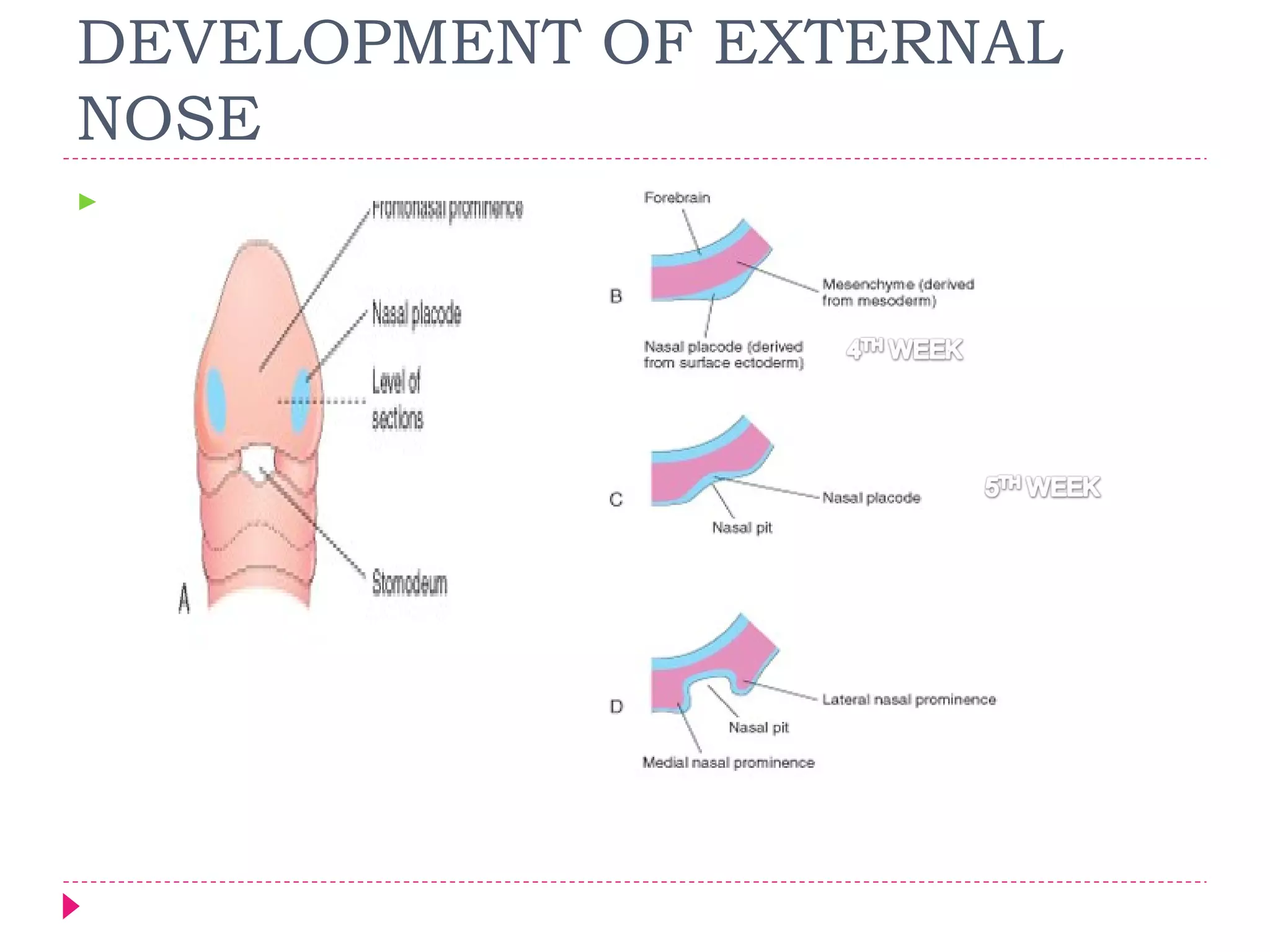
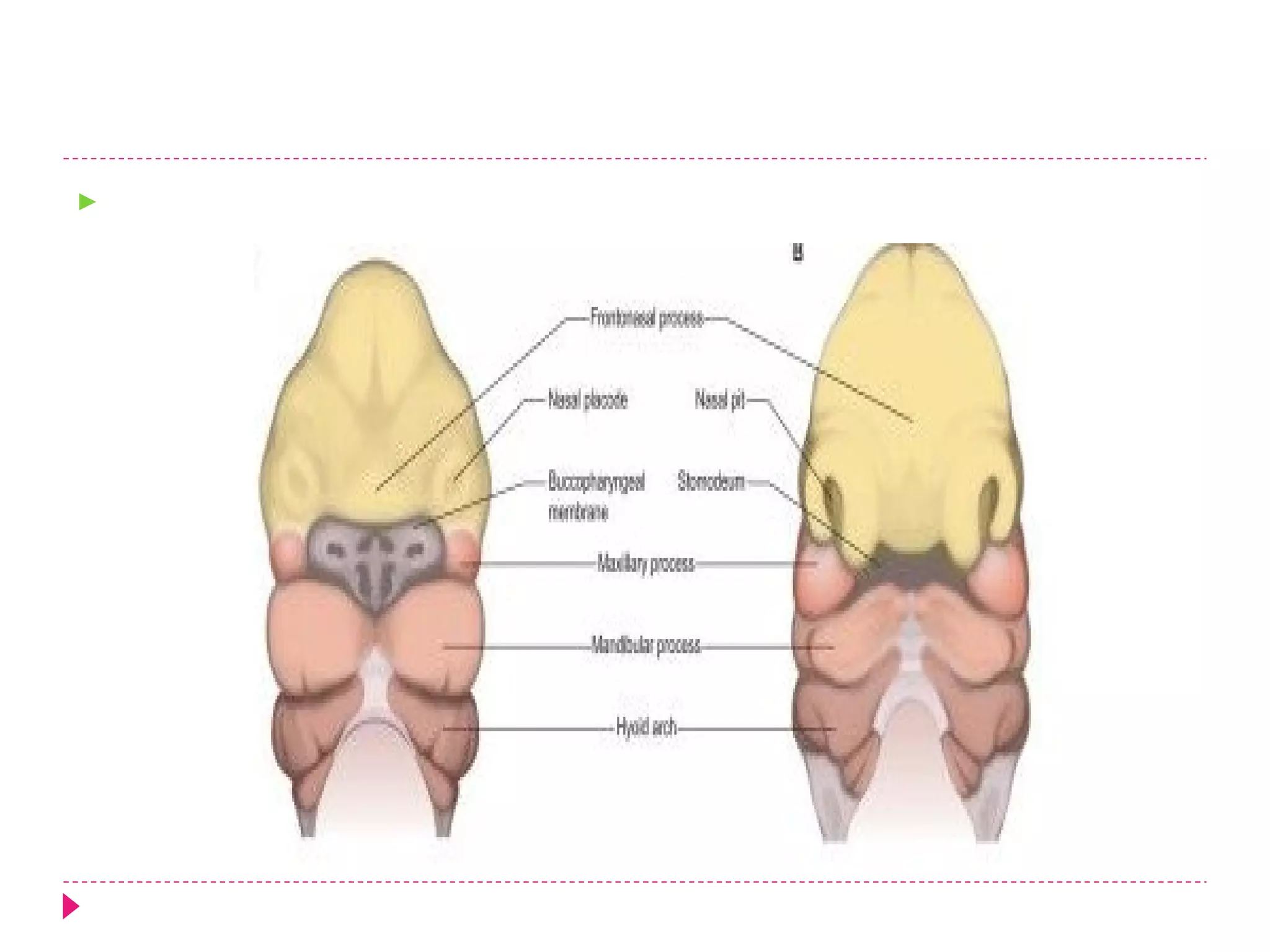
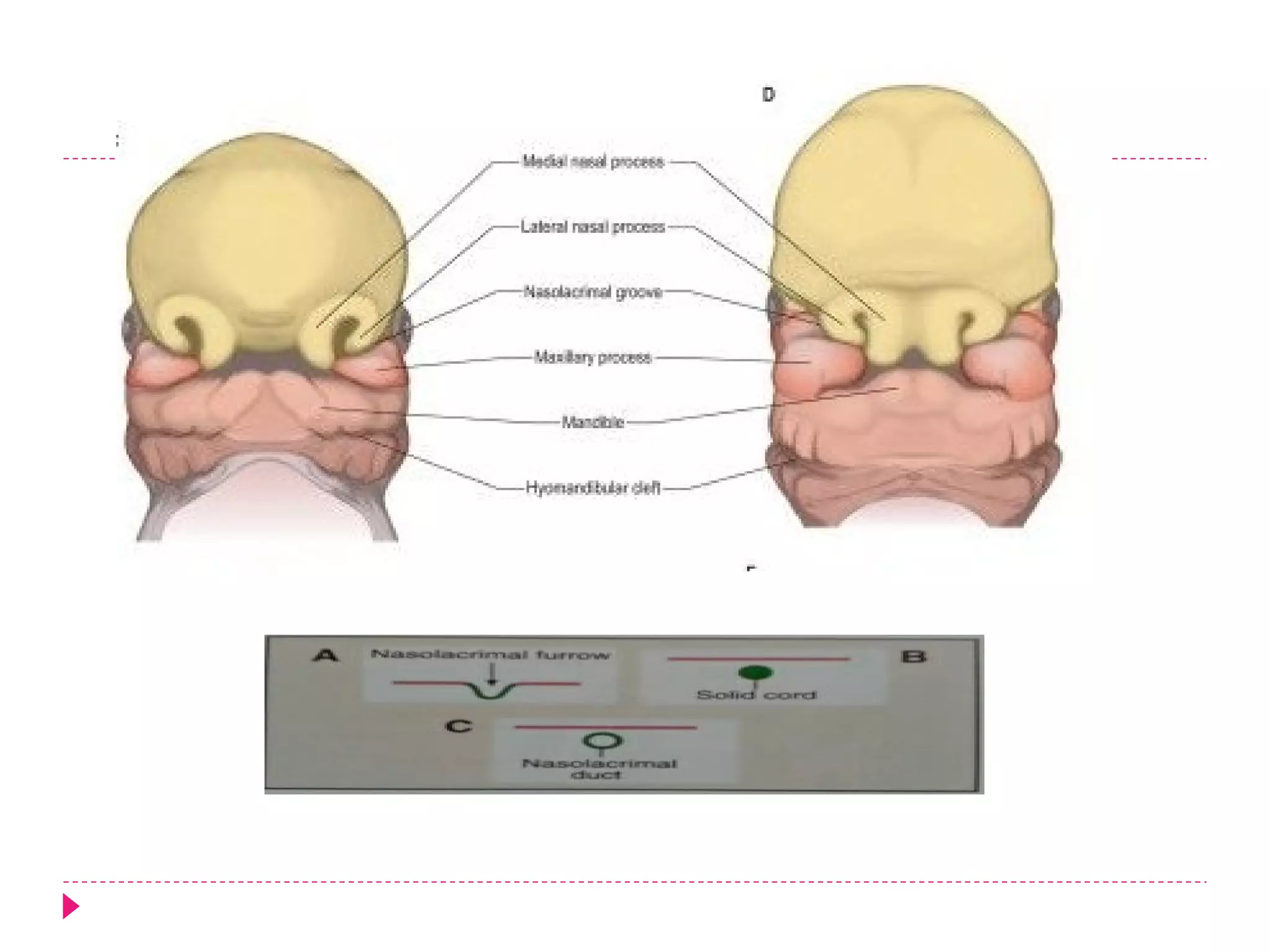
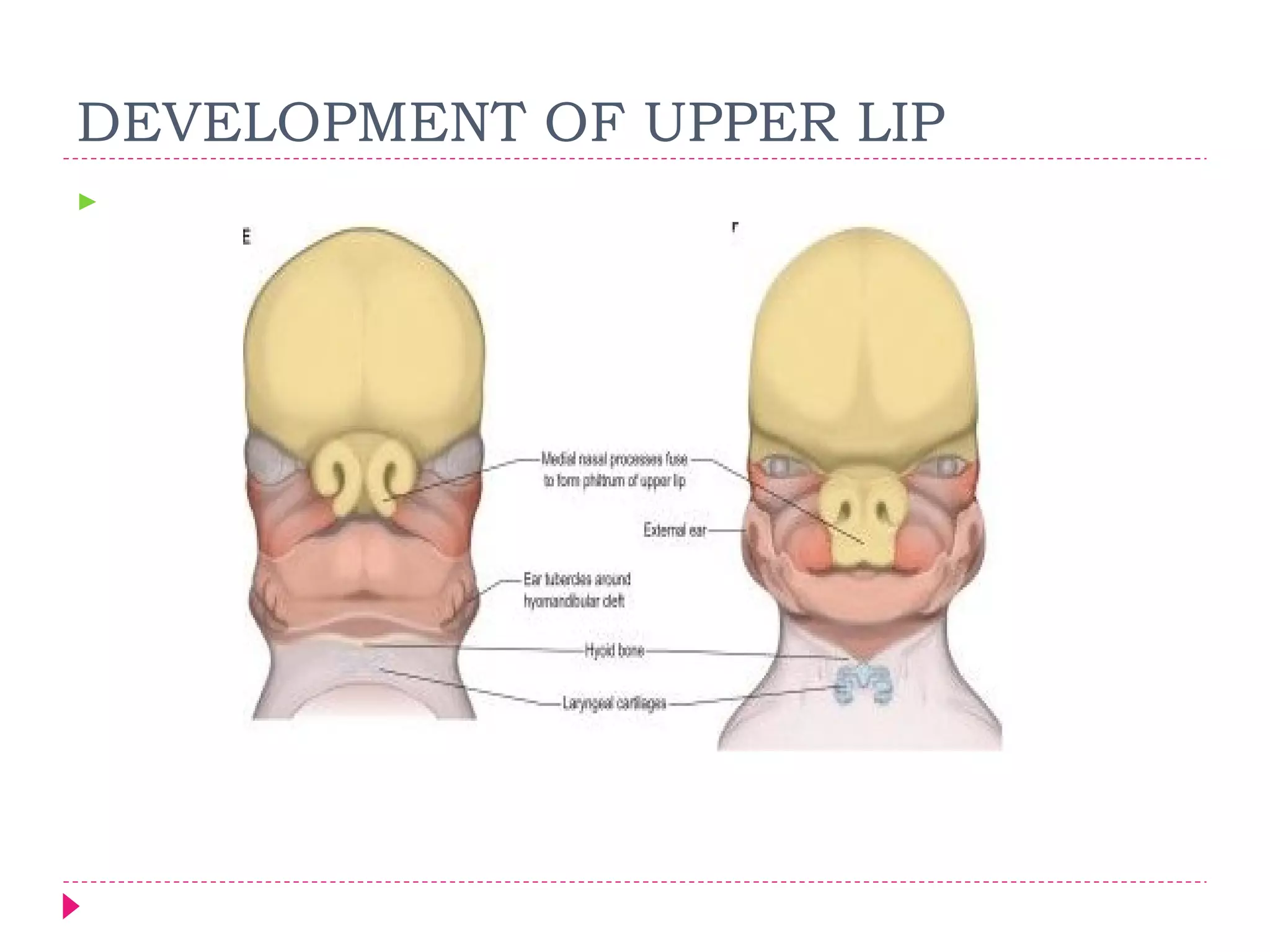
