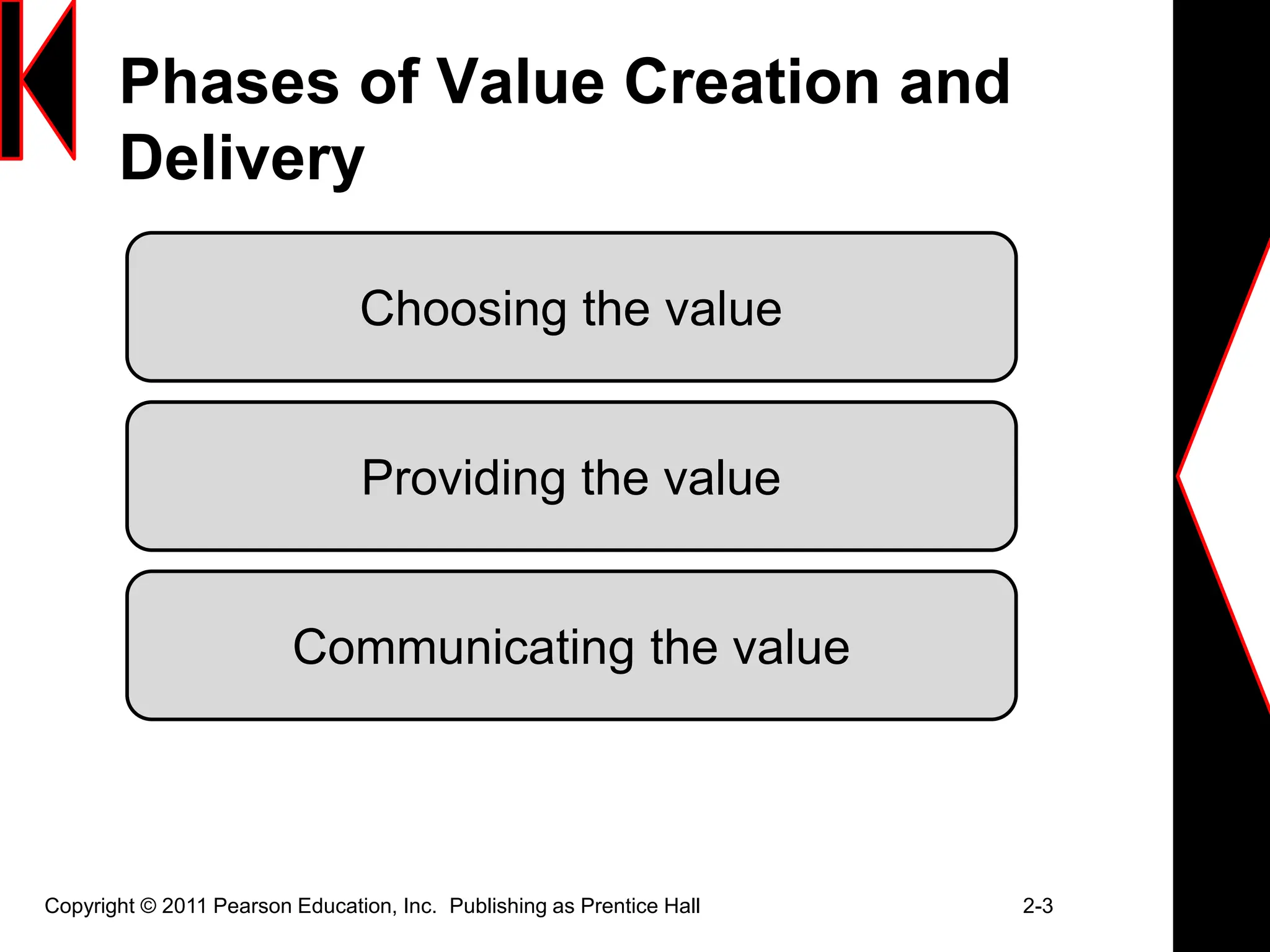
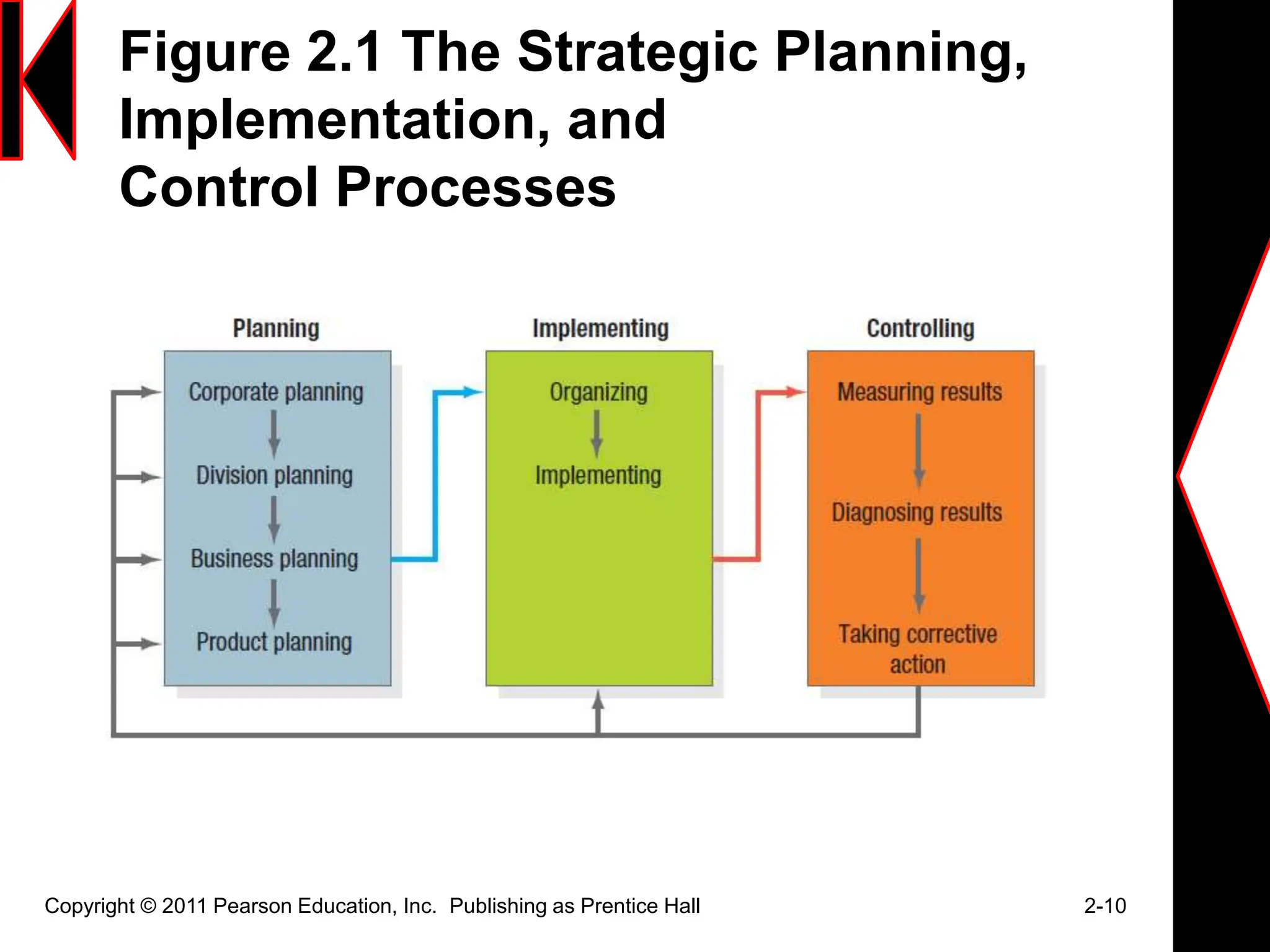
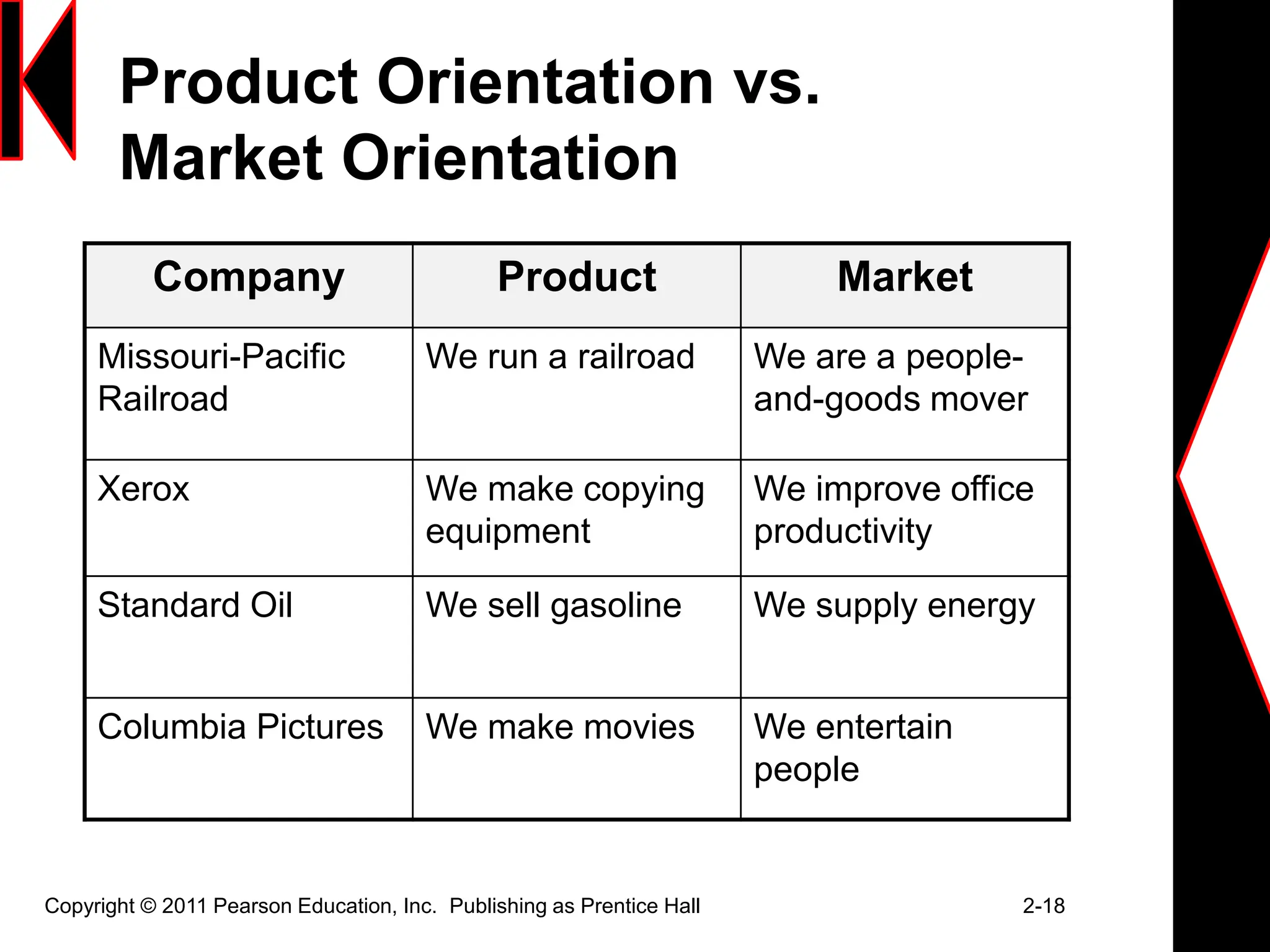
