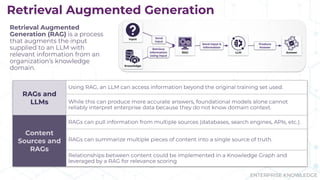
Does your AI tool have a hard time answering complex questions? Maybe you should consider GraphRAG!
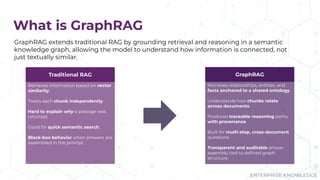
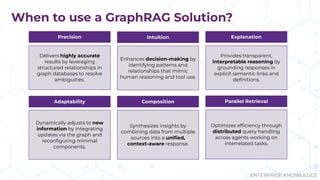
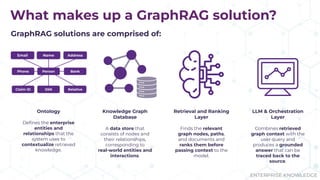
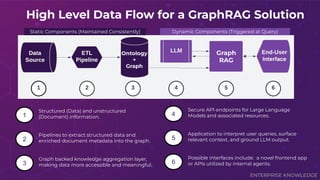
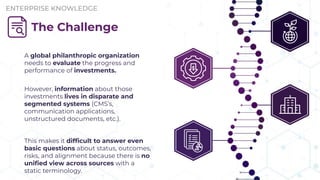
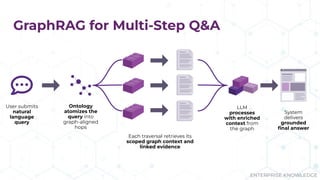
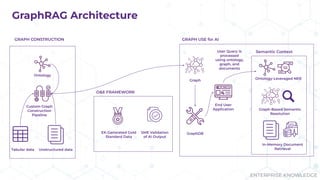
During their presentation “Tracing the Thread: Decoding the Decision-Making Process with GraphRAG” at Enterprise Search & Discovery 2025, Enterprise Knowledge’s Urmi Majumder and Kaleb Schultz discussed how GraphRAG extends traditional RAG by grounding retrieval in a semantic knowledge graph to create transparent and explainable AI. They shared a client success story that focused on enabling program officers at a global philanthropic organization to evaluate investment progress and performance more efficiently, specifically by unifying disparate data sources such as reports, memos, and financial data into a single, interconnected network.