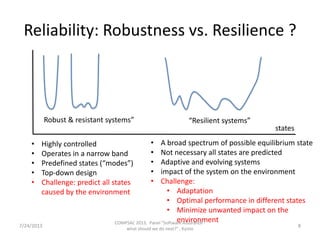
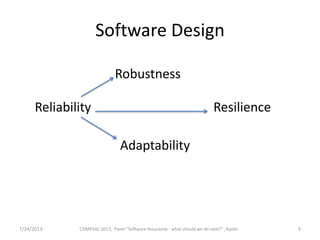
This document summarizes a panel discussion on software assurance and reliability. It discusses how reliability has traditionally focused on intended functions within stated conditions and time periods. However, modern software is more complex, ubiquitous, and dynamic. The document therefore questions whether reliability should instead focus on robustness, which aims to operate within a narrow band of predefined states, or resilience, which allows a system to adapt to an evolving environment and broad spectrum of states through monitoring and healing. Key challenges discussed include balancing composability with analyzability, and predictability with adaptability.