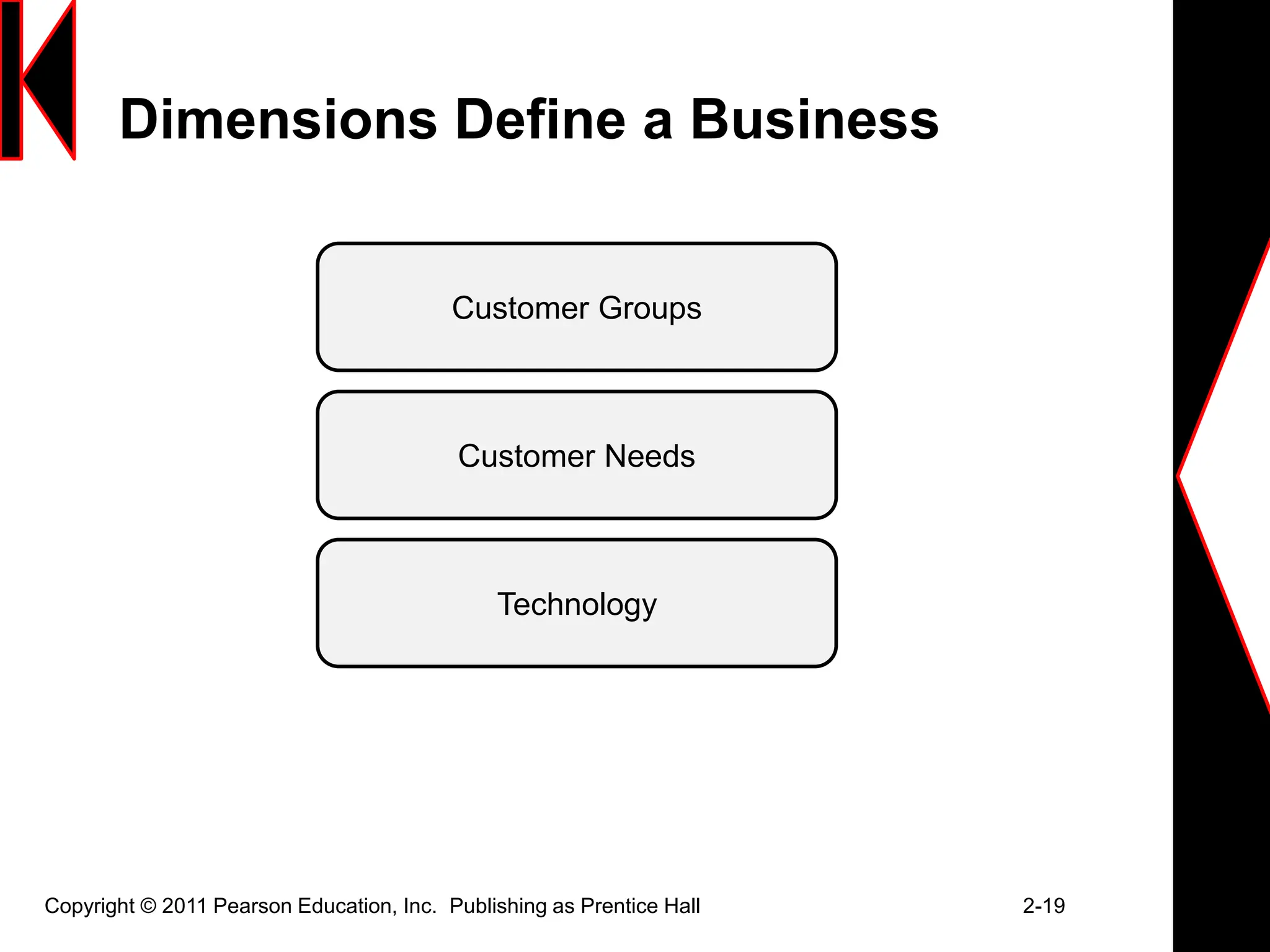
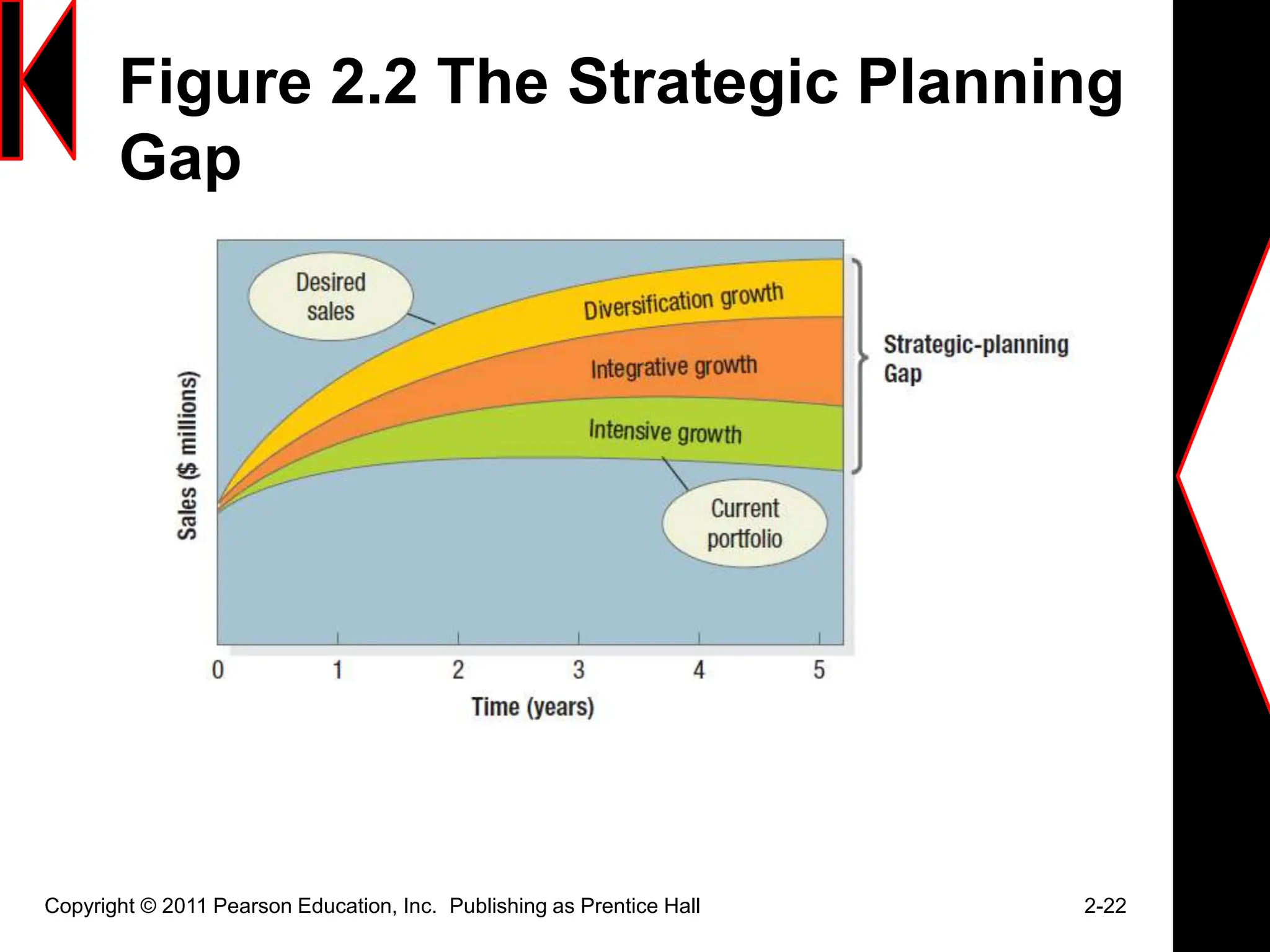
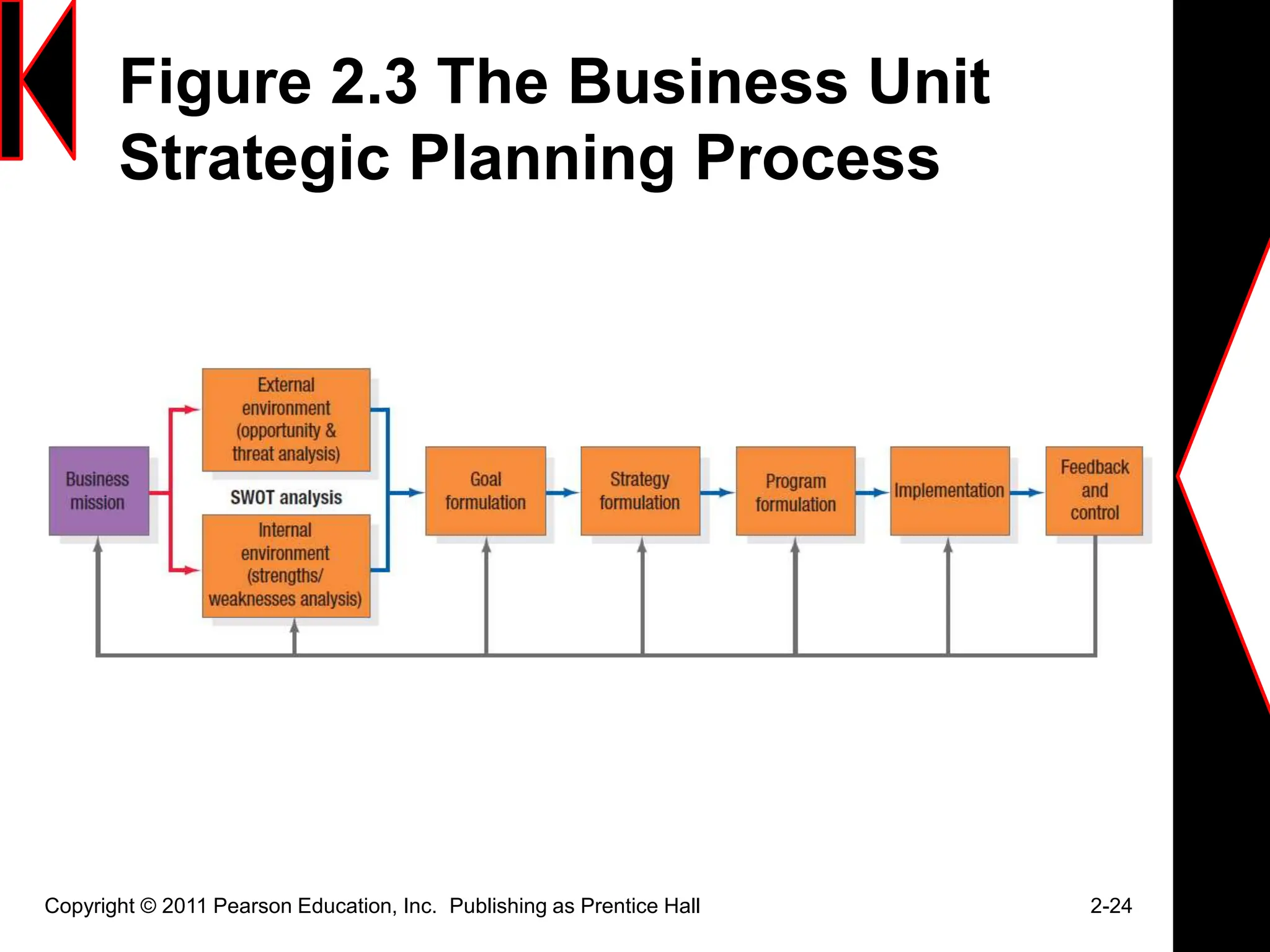
