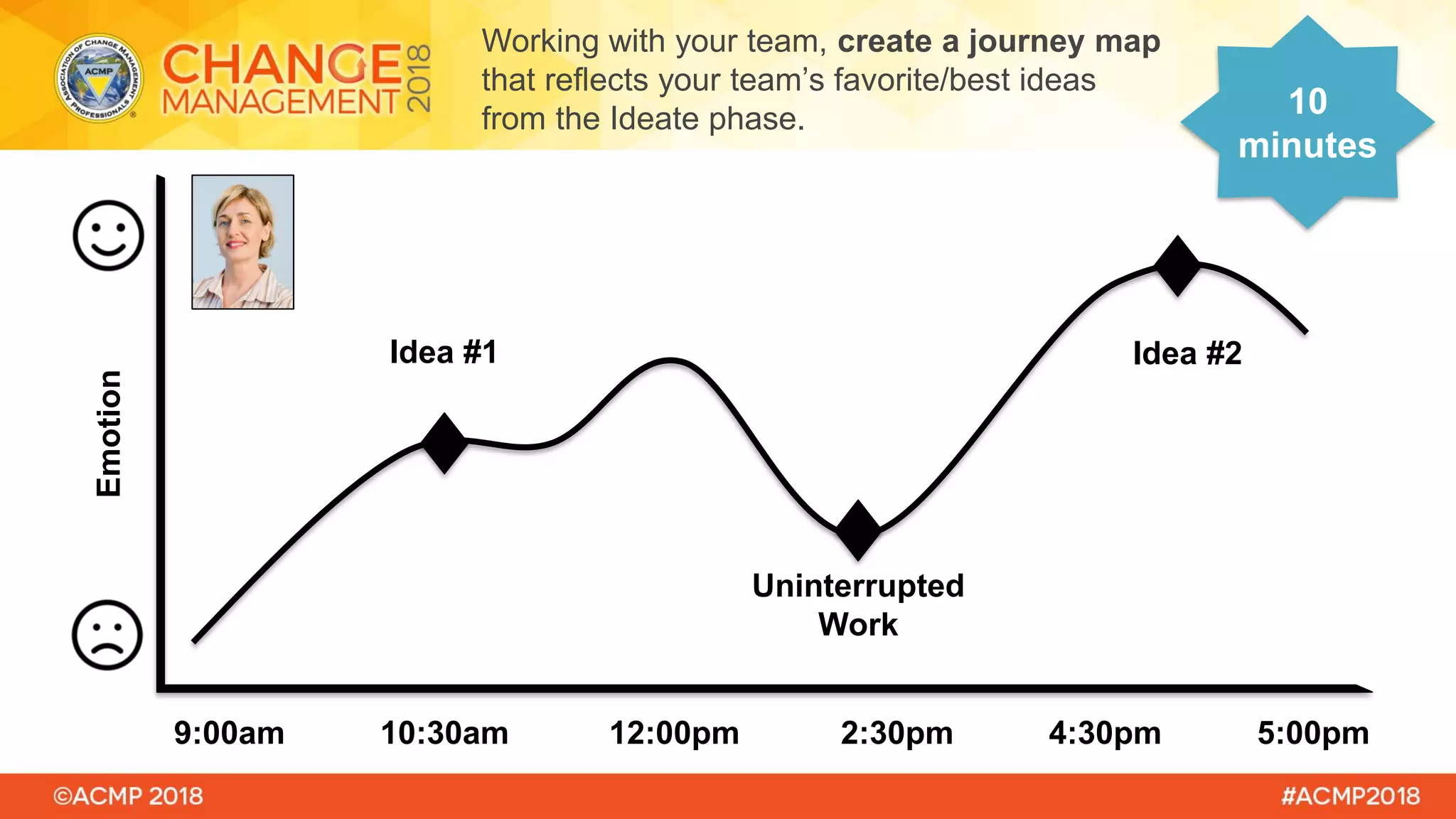
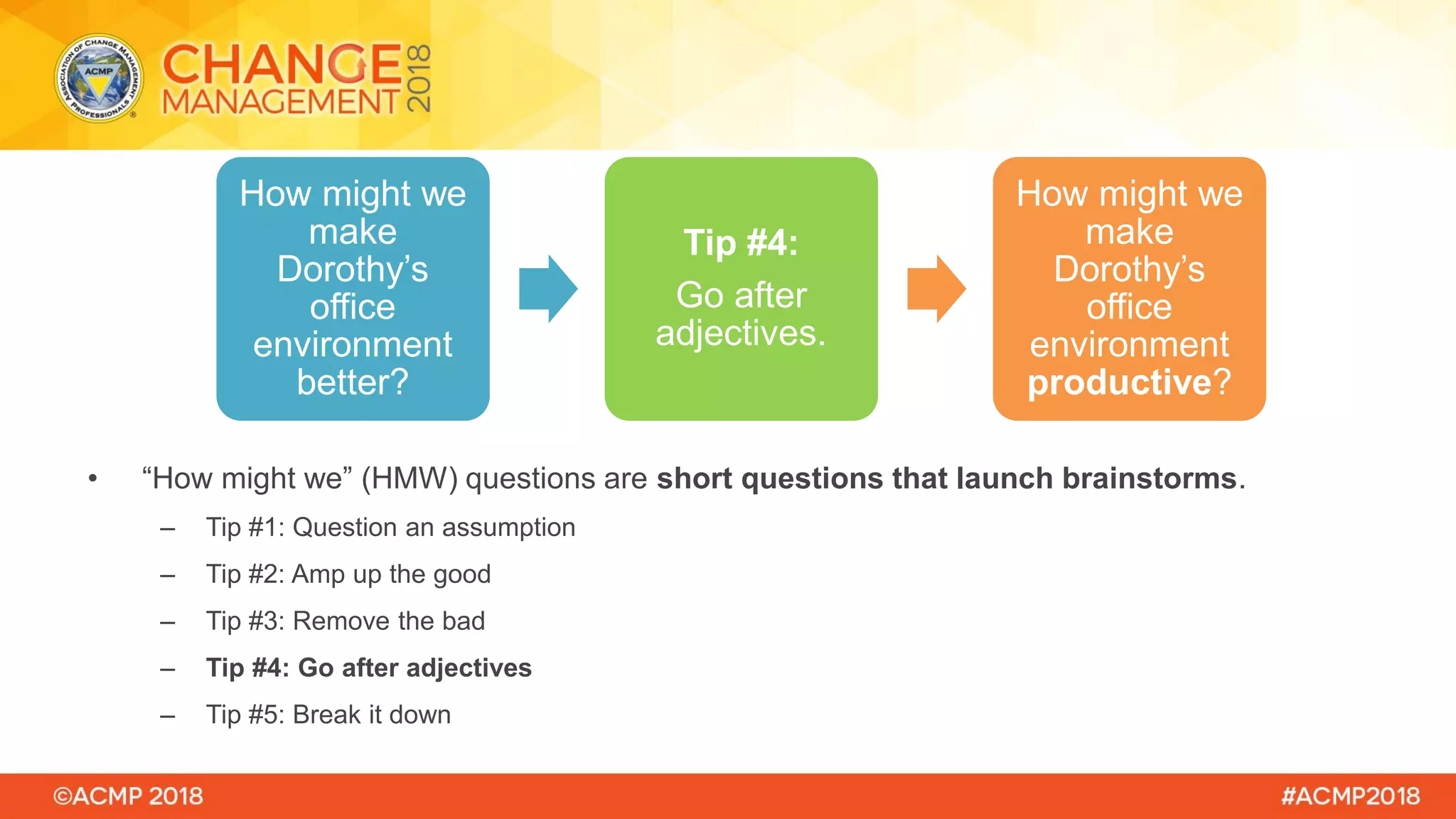
The document outlines a workshop on design thinking led by experts Claire Brawdy and Rebecca Wyatt, who aim to educate participants on the framework's phases and its application in co-designing solutions. Key objectives include understanding user needs, defining challenges, brainstorming, prototyping, and testing ideas in a collaborative and iterative manner. Participants will engage in hands-on activities to foster a human-centered approach to problem solving in various change initiatives.

















![Q: What do we like about [your brands, products, services] that
could be translated to our ideal office environment?
• e.g. Collaborative + WordPress = Open source, developed
and maintained by the community surrounding it
• e.g. Collaborative + WeWork = Communal desks and open
floor plans
• e.g. Collaborative + Lyft = Centralized information sharing
6
minutes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalacmp-180403131113/75/Design-Thinking-to-Co-Design-Solutions-Presented-at-ACMP-2018-20-2048.jpg)