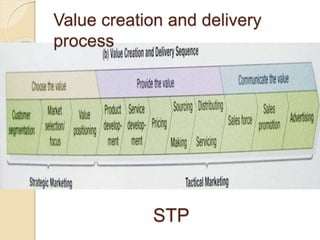
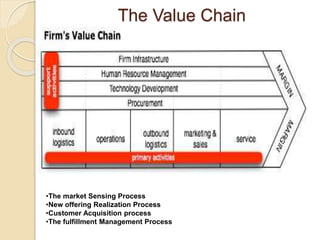
This document discusses marketing management strategies and developing a marketing plan. It covers determining customer value, strategic planning at different organization levels, and what elements a marketing plan should include. The plan development process involves situation analysis, defining objectives and strategies, identifying target markets, and selecting appropriate marketing mix elements. It also discusses assessing growth opportunities, developing goals, and contingency planning.