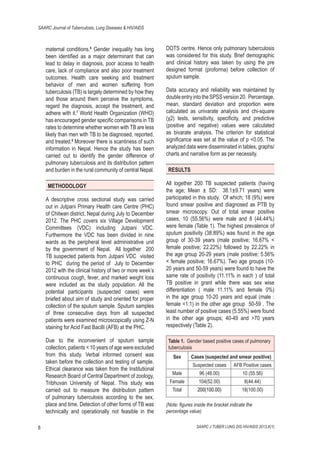
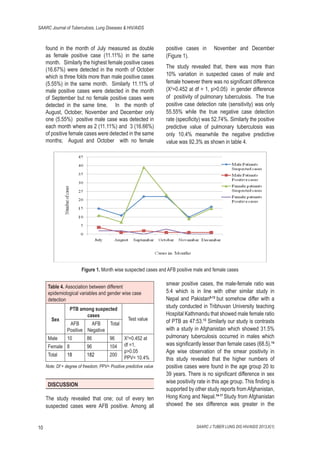
This study investigated the gender differences in case detection of pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) among suspected cases at the Jutpani Primary Health Centre in Chitwan, Nepal. Out of 200 suspected cases, 18 (9%) were confirmed as AFB positive, with a male-to-female ratio of 5:4, indicating that men are more likely to have PTB than women. The findings highlight the need for gender-specific case identification and preventive measures, particularly for the economically productive age group to mitigate the risk of TB.