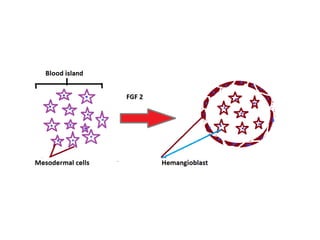
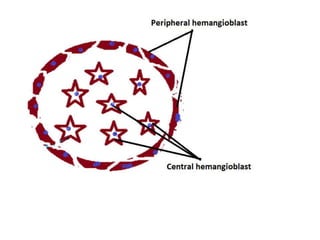
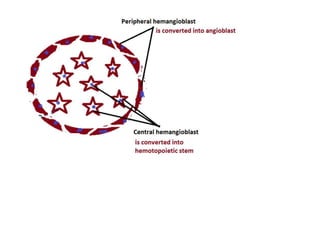
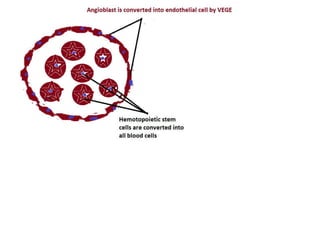
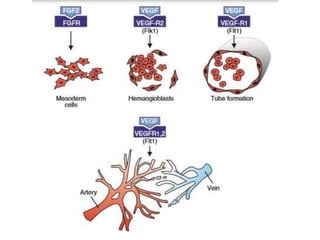
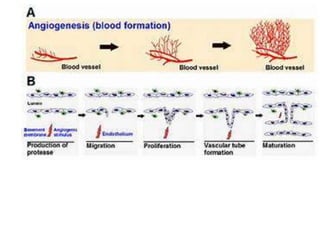
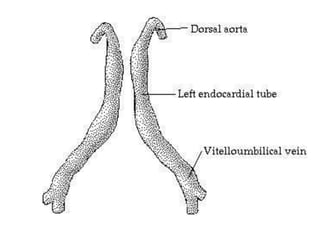
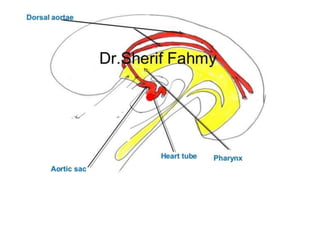
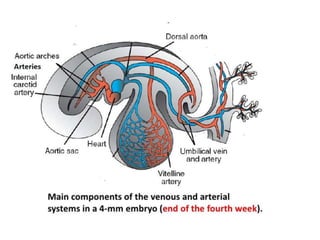
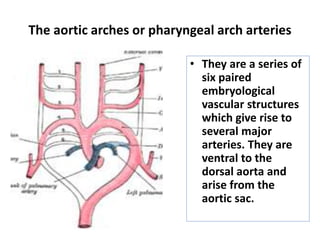
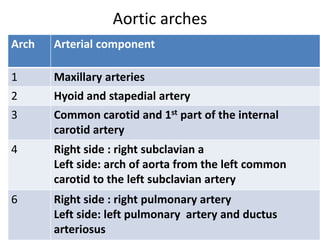
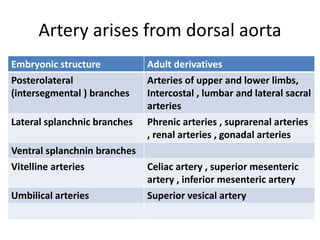
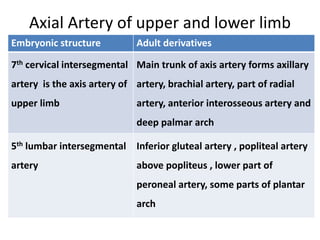
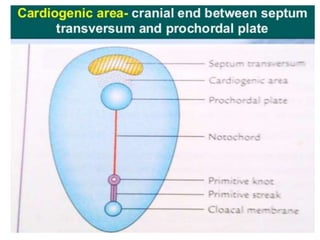
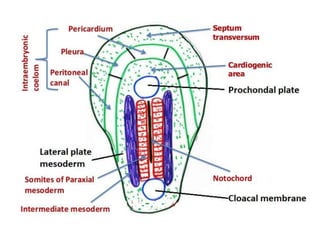
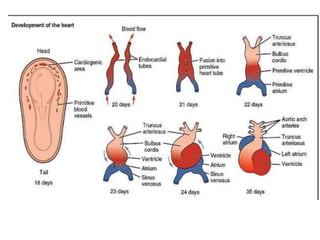
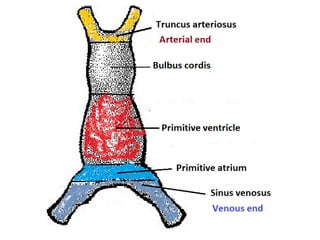
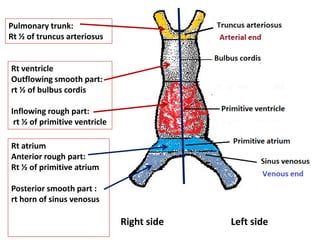
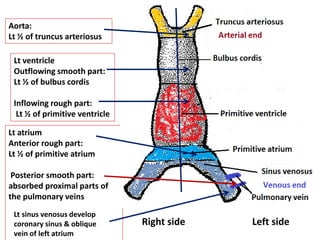
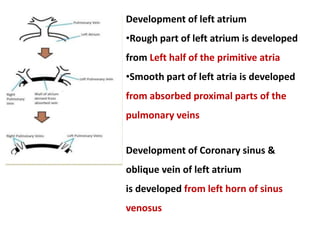
