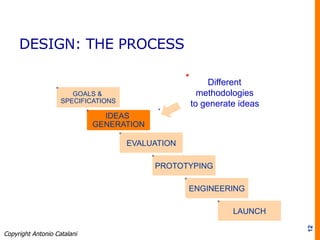
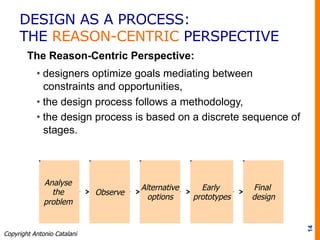
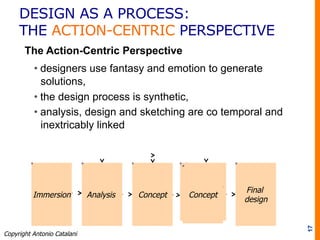
The document discusses various approaches to design, emphasizing the importance of defining design based on its application area and the impact it has on consumer behavior and brand identity. It outlines the design process as a series of steps that balance goals, constraints, and user needs while highlighting common pitfalls in design management. Ultimately, it stresses the role of designers as mediators between the environment and companies, utilizing both analytical and emotional strategies to achieve effective design solutions.