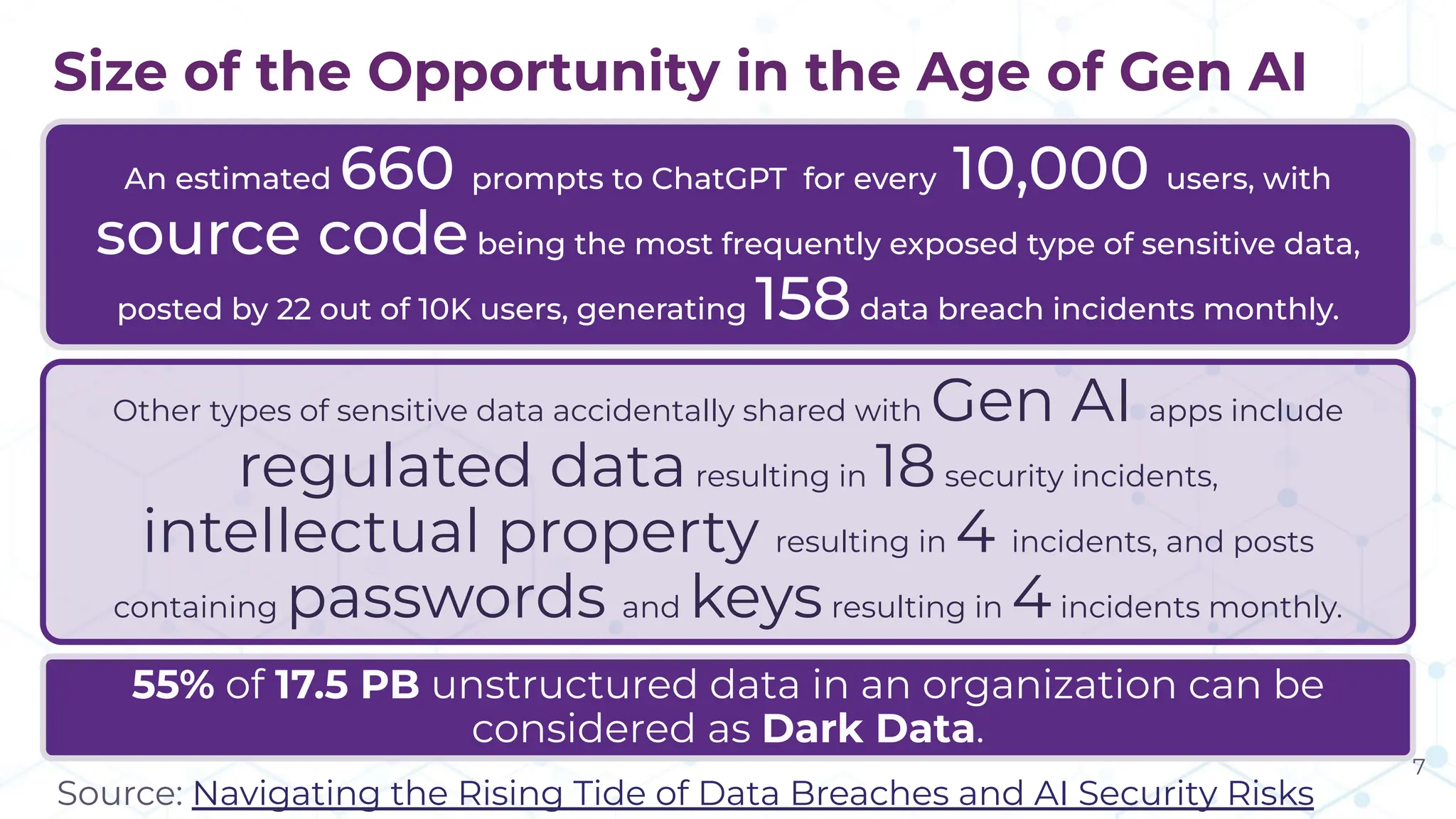
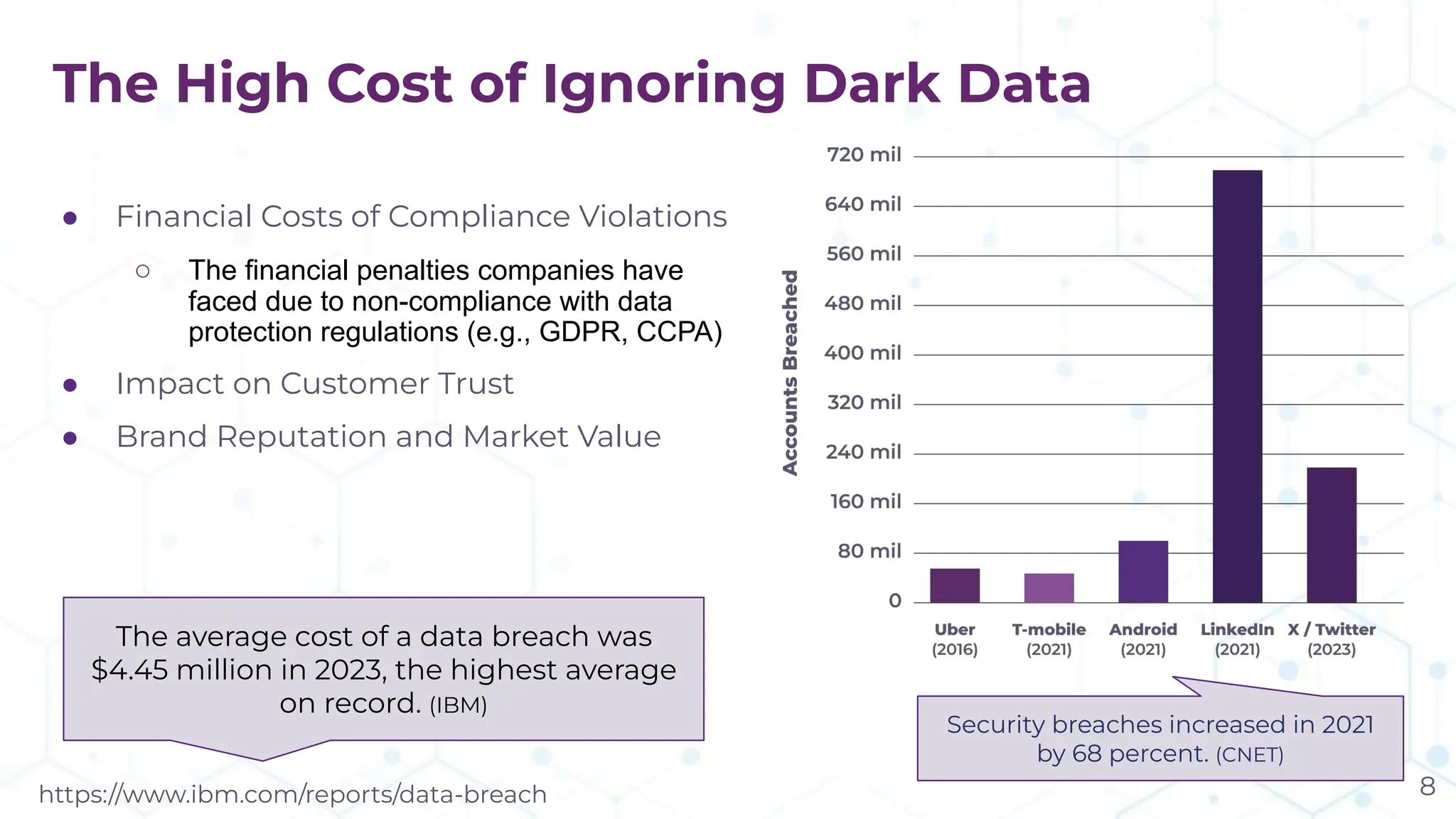
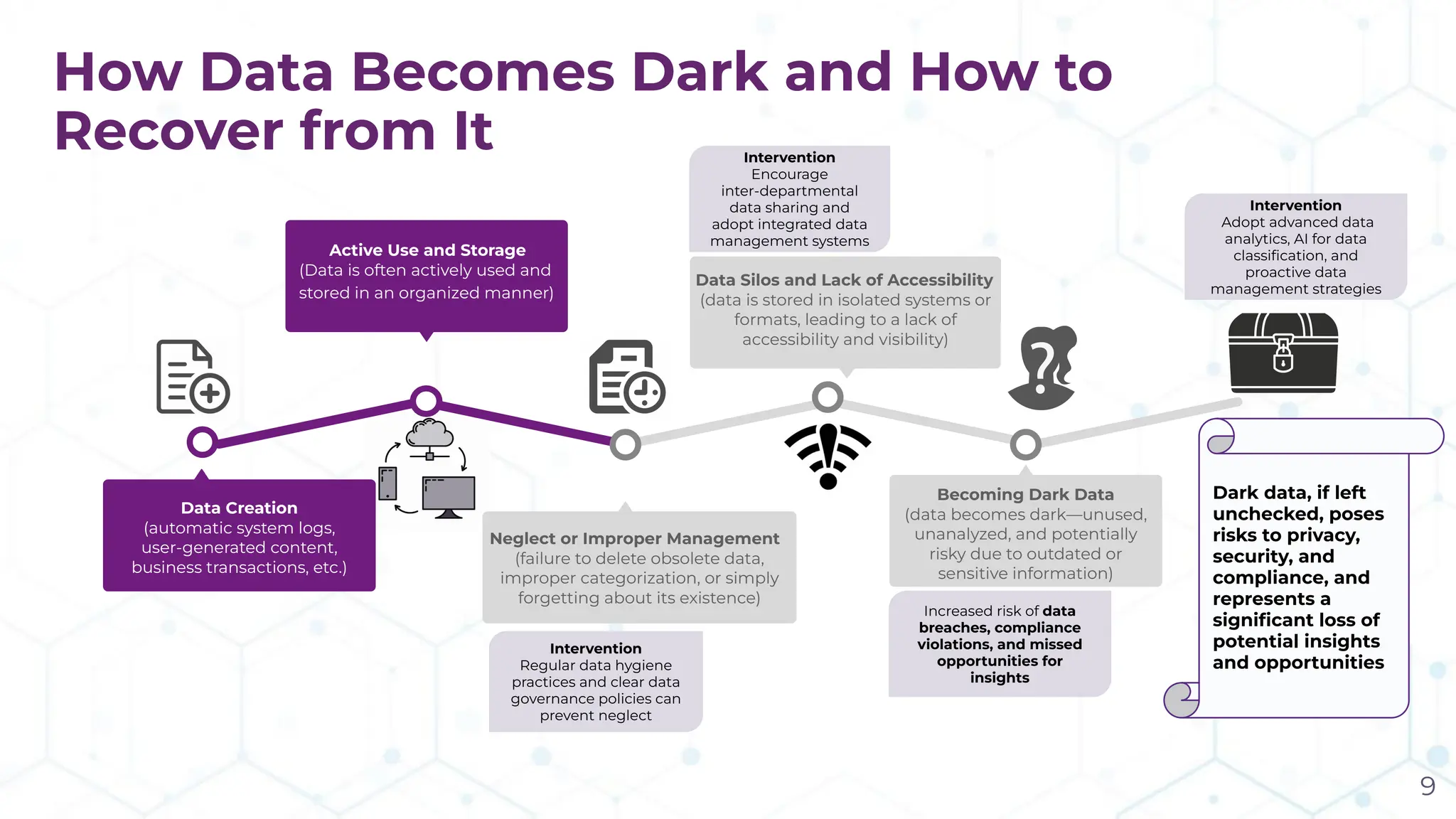