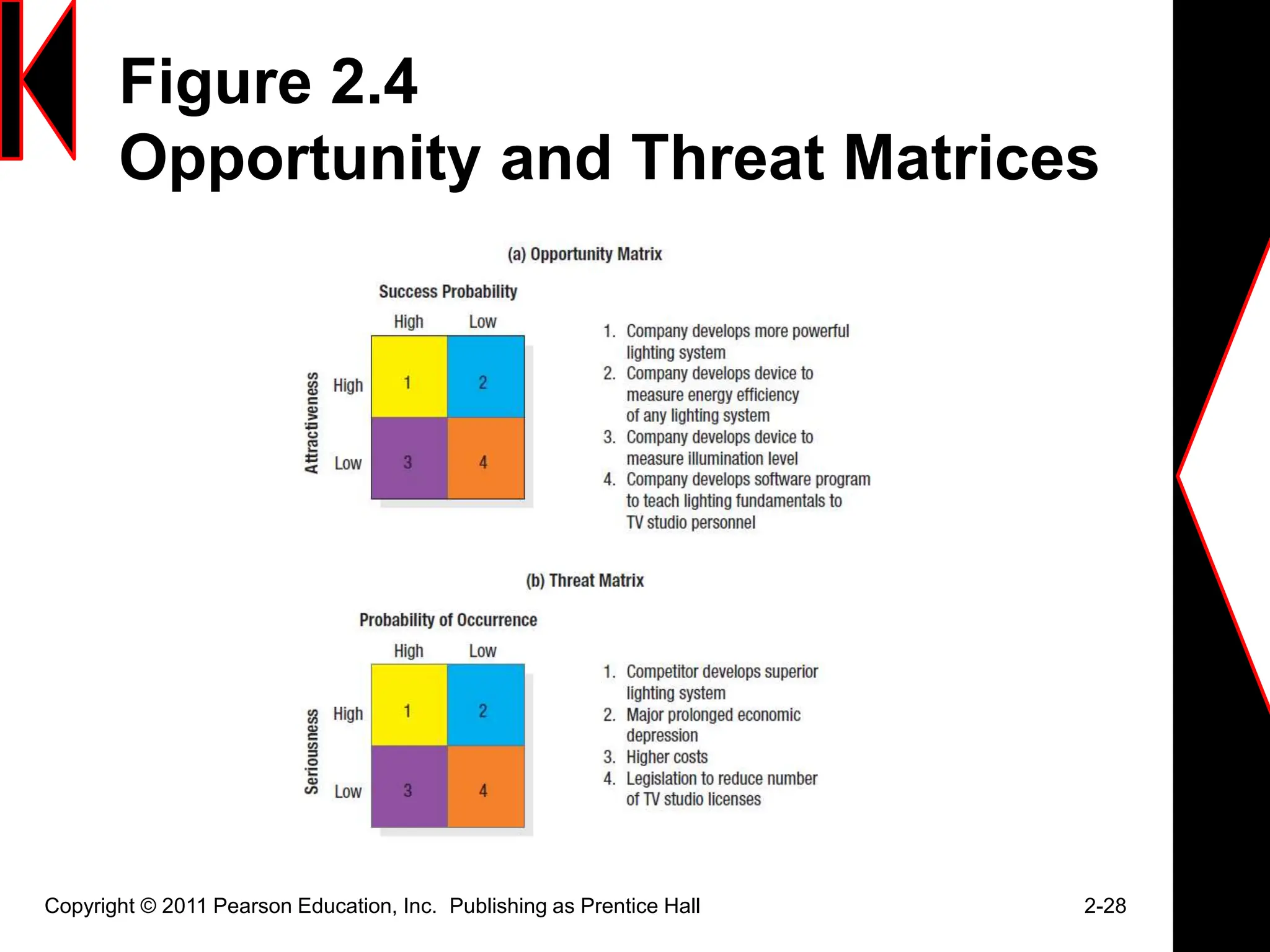
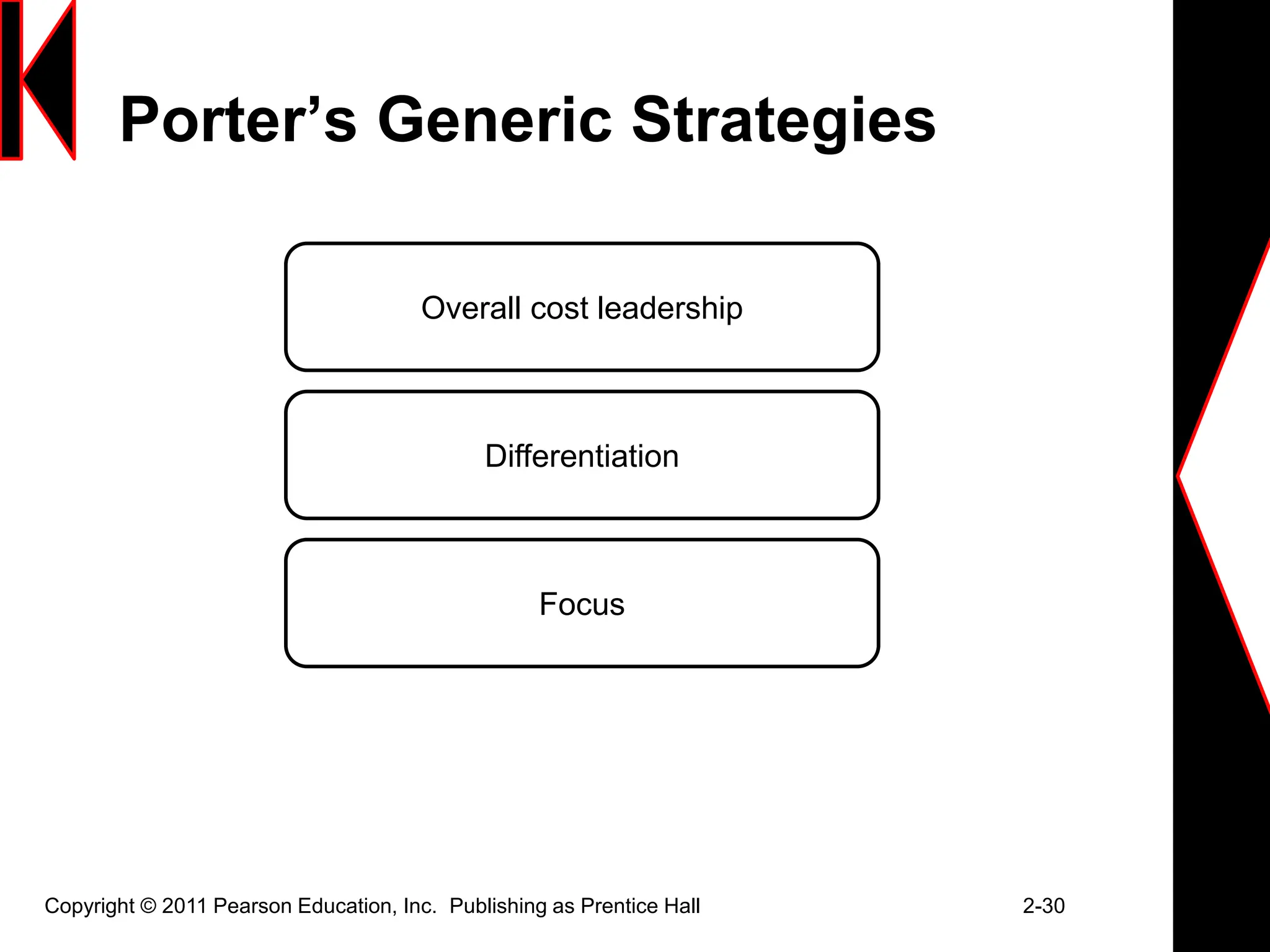
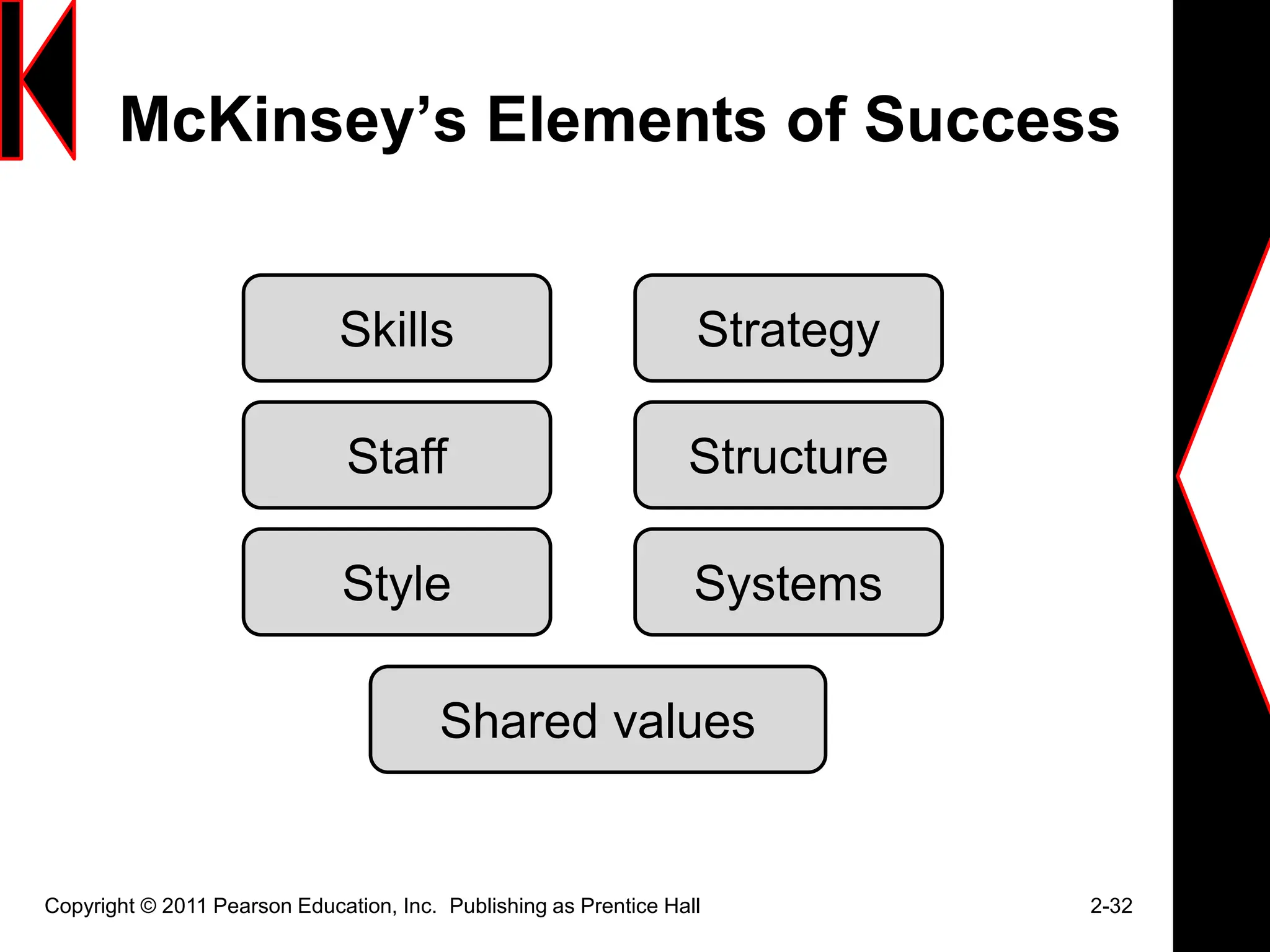
The document discusses marketing strategies and plans. It covers topics such as the value chain, core competencies, strategic planning processes, SWOT analysis, marketing opportunities, goals, generic strategies, marketing mix, and marketing plan contents. The marketing plan is the central instrument for directing marketing efforts and includes an executive summary, situation analysis, marketing strategy, financial projections, and implementation controls. Strategic planning is carried out at the corporate level to define missions and assess growth opportunities, and at the business unit level through SWOT analysis and identifying marketing opportunities.