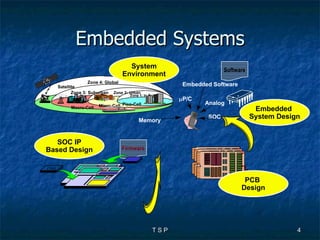
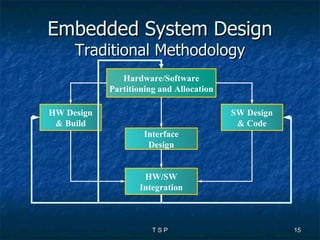
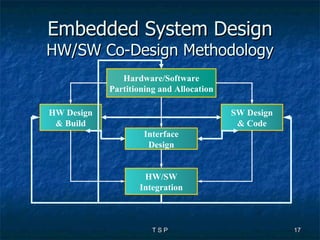
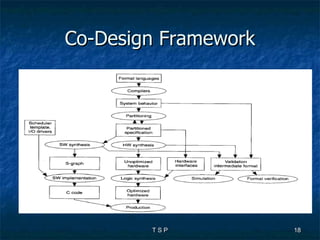
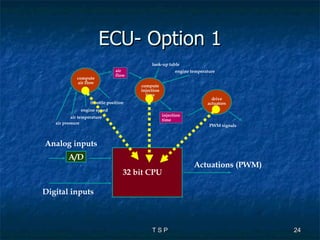
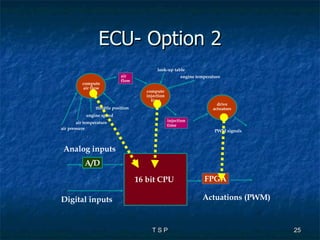
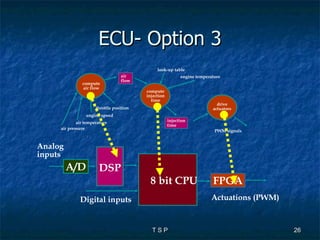
The document discusses hardware/software co-design of embedded systems. It describes how embedded systems use computers for dedicated functions and discusses issues in designing these systems like hardware/software partitioning and choosing processors. It also explains that co-design frameworks allow evaluating different hardware and software architectures through simulation before building prototypes. This helps address issues like bottlenecks and improves performance through better allocation of tasks between processors.