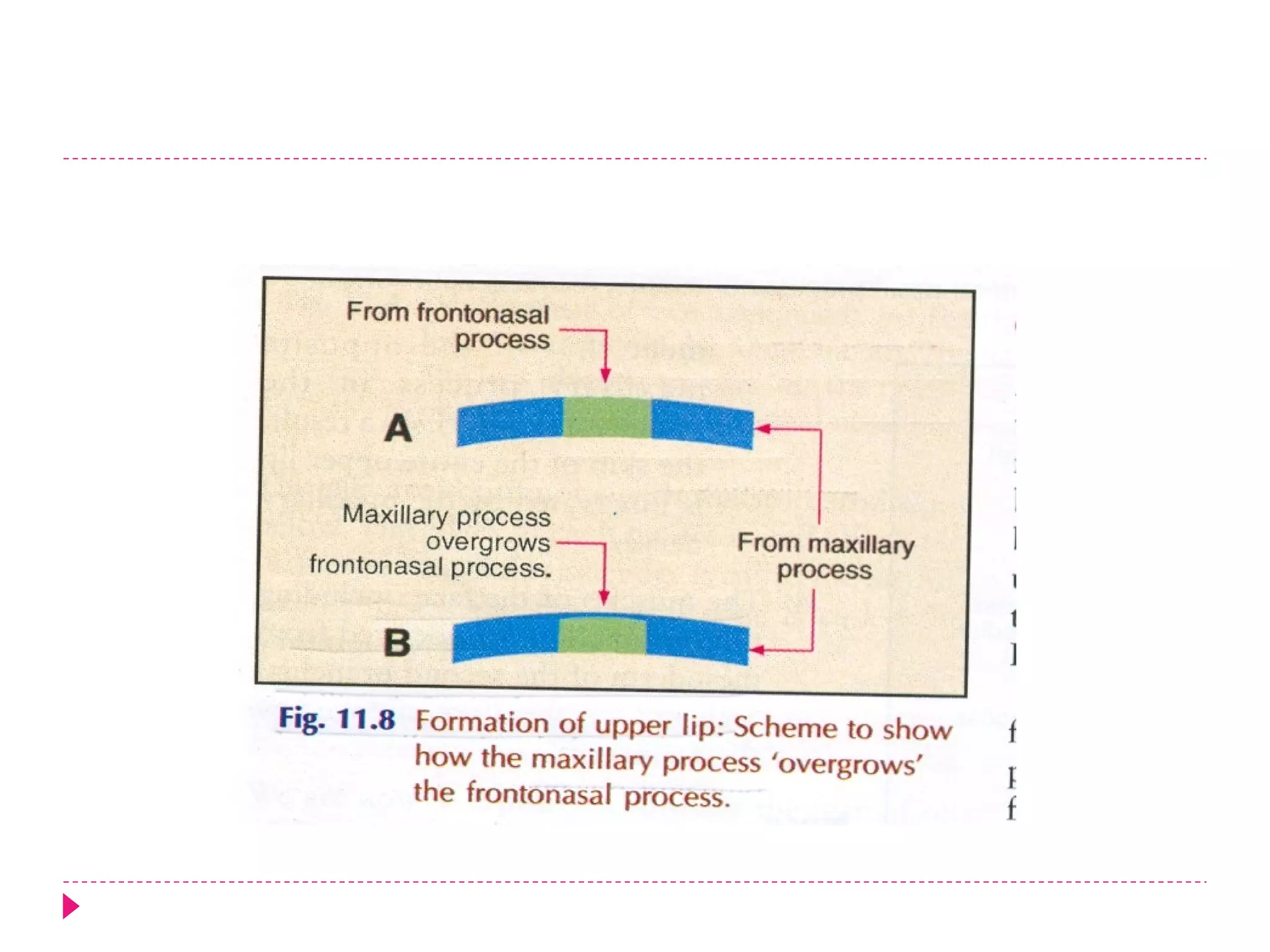
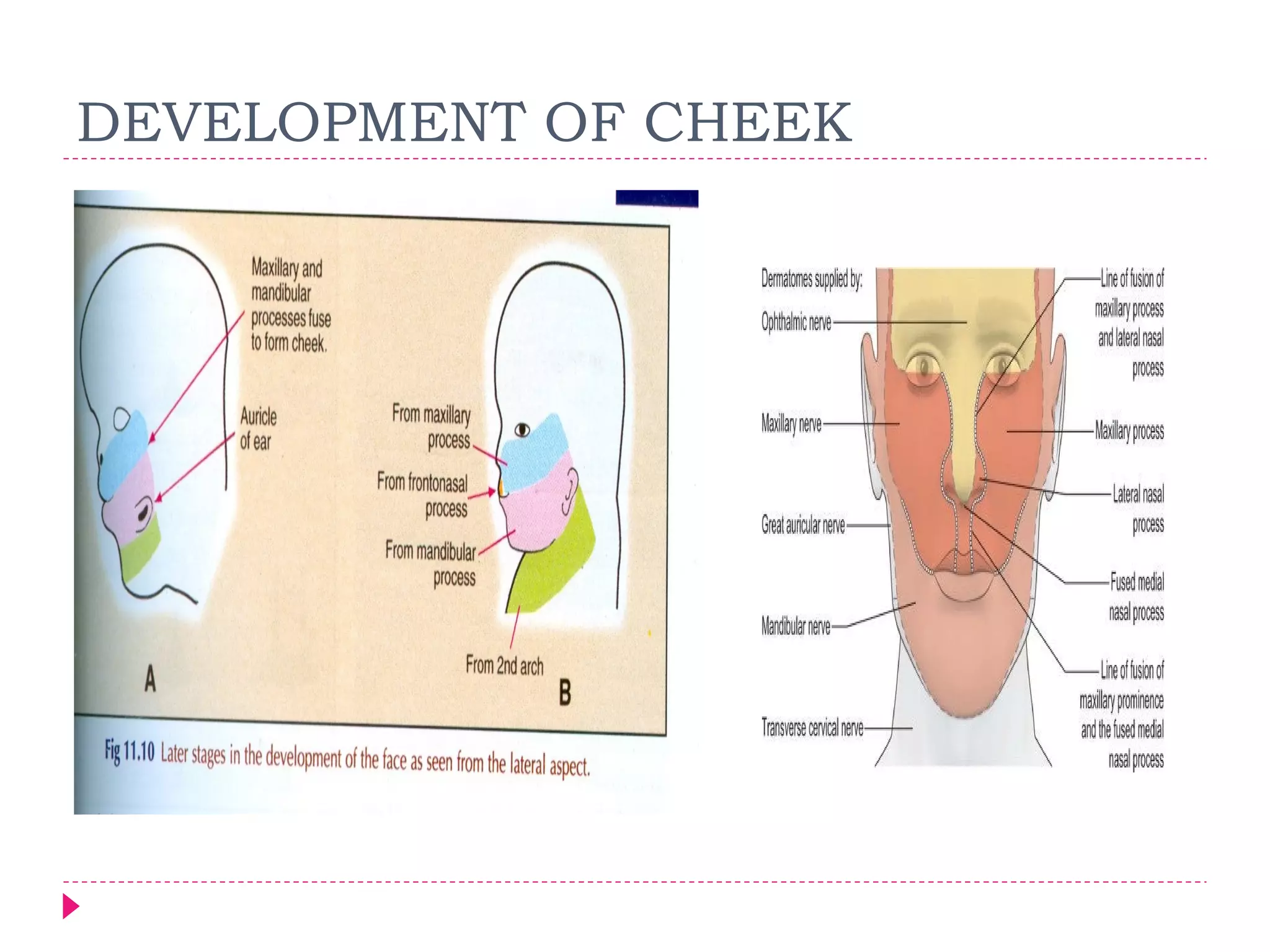
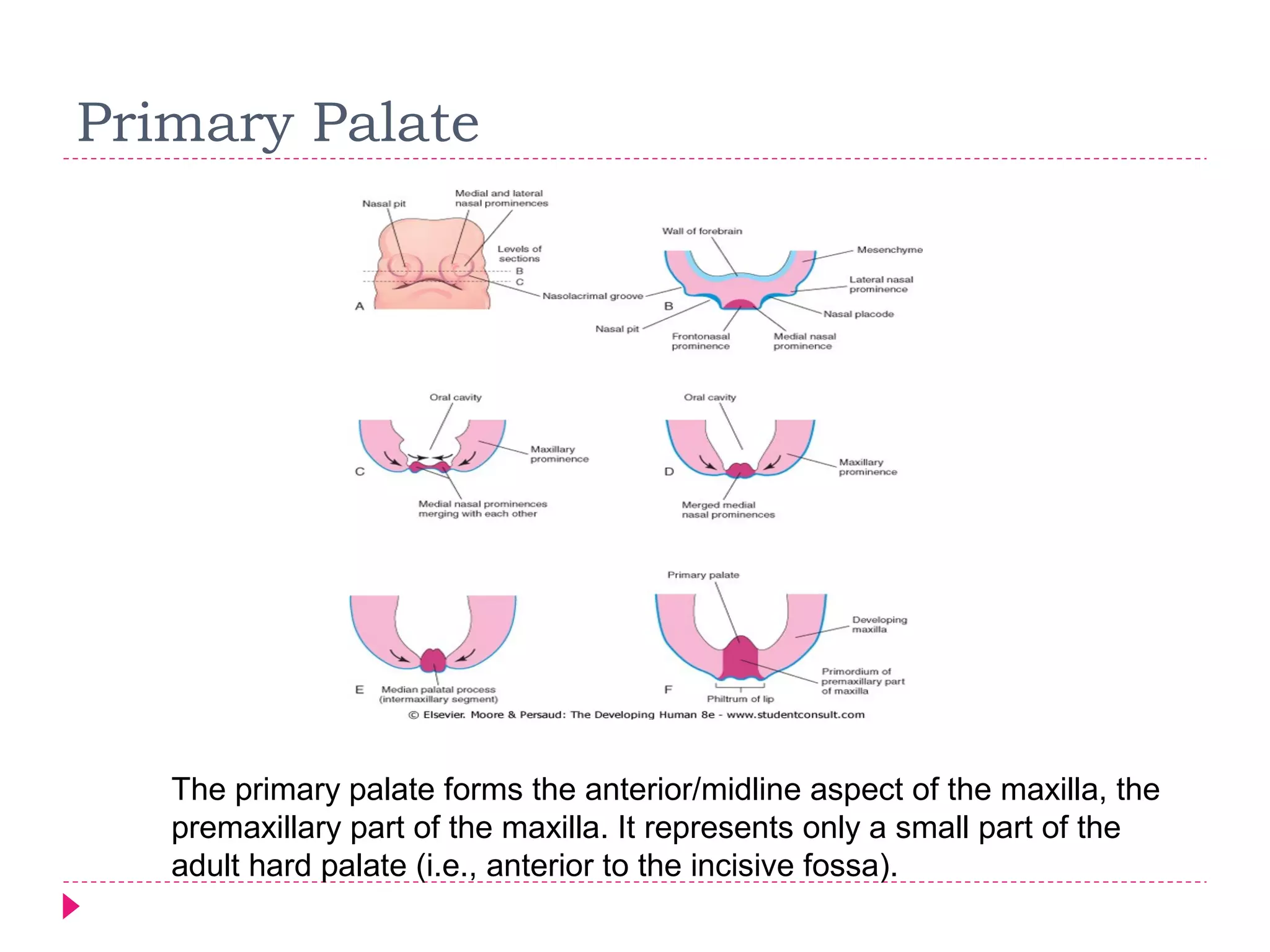
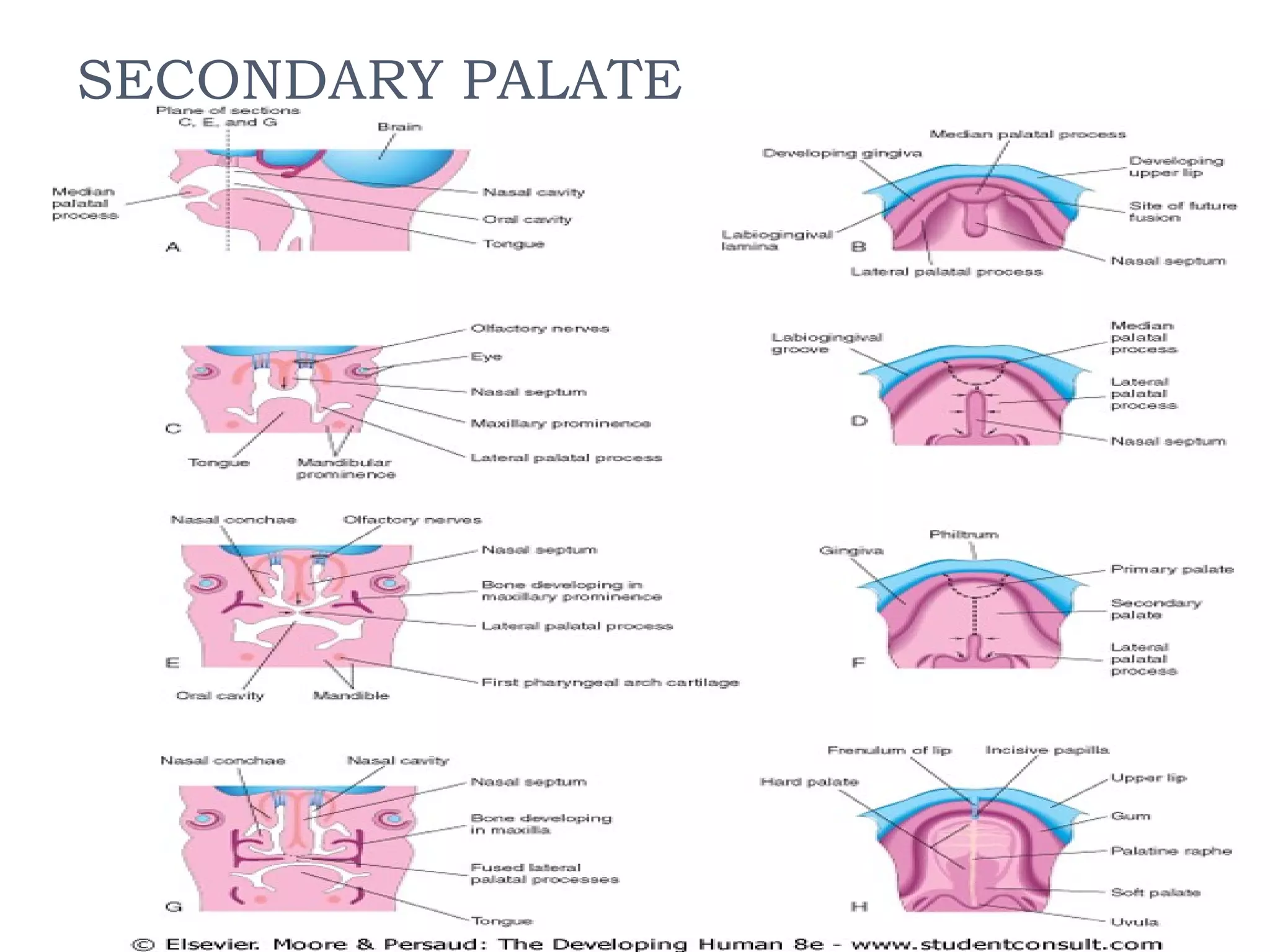
