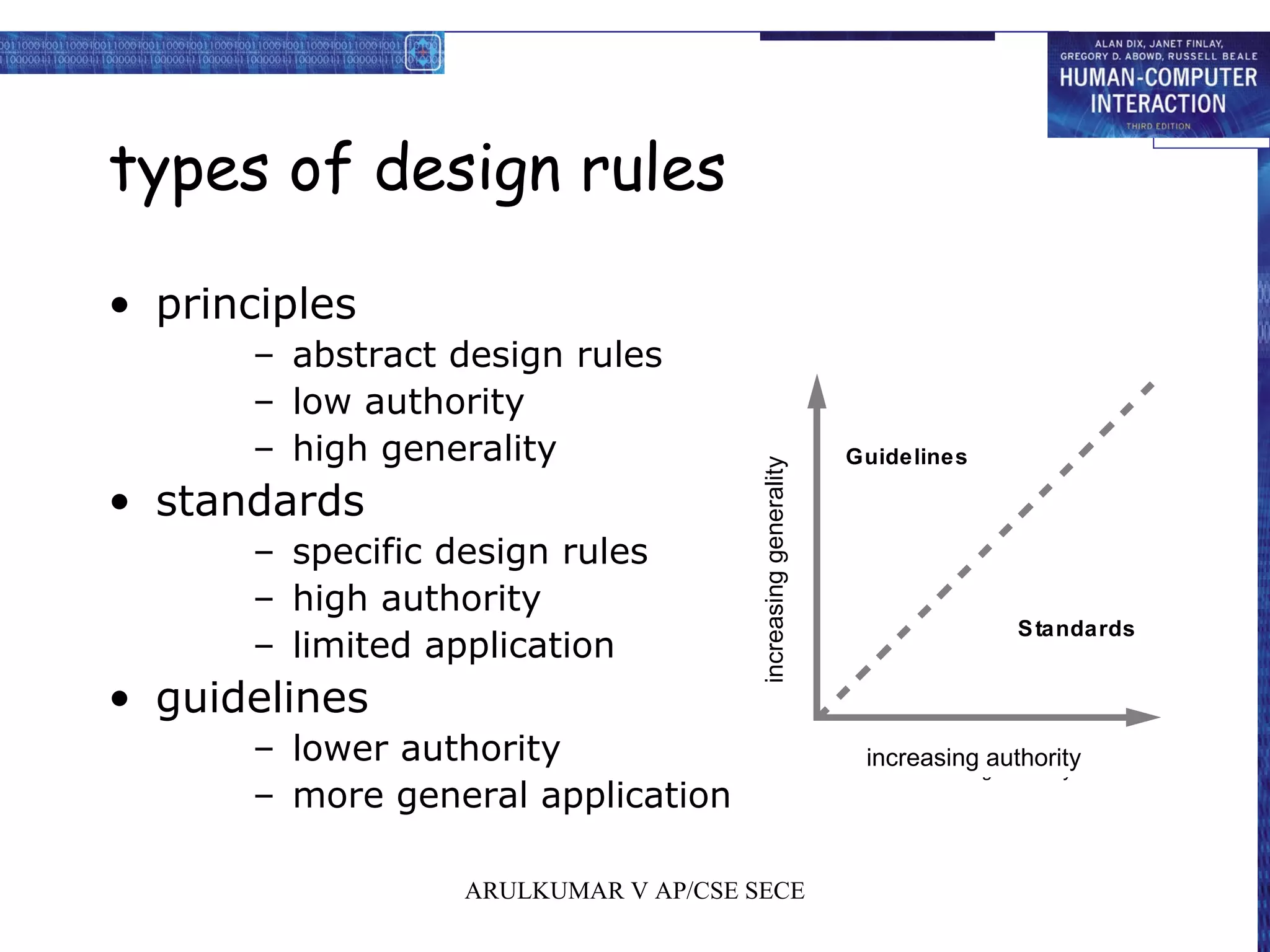
1. Design rules for usability include principles, standards, guidelines, and patterns which provide direction for interaction design.