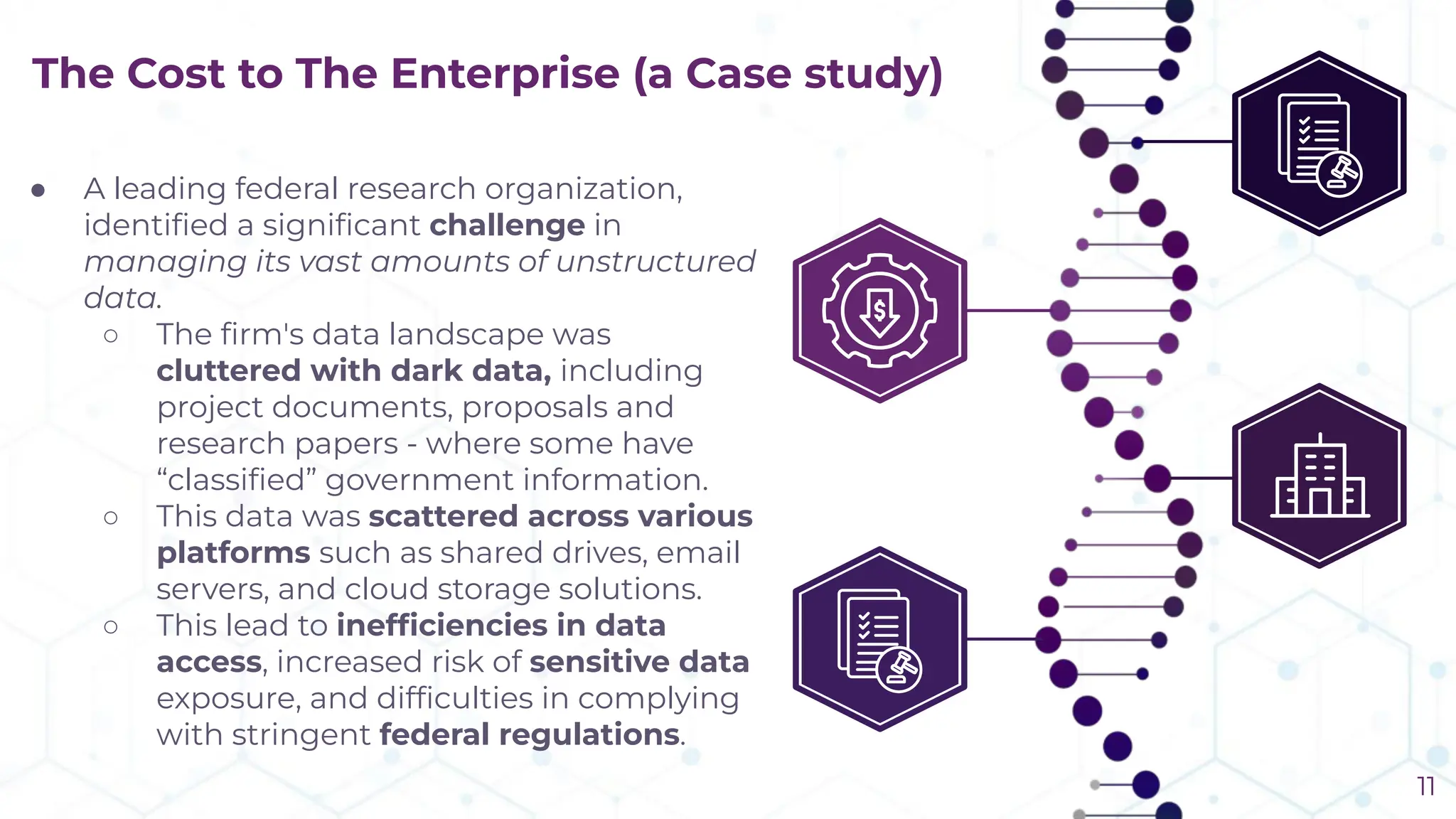
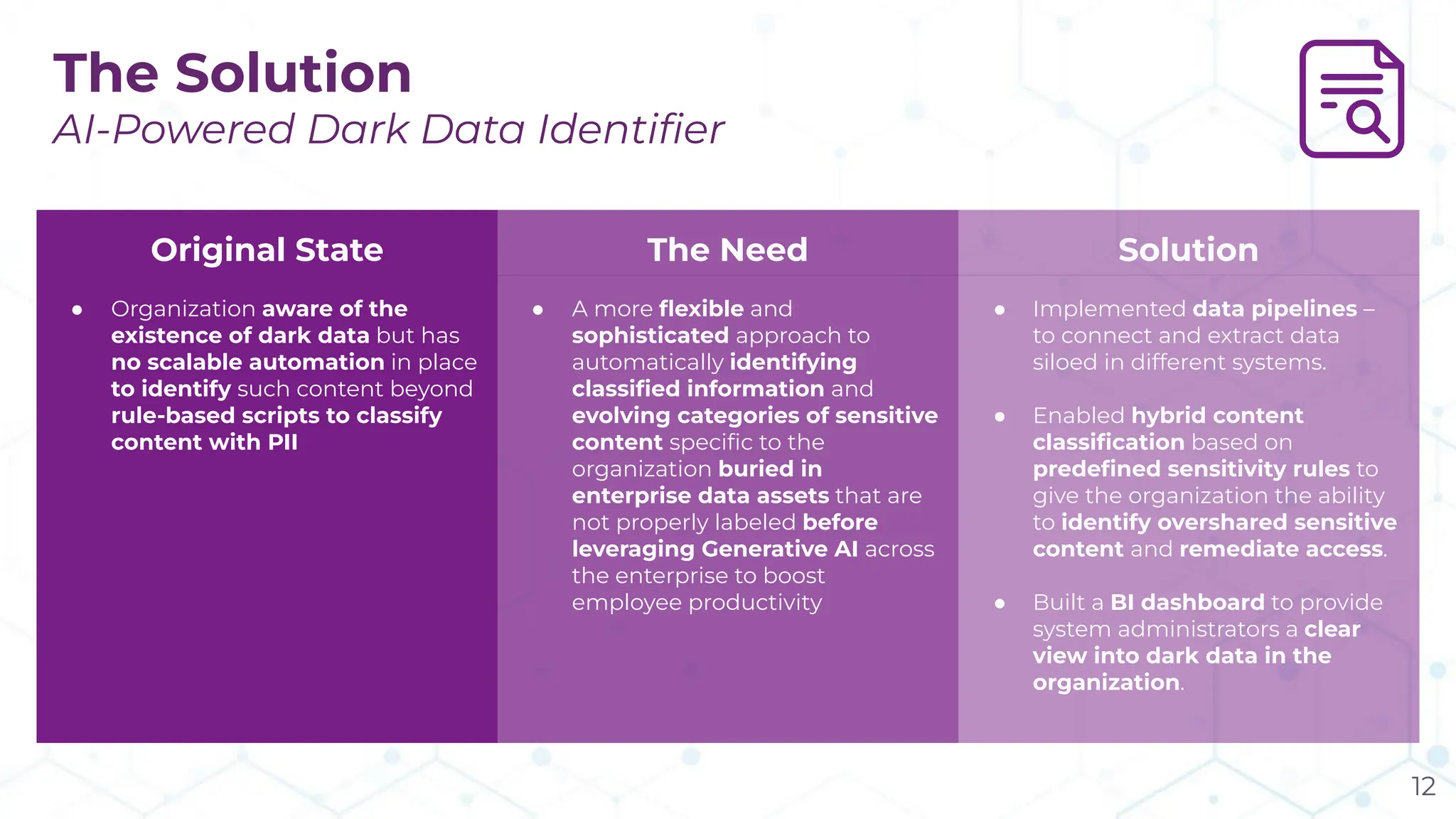
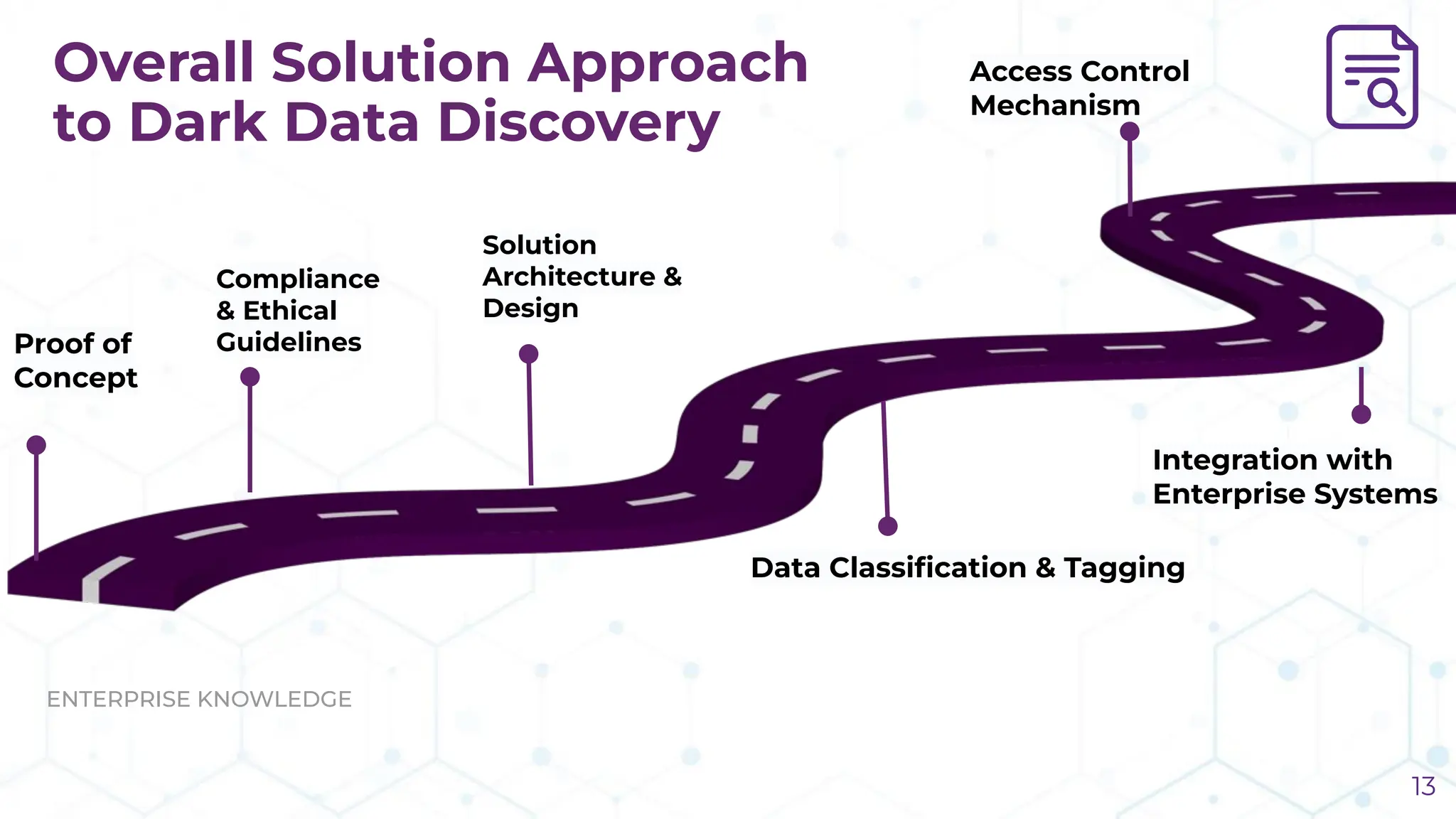
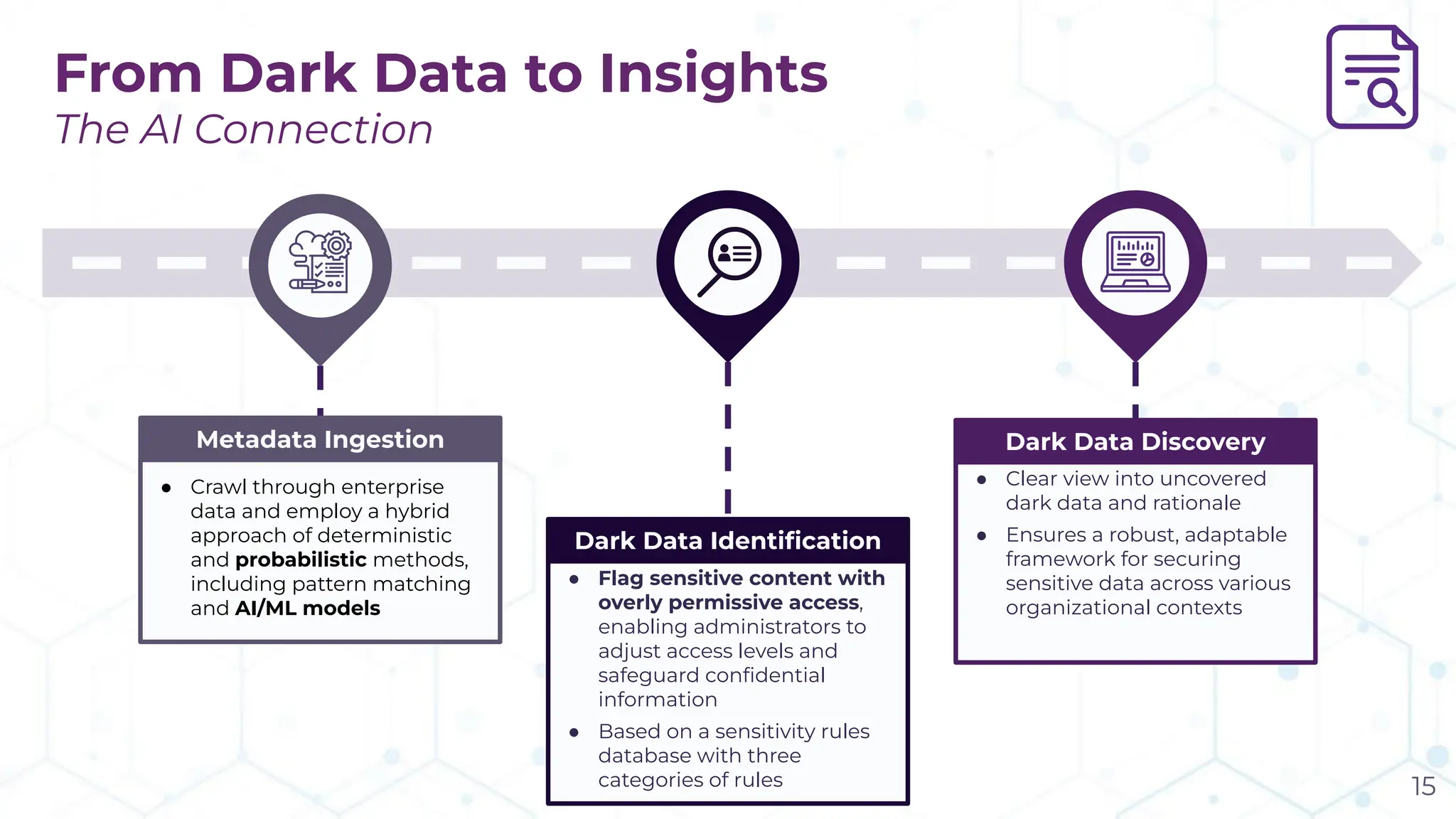