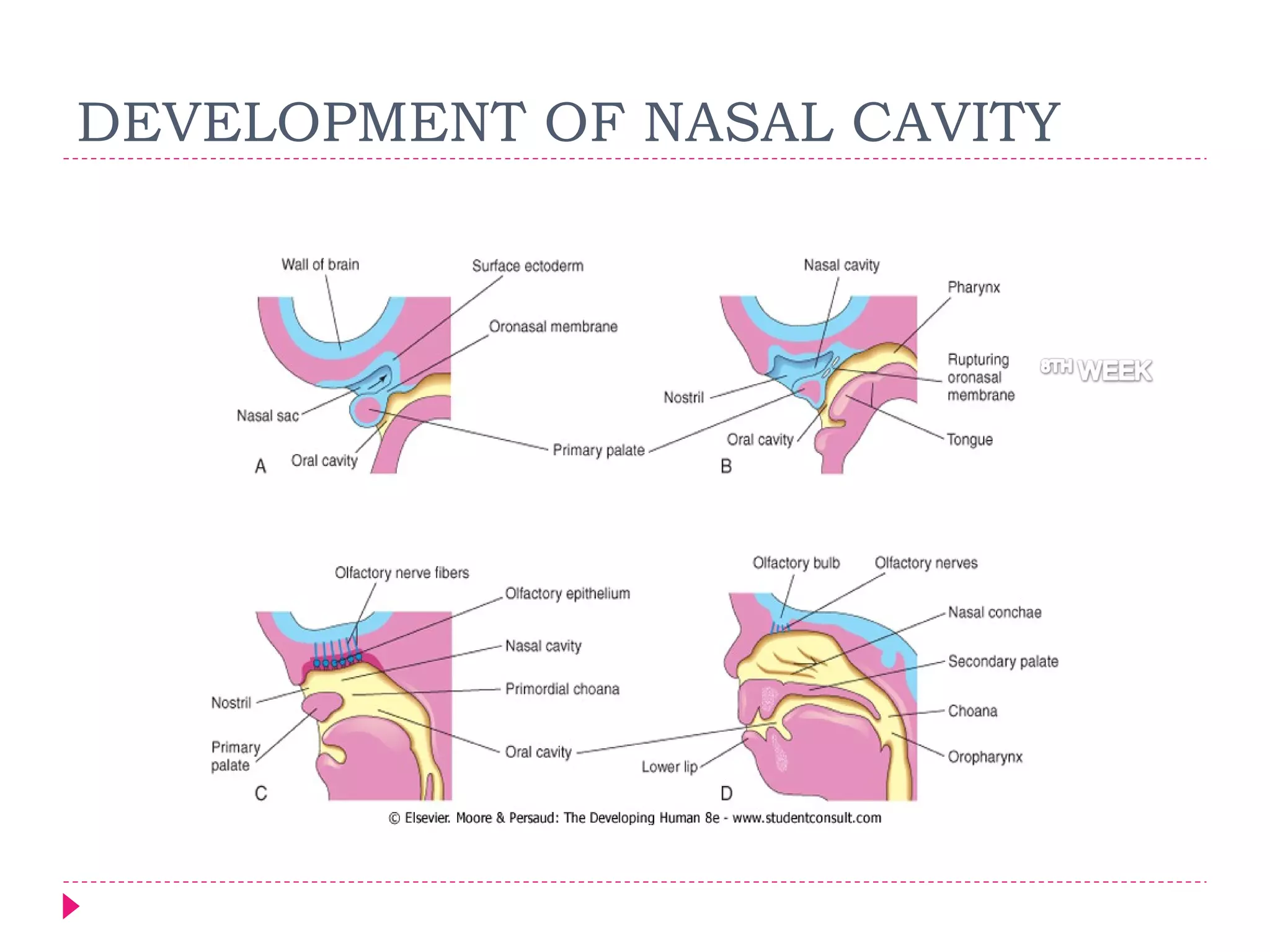
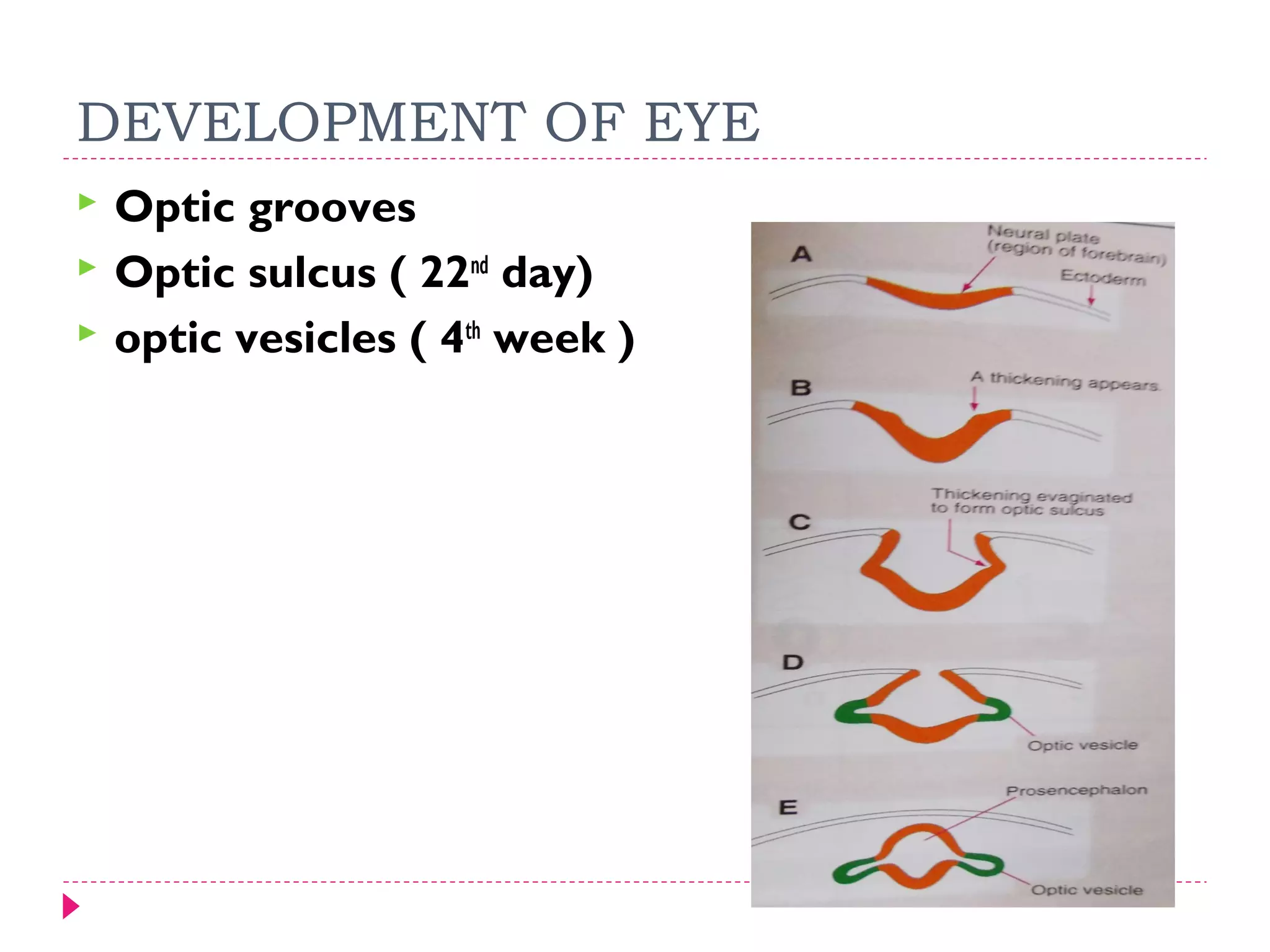
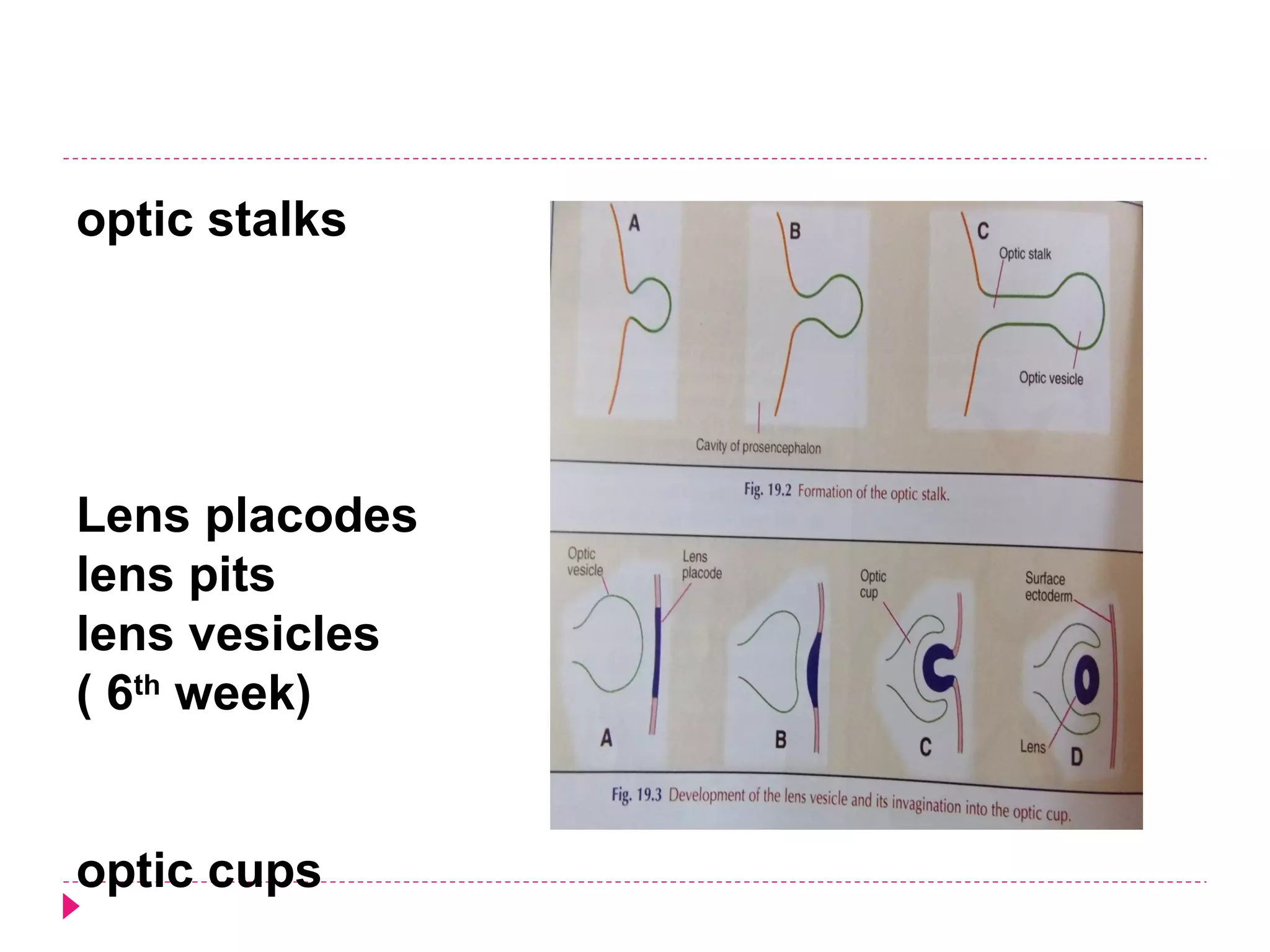
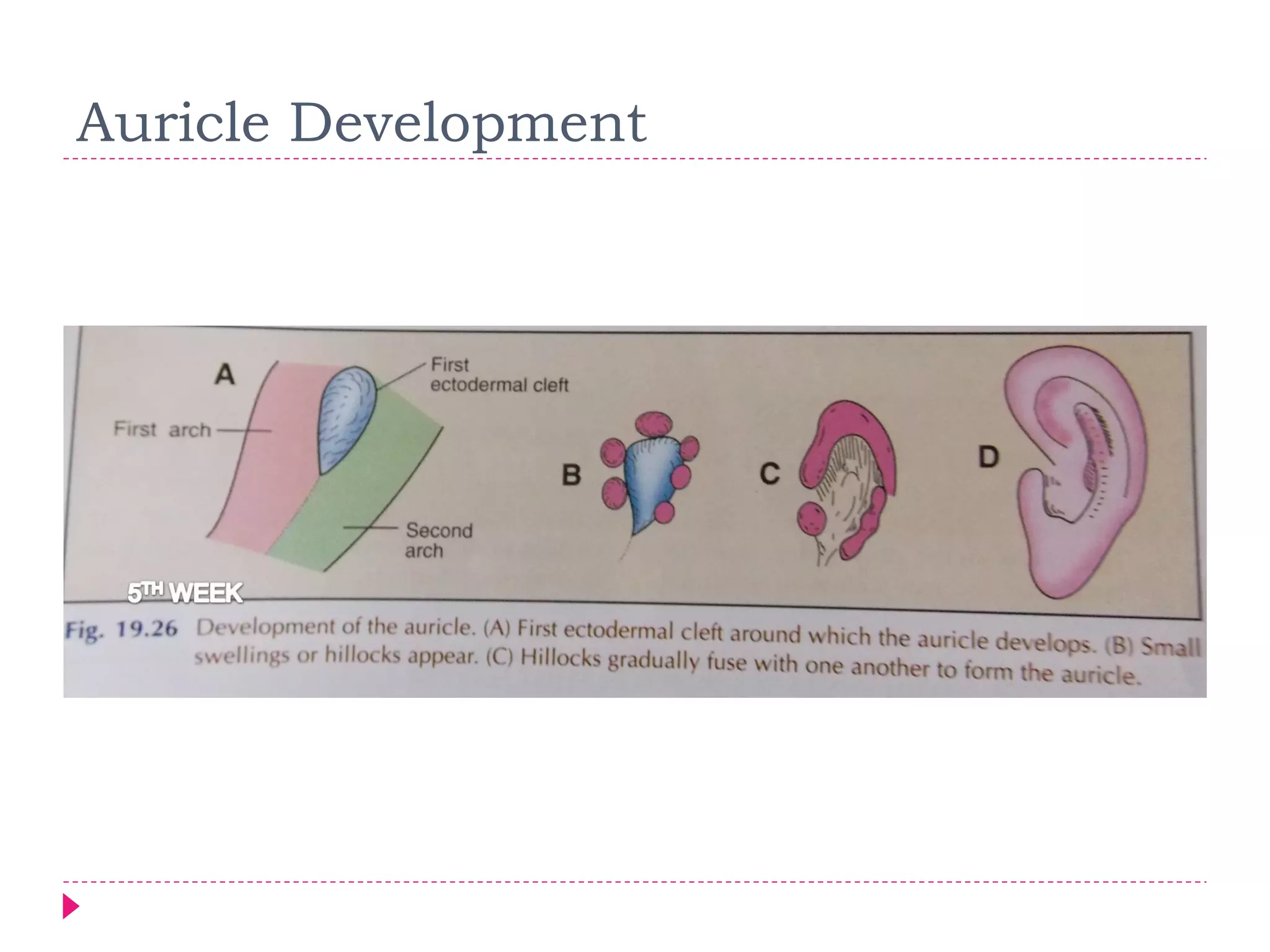
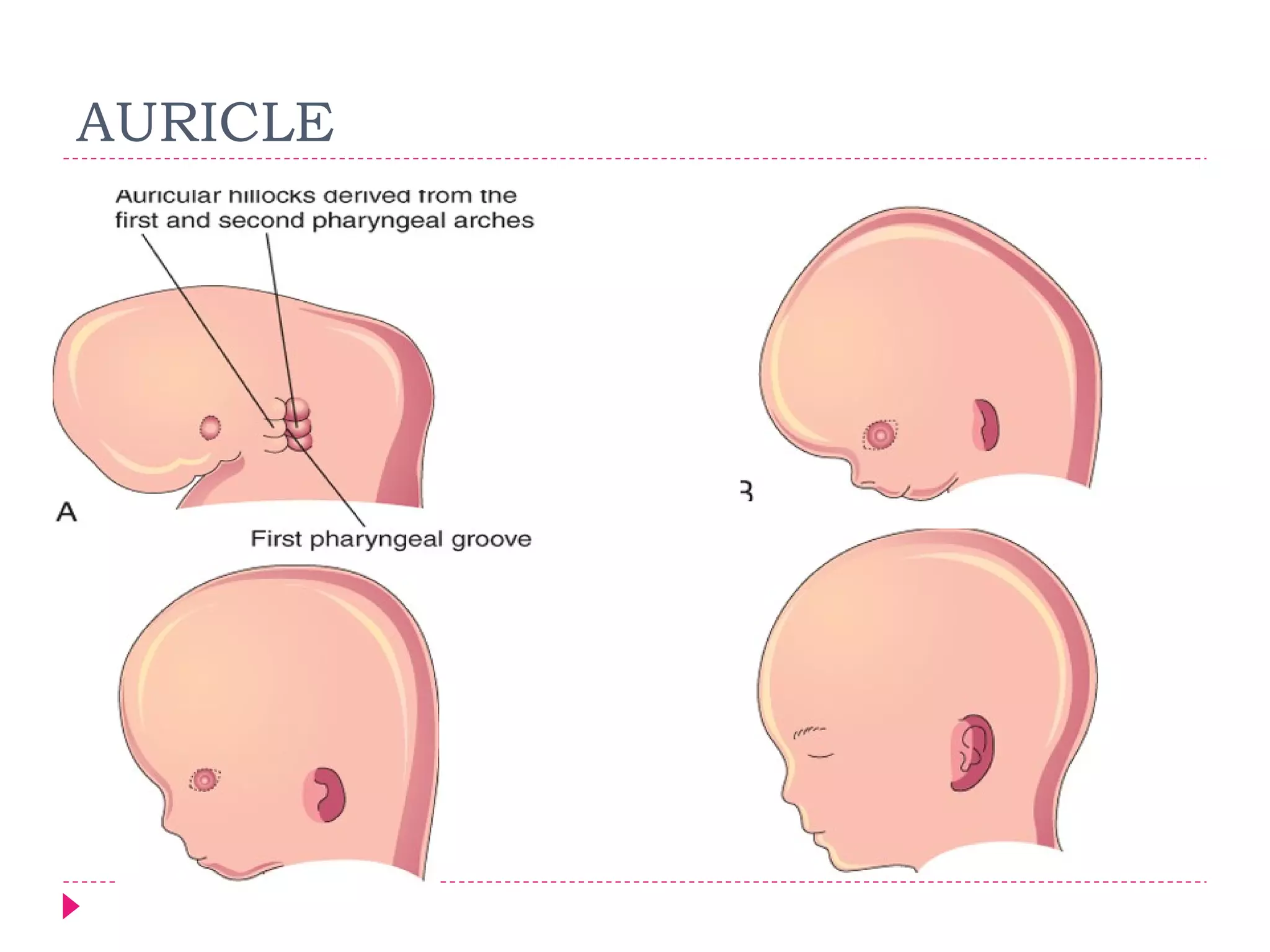
