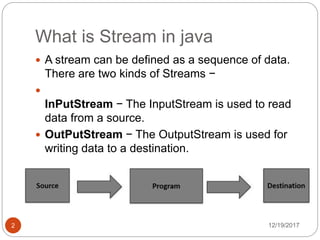
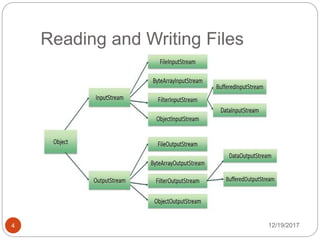
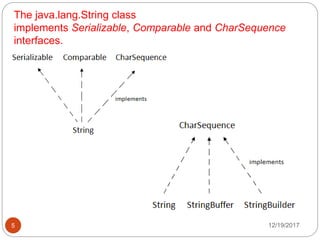
The document discusses streams and strings in Java. There are two types of streams - input streams which read data from a source, and output streams which write data to a destination. An example is provided that copies the contents of one file to another using input and output streams. The Java String class implements various interfaces and provides many methods for string operations like compare, concat, length, and substring. Further code examples demonstrate creating strings and using the charAt method.

![12/19/20173
Example
import java.io.*;
public class CopyFile {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream("input.txt");
out = new FileOutputStream("output.txt");
int c;
while ((c = in.read()) != -1)
{
out.write(c); } }
finally {
if (in != null)
{ in.close(); } if (out != null) { out.close(); } } } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streamsio-171219100321/85/Streams-amp-io-3-320.jpg)

![String Example
12/19/20177
public class StringExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
String s1="java";//creating string by java string literal
char ch[]={'s','t','r','i','n','g','s'};
String s2=new String(ch);//converting char array to string
String s3=new String("example");//creating java string by
new keyword
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streamsio-171219100321/85/Streams-amp-io-7-320.jpg)
![String methods ex
12/19/20178
public class CharAtExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
String name="javatpoint";
char ch=name.charAt(4);//returns the char value at the 4th index
System.out.println(ch);
}}
public class CharAtExample{
public static void main(String args[]){
String name="javatpoint";
char ch=name.charAt(10);//returns the char value at the 10th
index
System.out.println(ch);
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/streamsio-171219100321/85/Streams-amp-io-8-320.jpg)