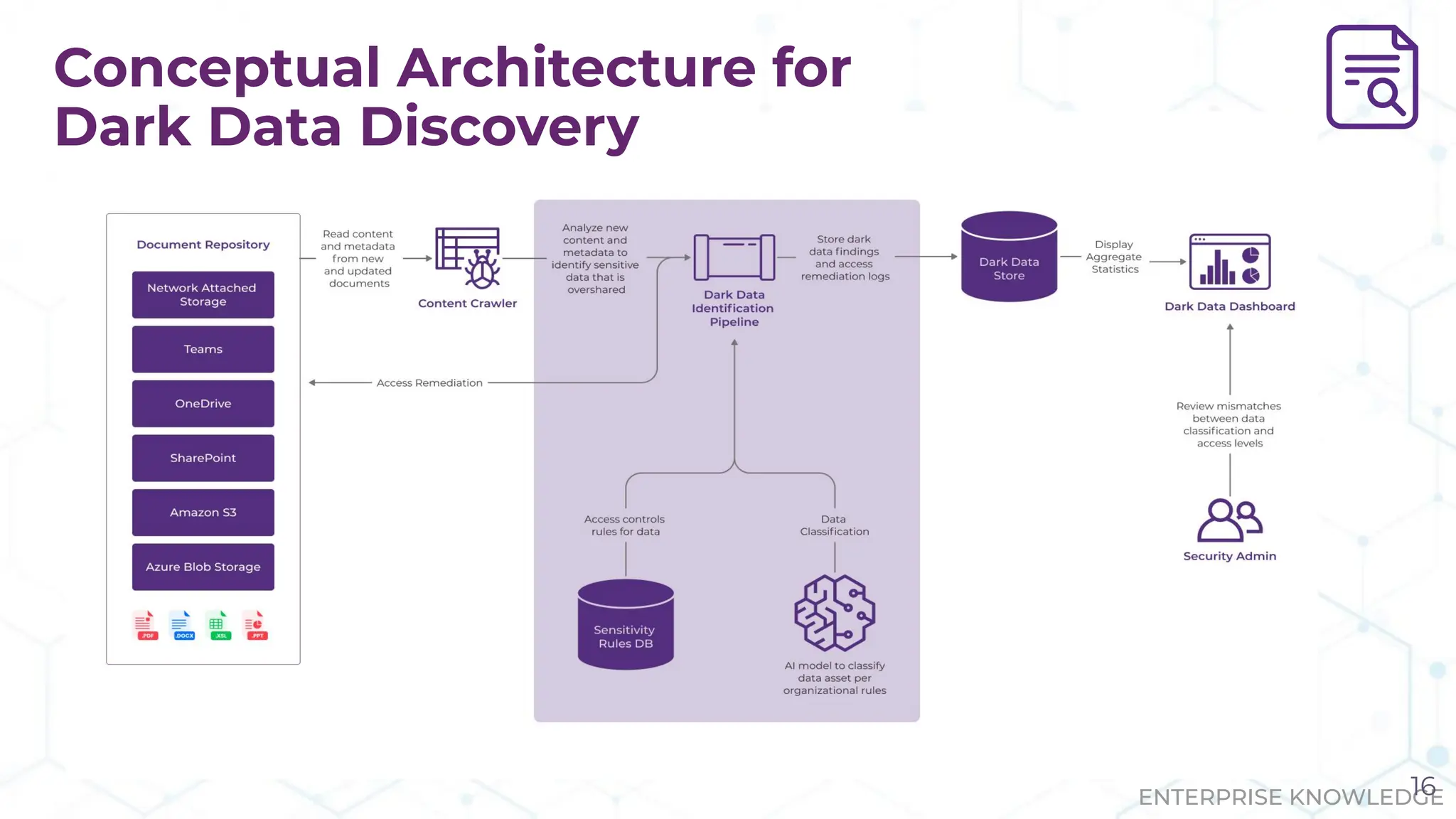
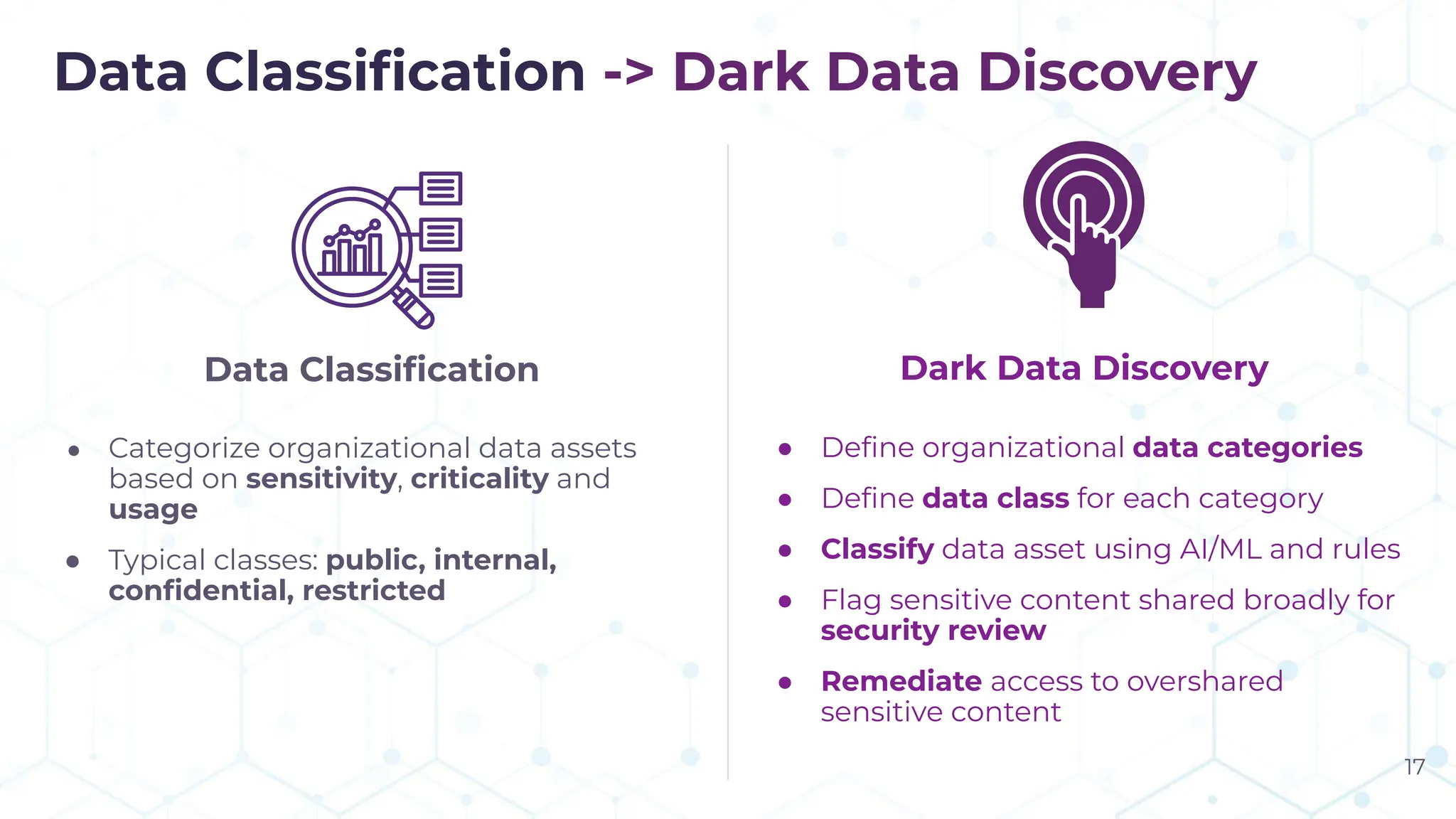
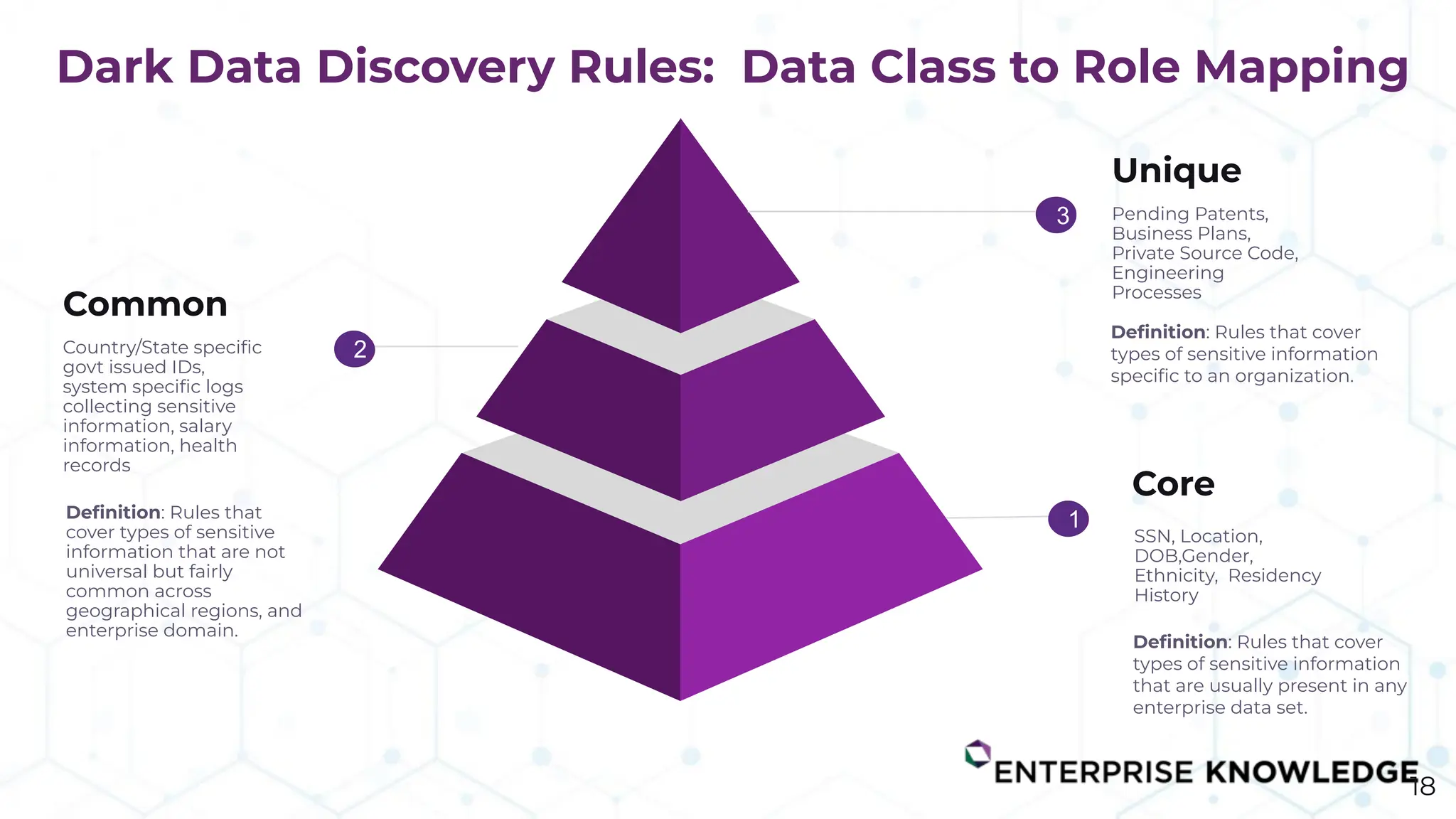