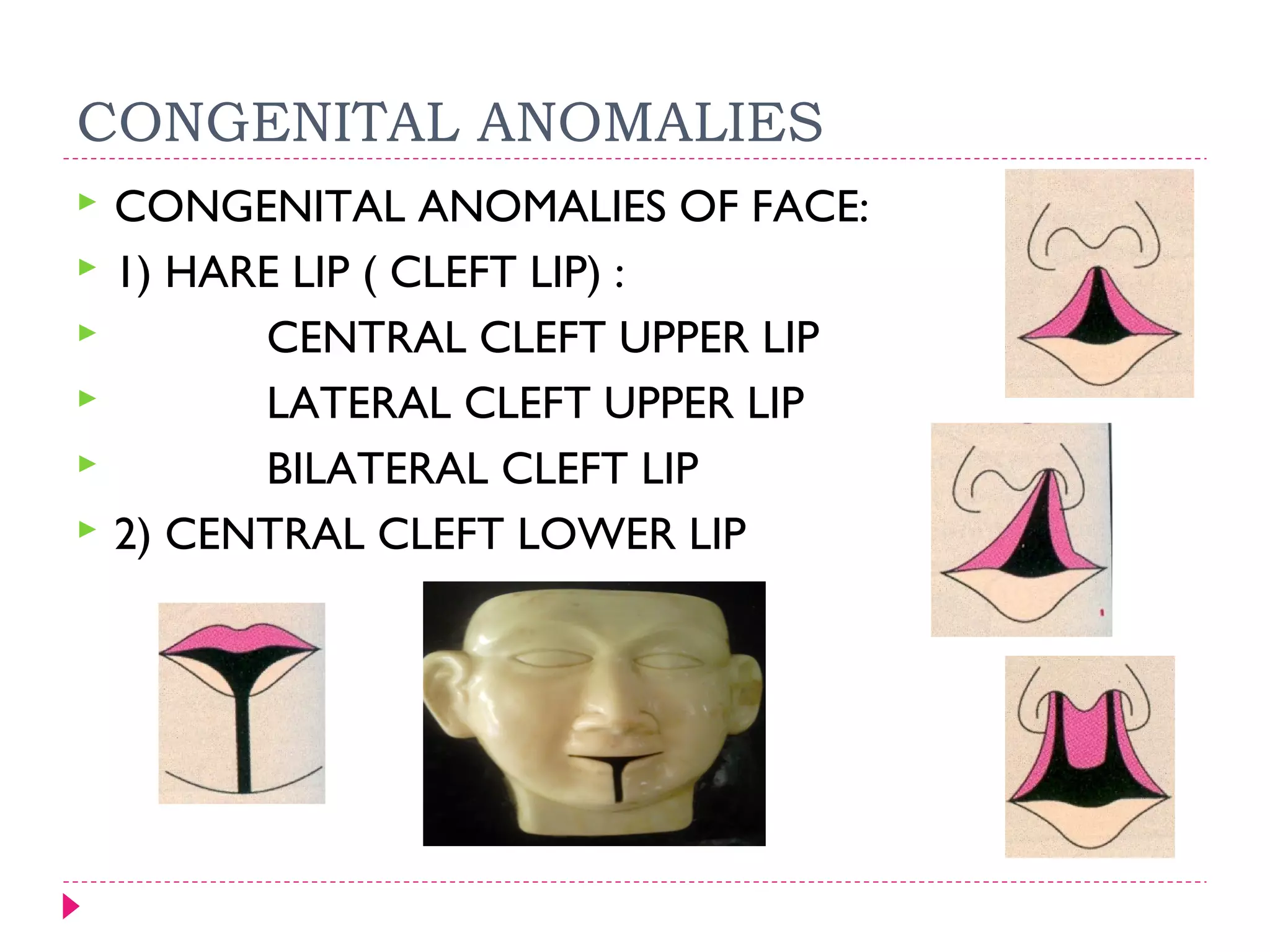
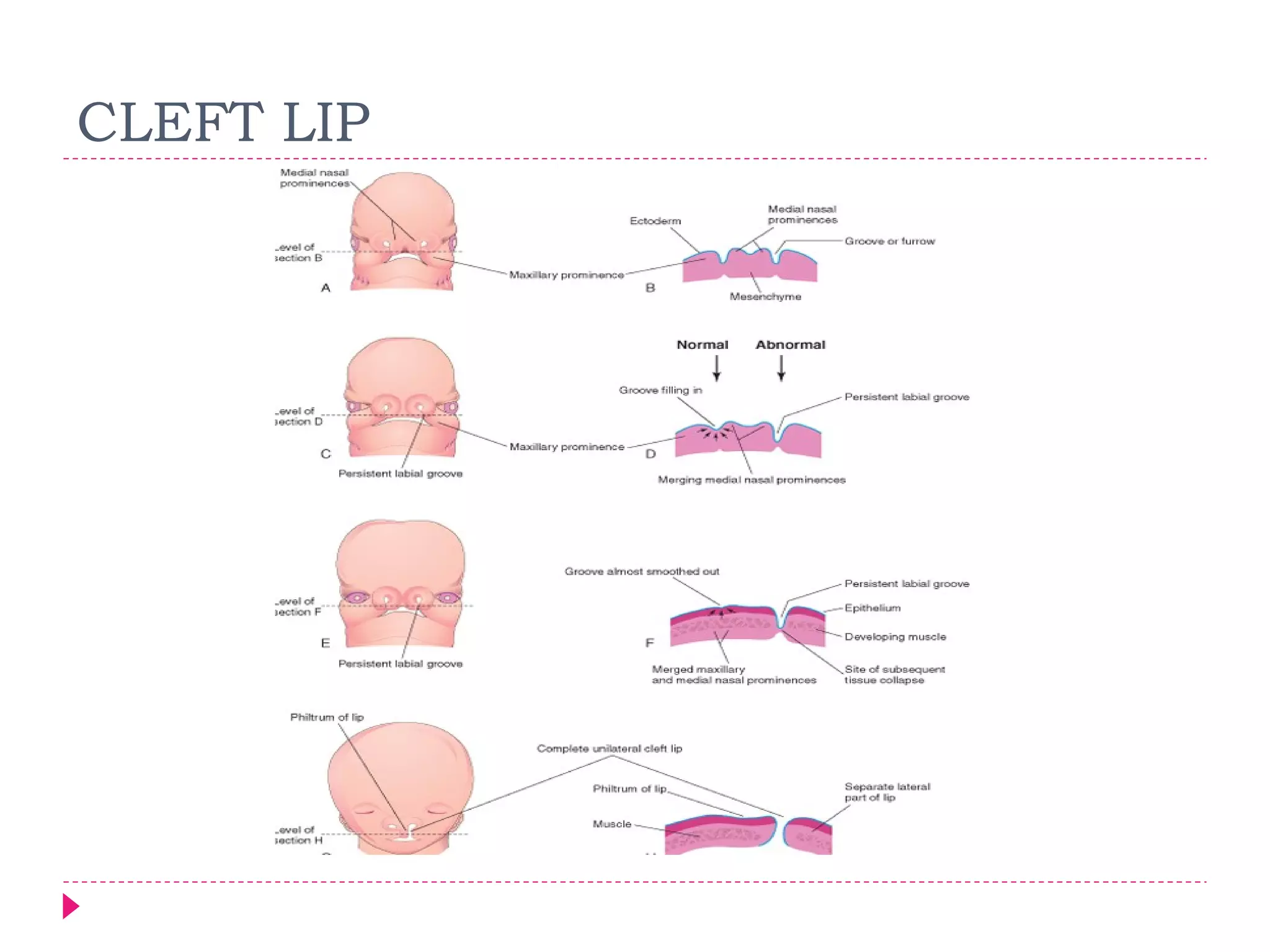
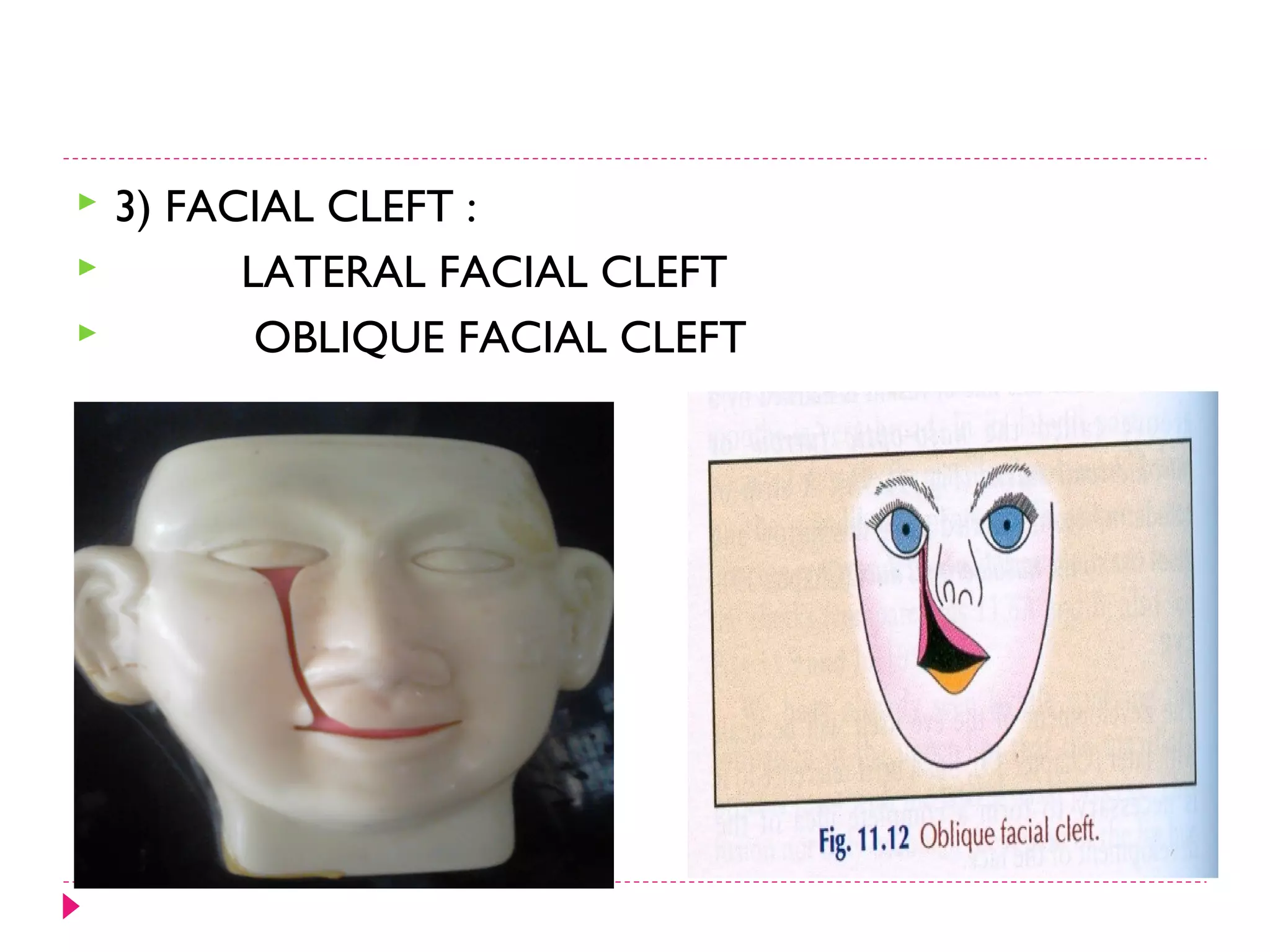
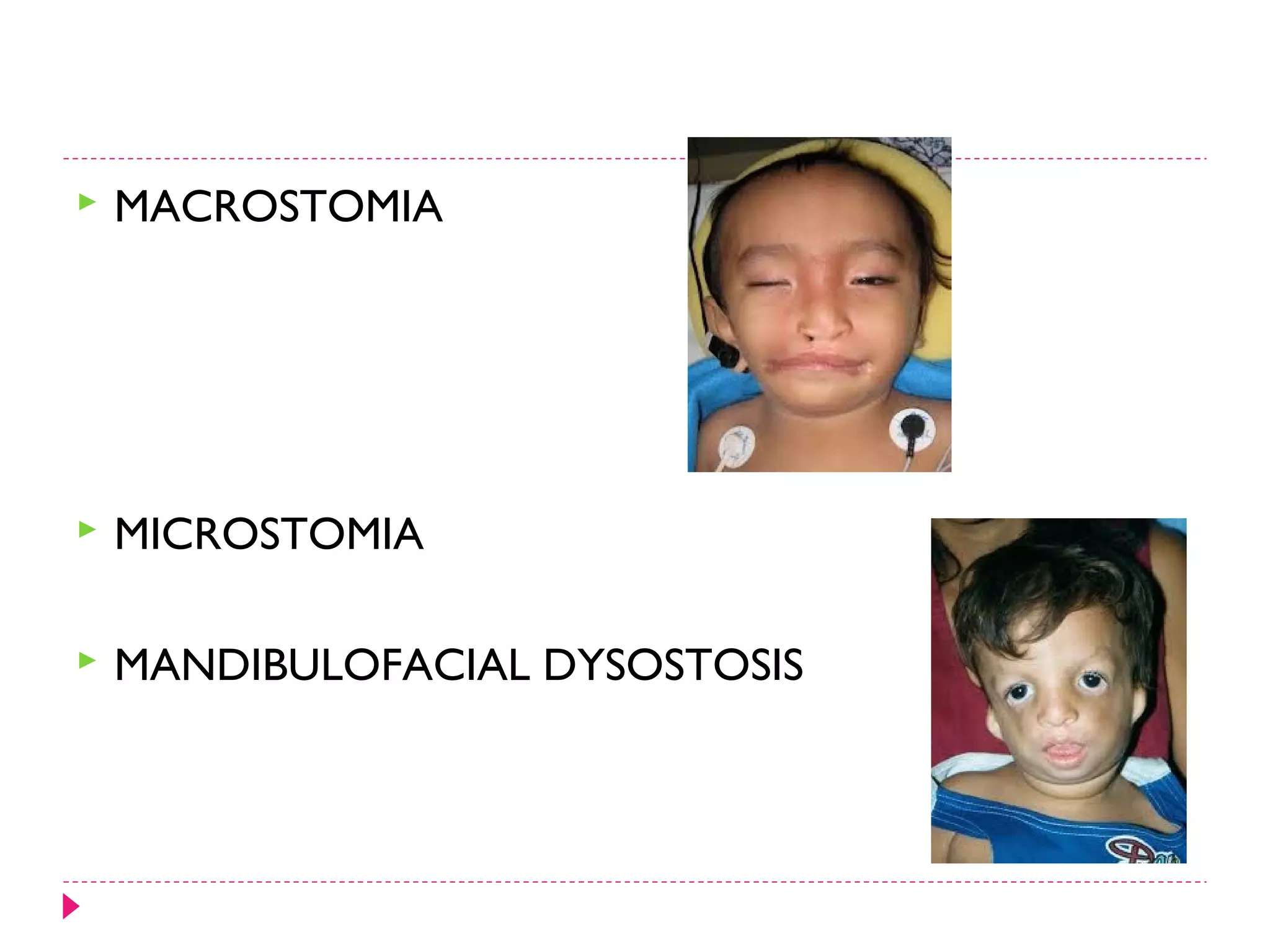
