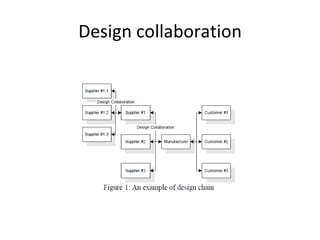
Design collaboration involves integrating suppliers into the product design process. This leads to lower costs, improved quality, and decreased development times. For example, when Gold Corp collaborated with two Australian mining companies on 3D mine depictions, its production increased by over 450,000 ounces annually while costs decreased. Effective design collaboration considers logistics, manufacturability, and gaining mutual understanding between partners. It allows 80% of product costs determined early to be lowered and coordination of multiple suppliers.