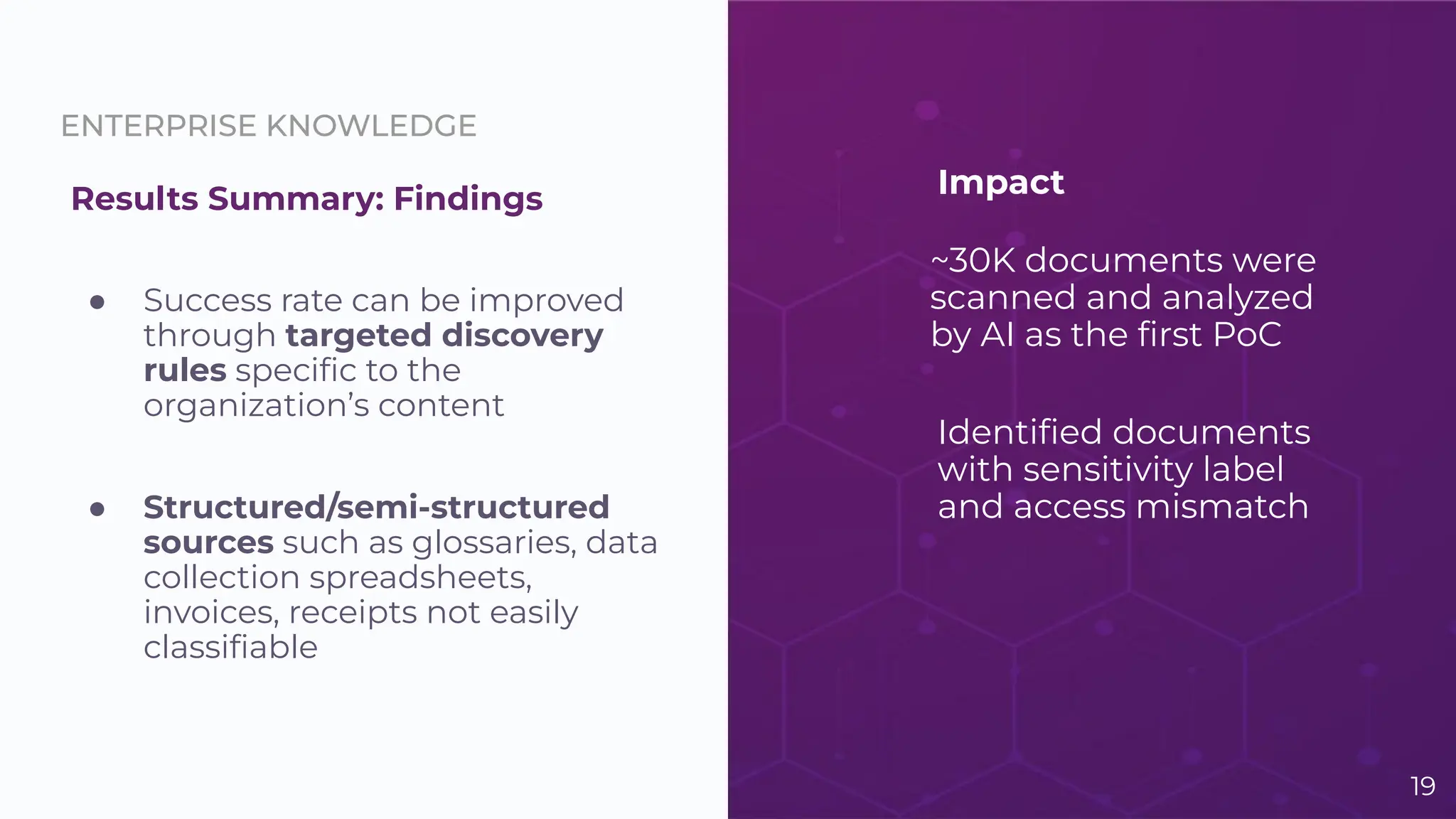
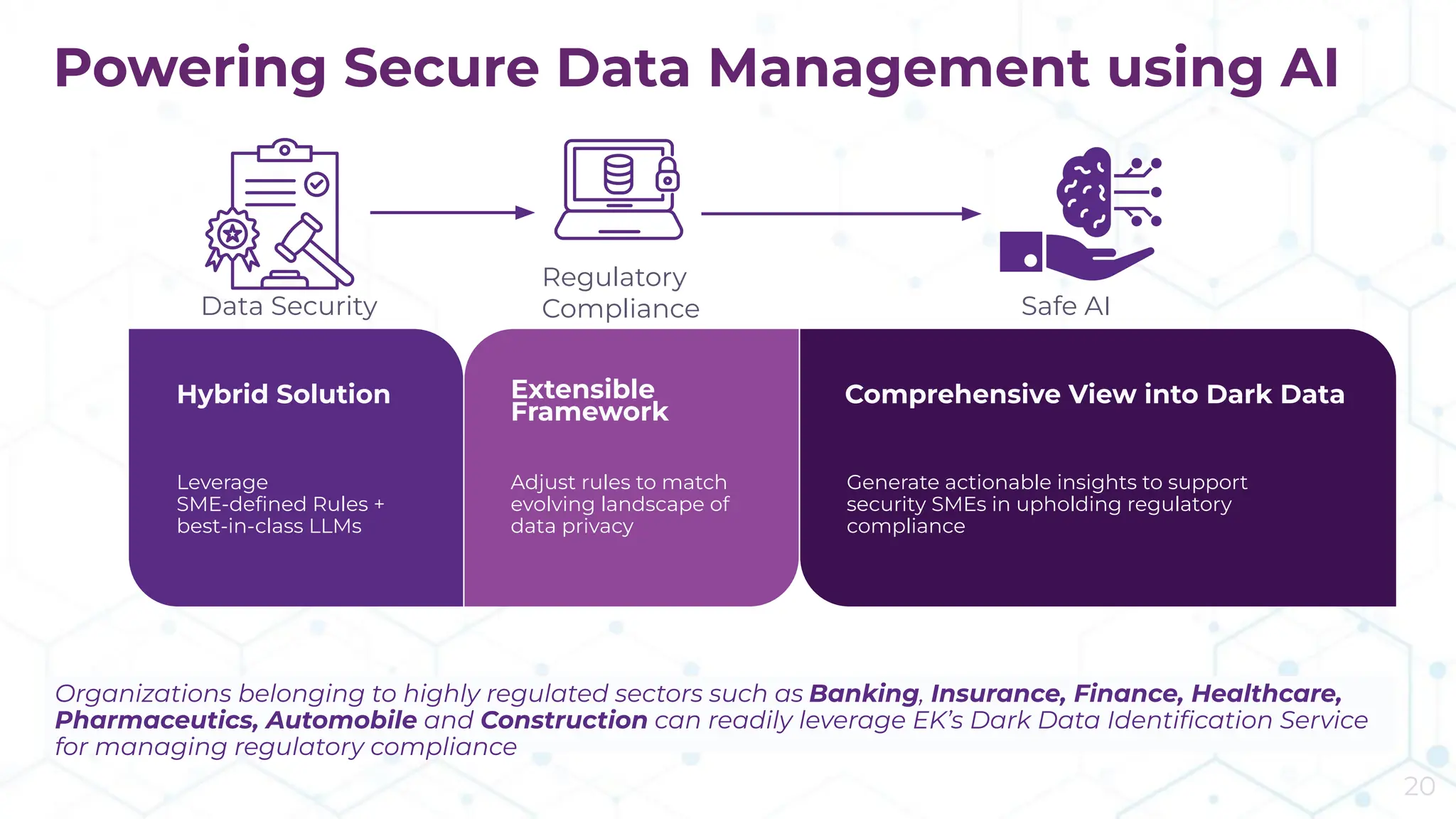
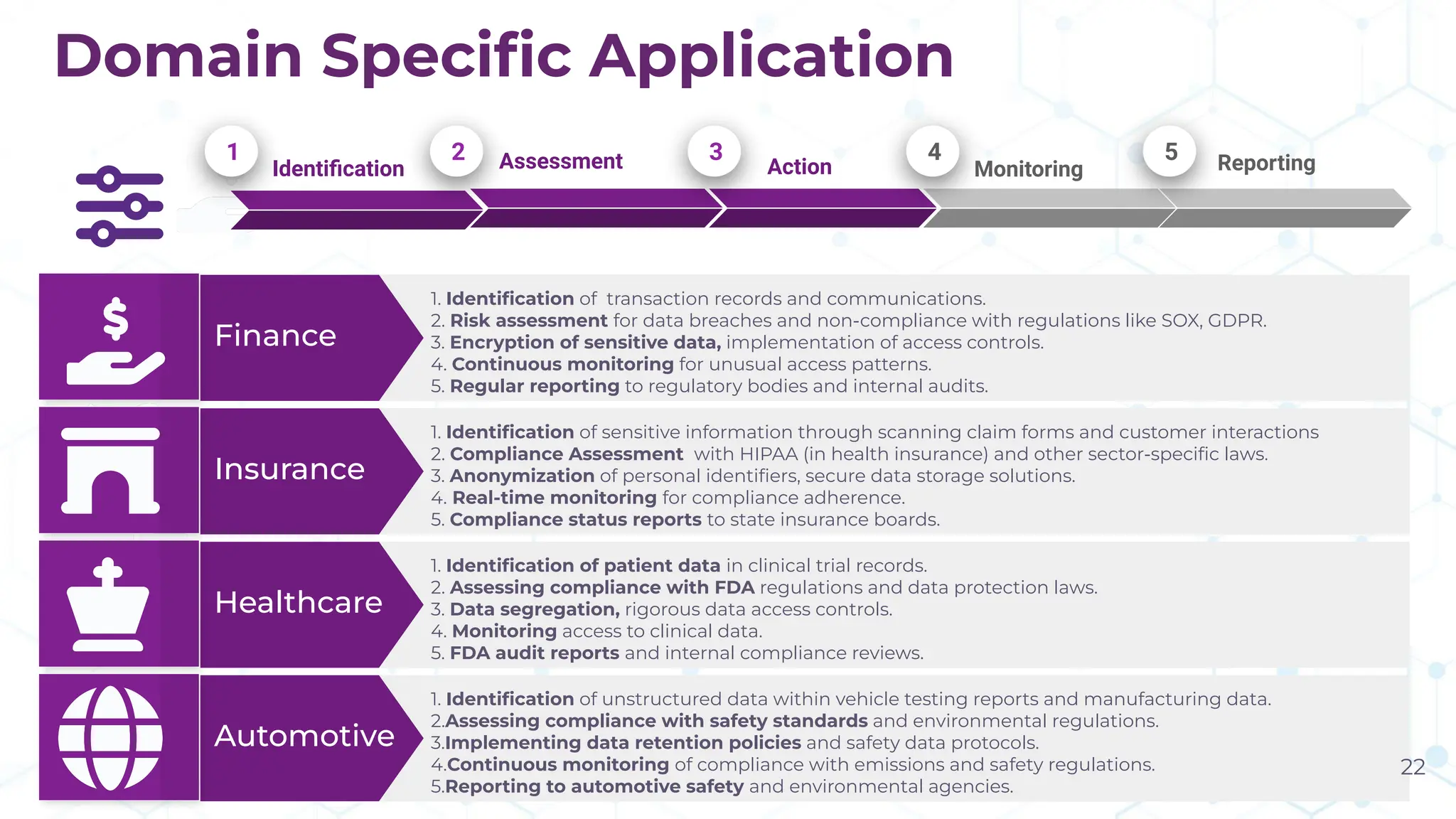
