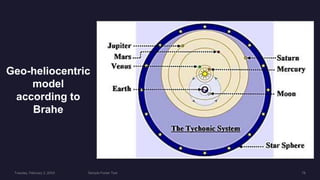
The document provides information about models of the universe including:
1) The Ptolemaic model which placed Earth at the center with celestial bodies revolving in epicycles,
2) The Copernican model which established a heliocentric system with Earth and planets revolving around the Sun, and
3) The Tychonic model which was a hybrid with Earth at the center and planets revolving around the Sun.
It also discusses Kepler's three laws of planetary motion derived from Tycho Brahe's astronomical data, including elliptical orbits, equal areas swept in equal times, and the harmonic relationship between orbital periods and distances.