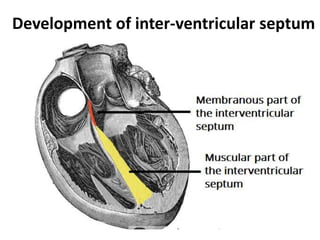
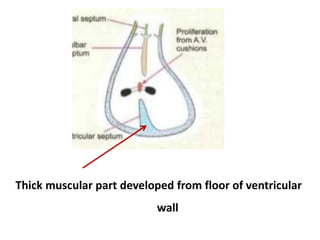
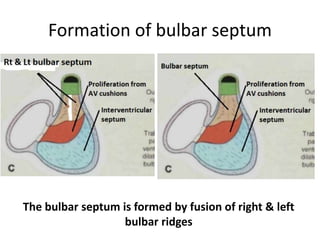
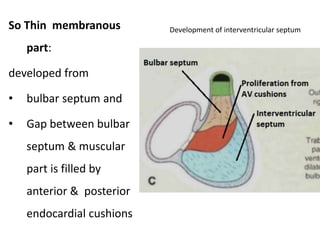
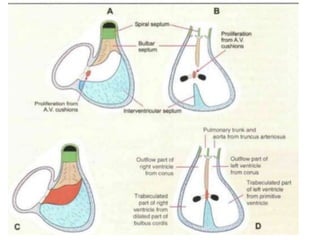
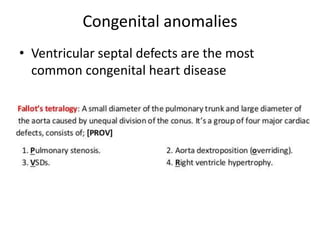
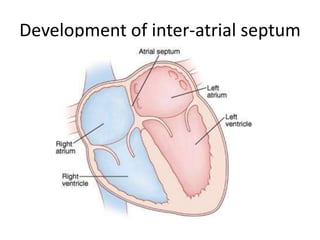
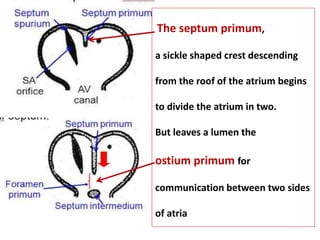
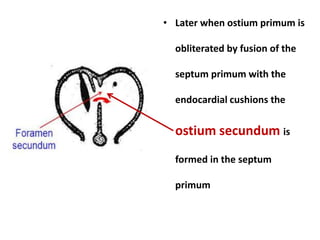
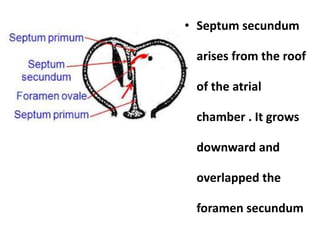
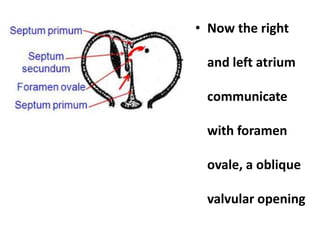
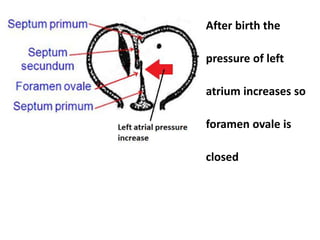
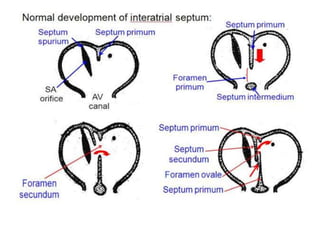
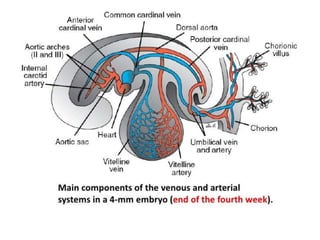
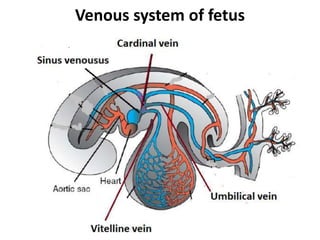
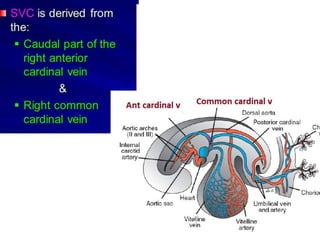
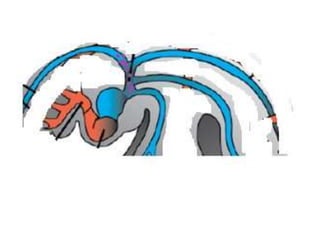
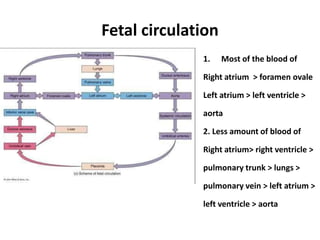
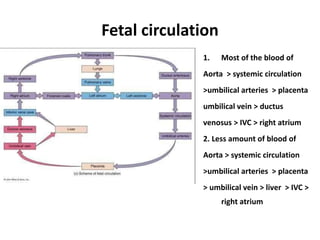
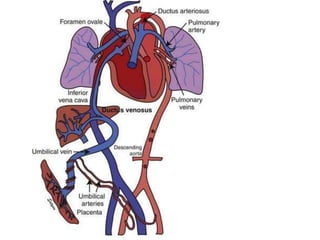
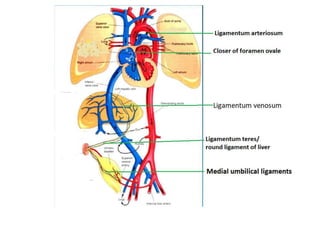
The document describes the process of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis in embryonic development. Vasculogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels from mesodermal blood islands, involving the differentiation of hemangioblasts into endothelial cells and blood cells. Angiogenesis is the formation of new vessels from existing ones. It also discusses the development of the heart, including the formation of the atrial and ventricular septa by fusion of endocardial cushions. The fetal circulatory system is described, which involves blood shunting from the right atrium to left via the foramen ovale and ductus venosus/arteriosus, allowing most blood to bypass the lungs. After birth, these fetal circulatory