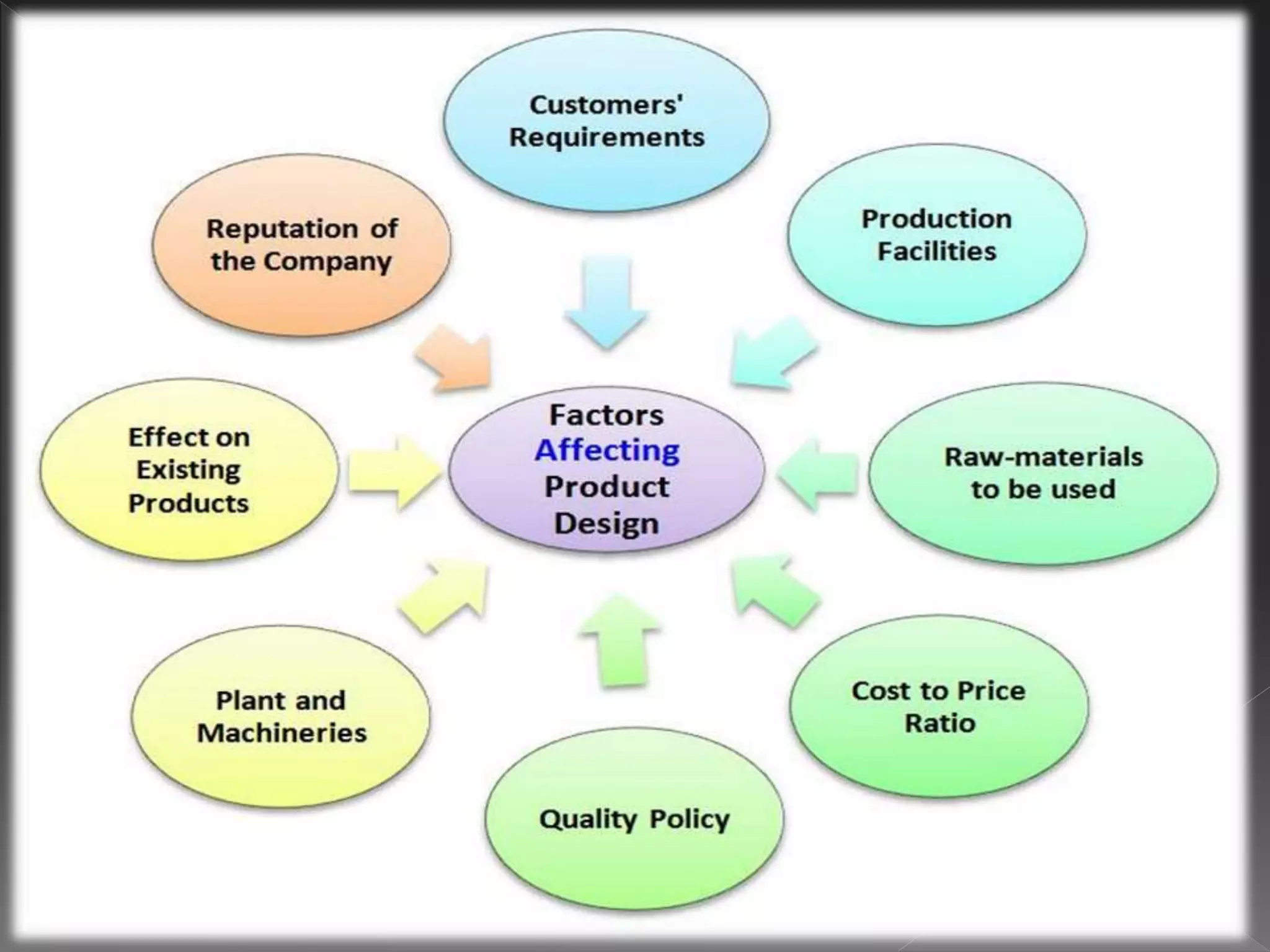
Product design is a process that involves generating ideas for new products, prototyping, testing, and finalizing the design. The goals of product design are to meet customer needs, reduce costs, ensure product quality and functionality, and generate profits. Effective product design considers factors like appearance, reliability, manufacturability, and other specifications.
























![ Create the Manufacturing Bill of
Material[MBOM]
“design” the cost before design the product
Make a Pareto graph of cost
Don't miss the hidden cost
Time is money](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/productdesignppt-171230150109/75/Product-design-By-Arun-raj-v-26-2048.jpg)


