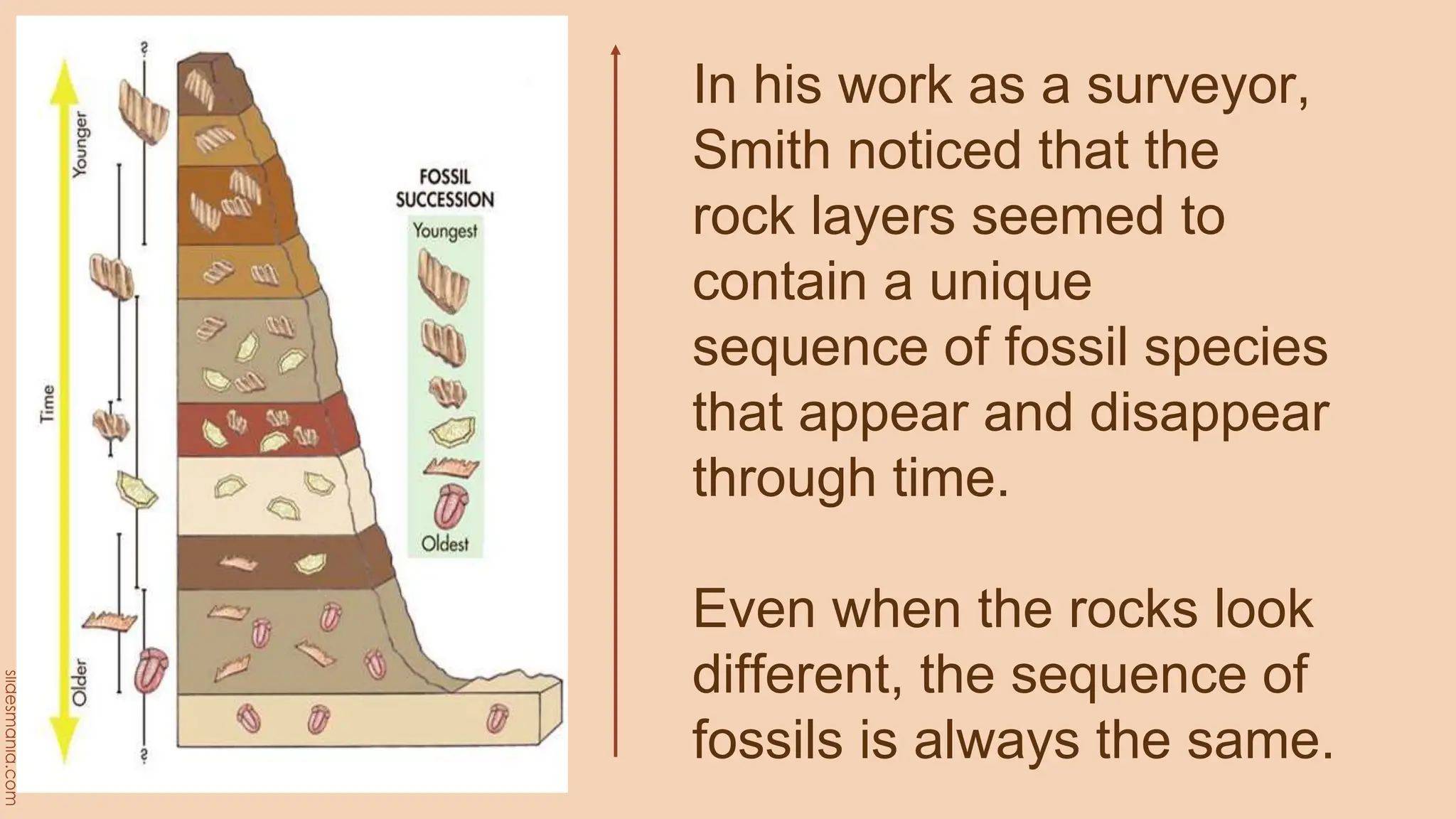
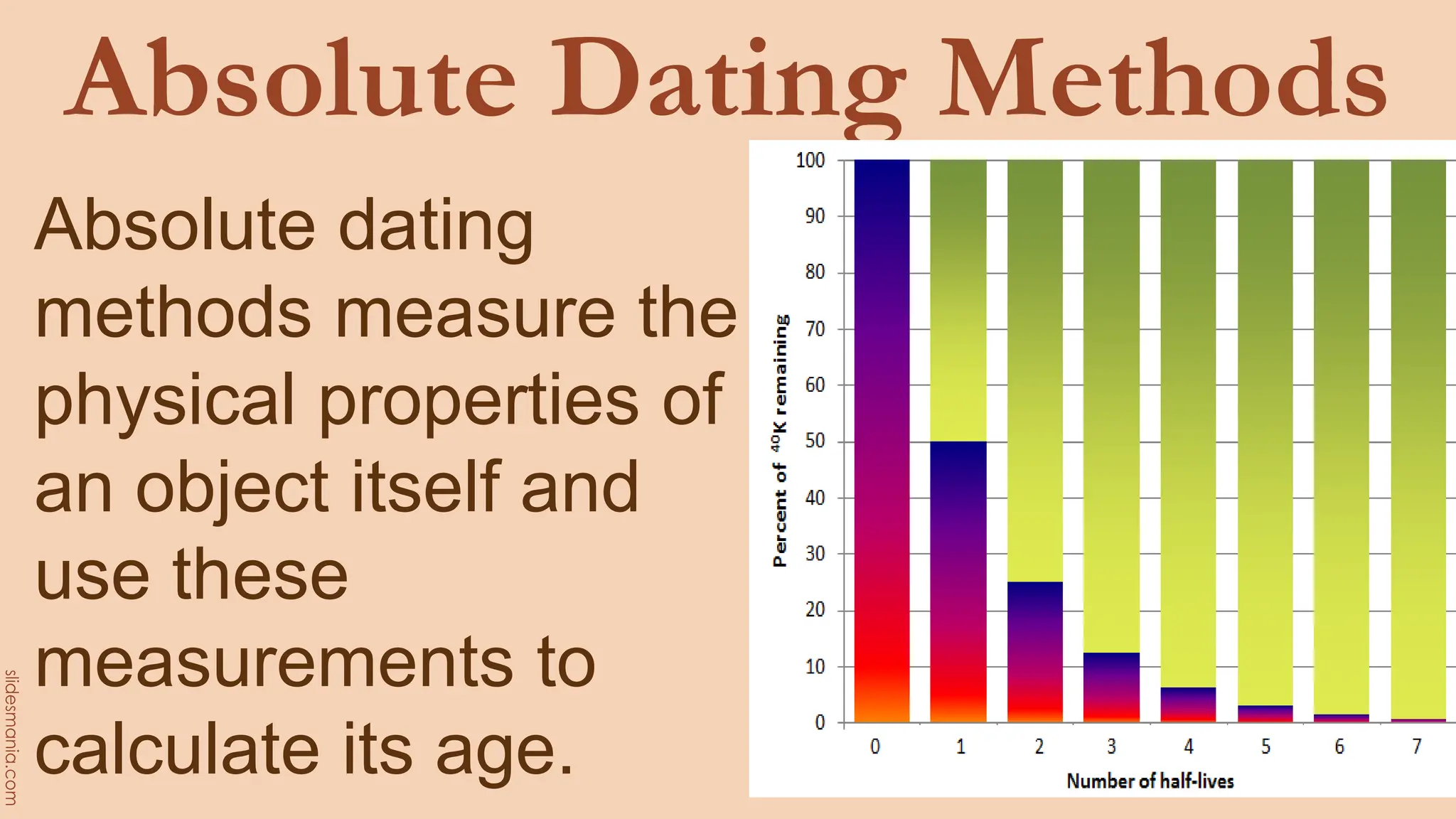
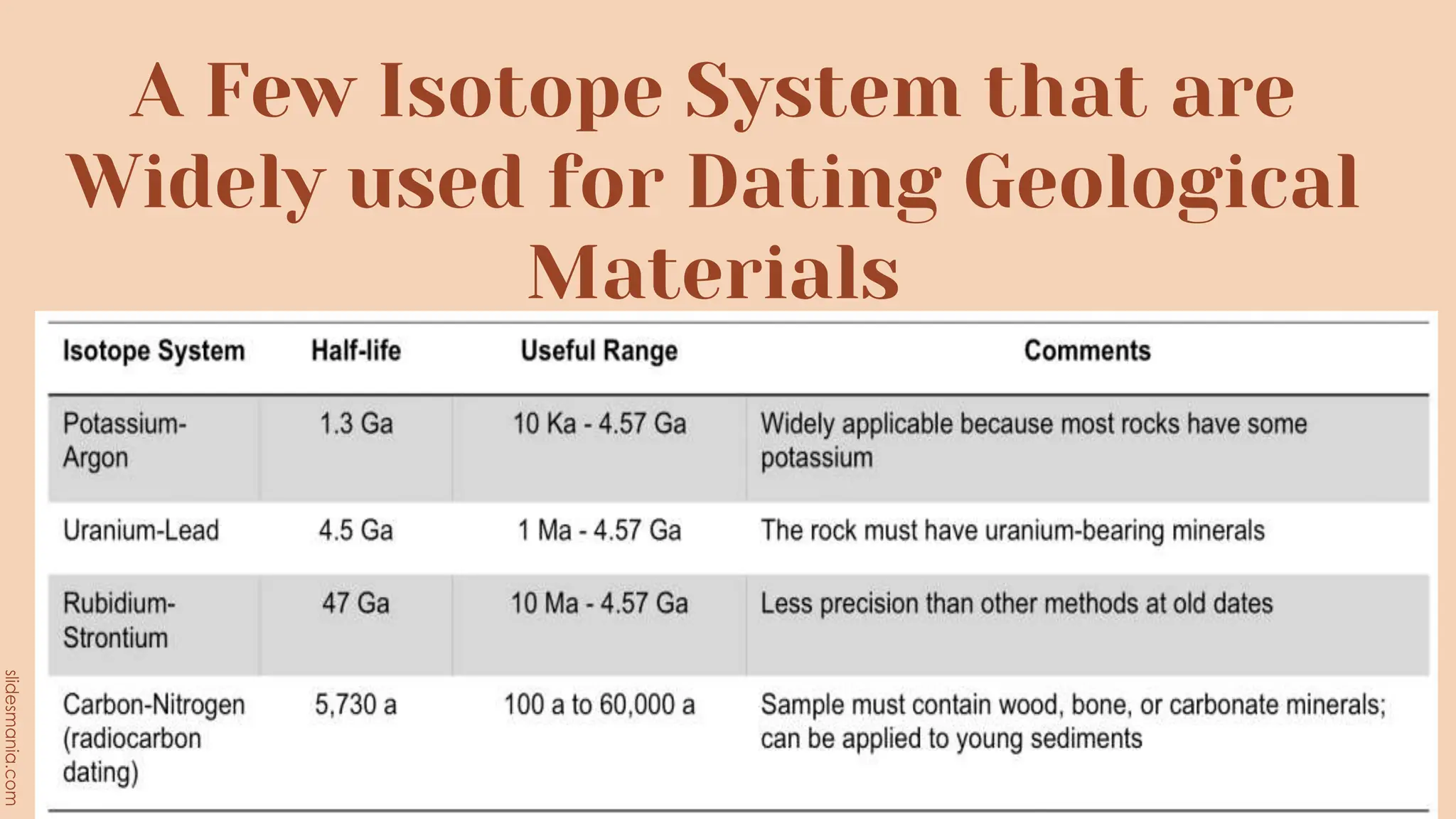
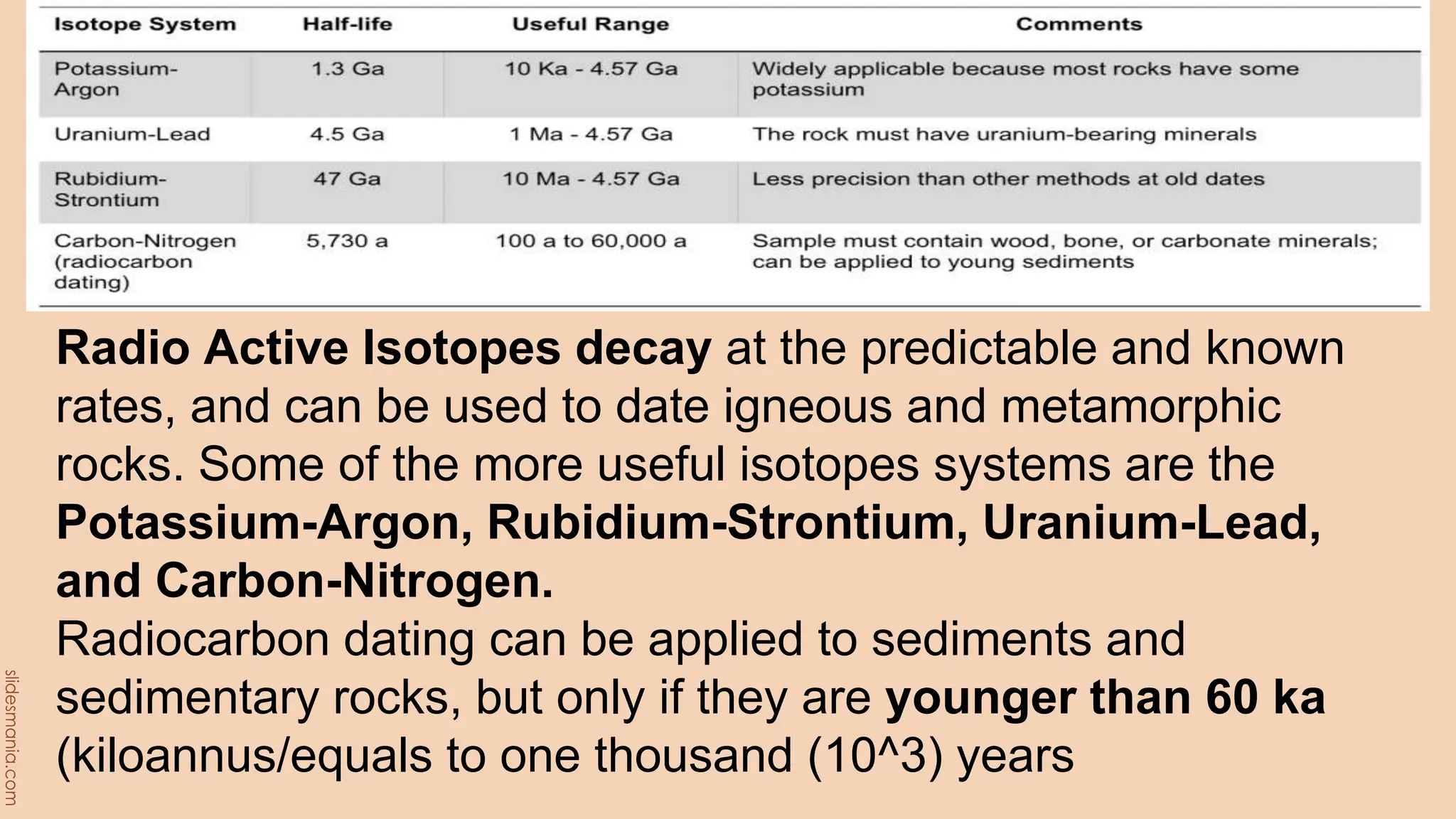
The document discusses methods for determining the geologic time scale and dating geological features. It describes the four eons the geologic time scale is divided into and explains both relative and absolute dating techniques. Relative dating looks at relationships between geological features, while absolute dating uses measurements of radioactive isotopes in rocks and minerals to calculate their precise ages. Examples provided include William Smith's work identifying distinctive fossil sequences to correlate rock layers and the potassium-argon dating method.