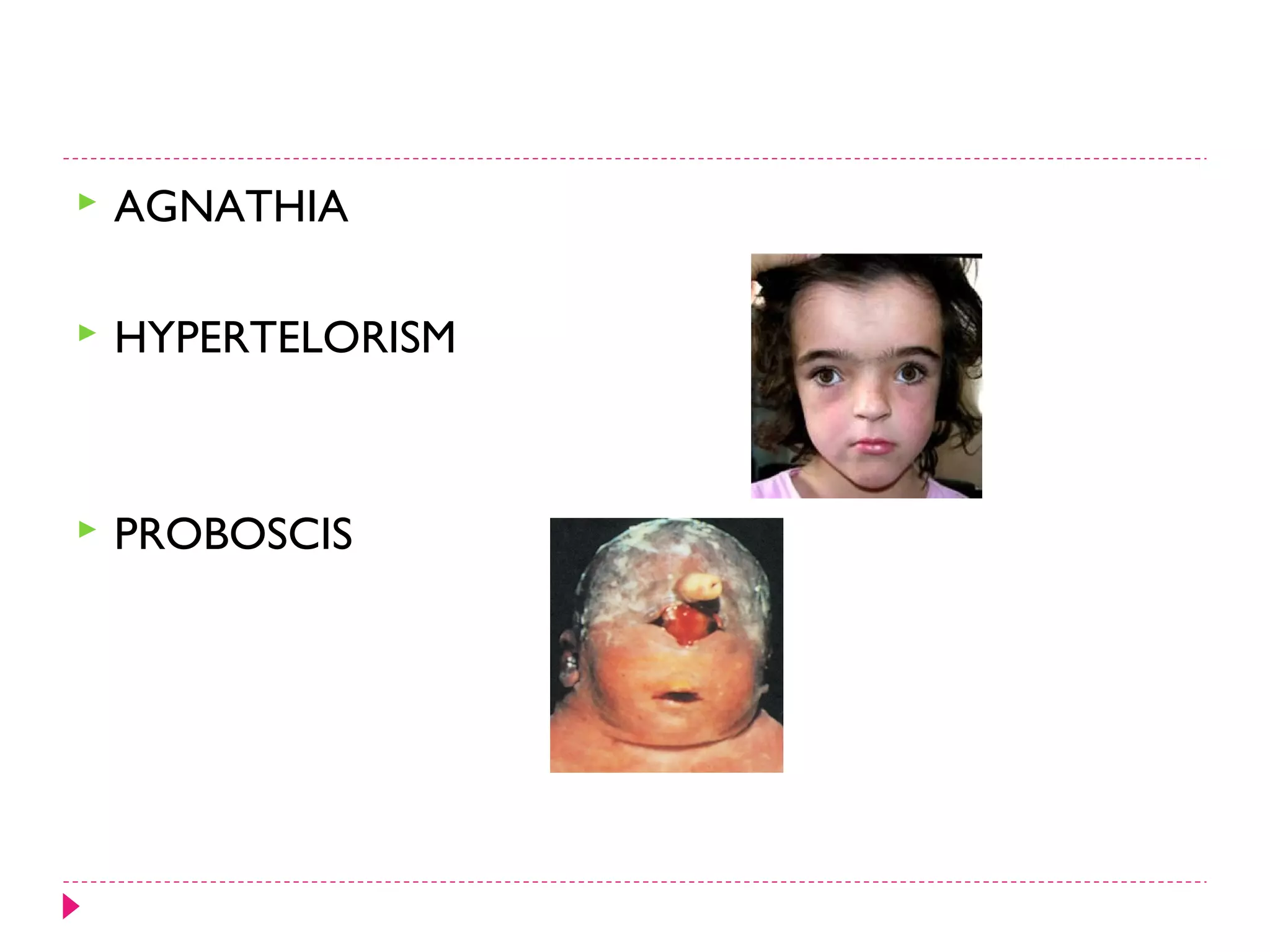
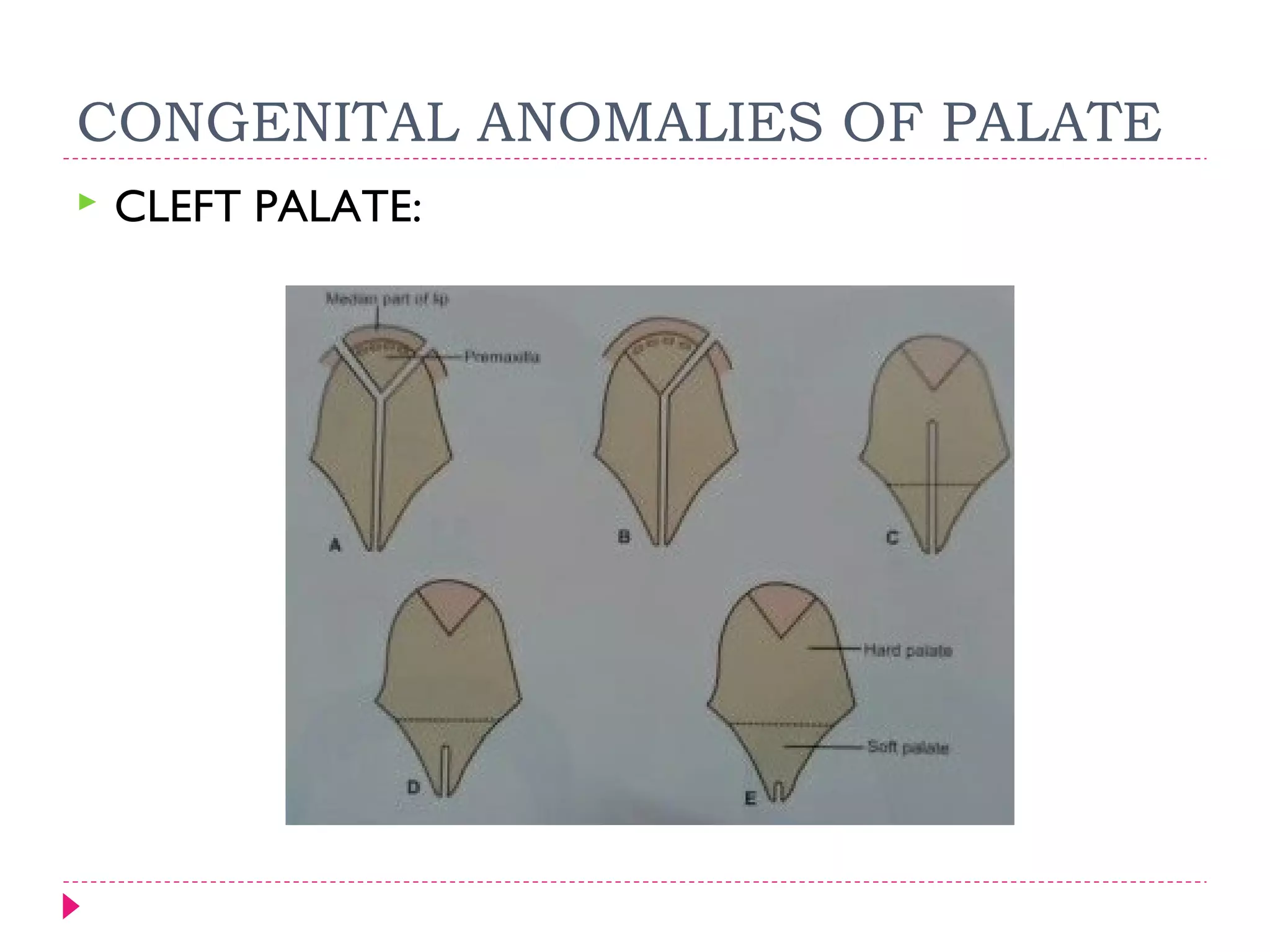
The document discusses the development of facial structures from prominences that appear around the fourth week of development. It describes how the frontonasal prominence forms parts of the forehead and nose. The maxillary prominences form parts of the upper lip, maxilla, and secondary palate. The mandibular prominences contribute to lower facial development. Specific structures that develop include the external nose, upper and lower lips, cheeks, primary and secondary palates, nasal cavity, eyes, and auricles. Congenital anomalies that can occur in facial development are also reviewed.