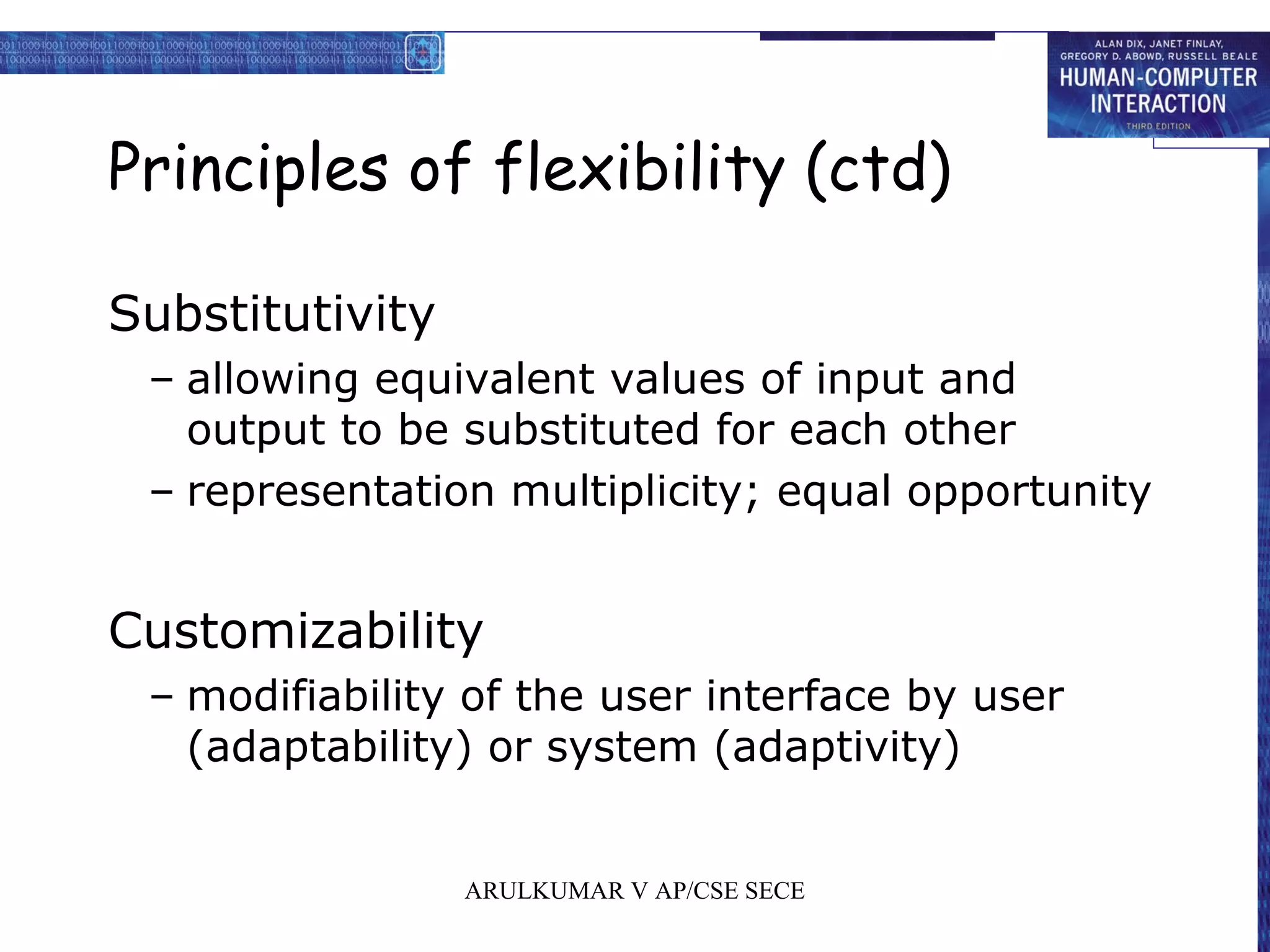
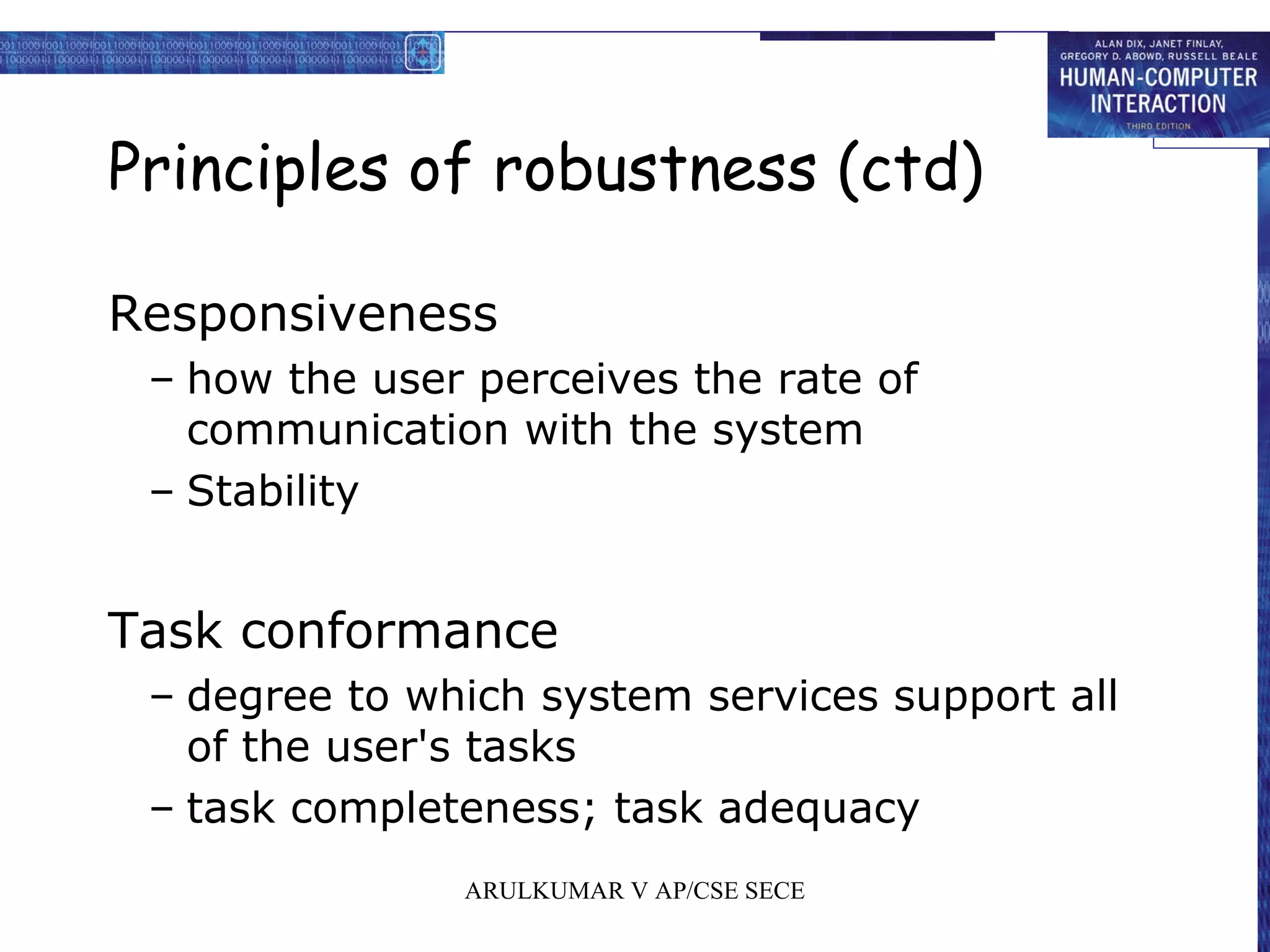
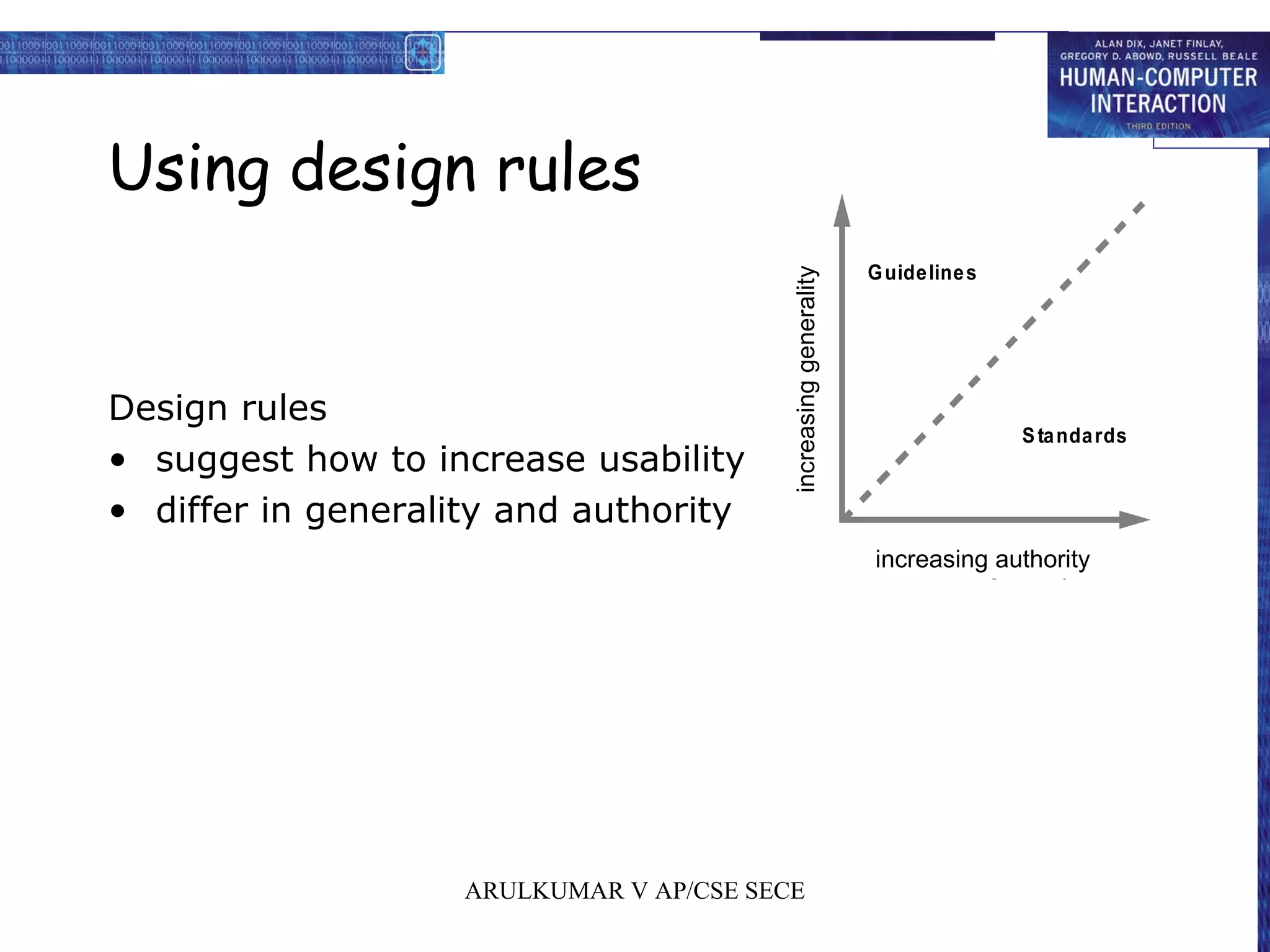
2. Principles for usability focus on learnability, flexibility, and robustness to support users. Standards have high authority while guidelines are more suggestive.
3. Understanding design rules from different levels of generality and authority helps increase usability through consistent and predictable systems.