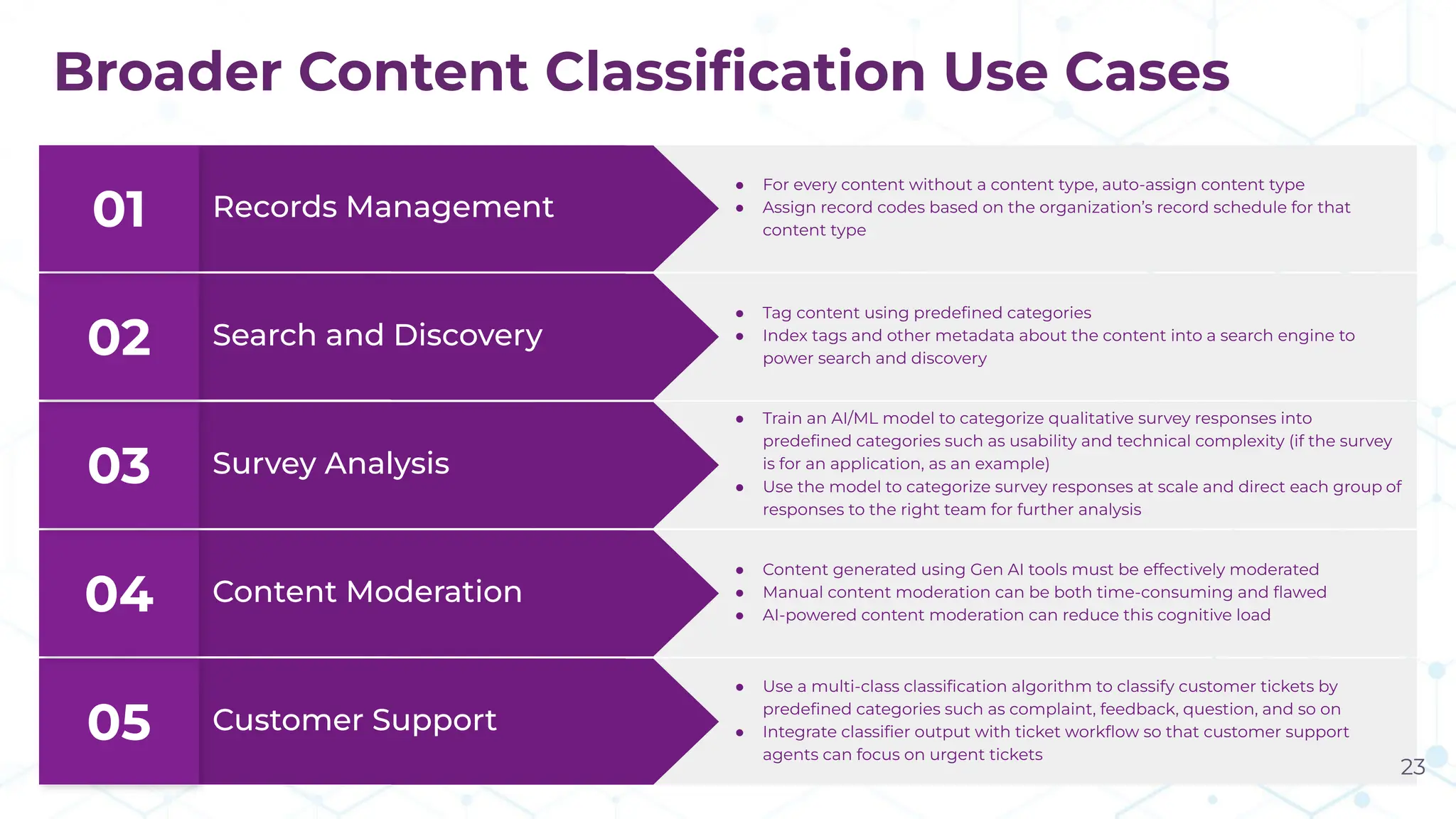
The document discusses the challenge of managing dark data, which refers to unstructured, often unused data within organizations that can pose security and compliance risks. It highlights the need for AI-powered systems to identify and manage this data, providing a case study of a federal research organization that successfully implemented such a solution. The paper emphasizes the importance of data governance and proactive management strategies to ensure compliance and maximize insights from available data.