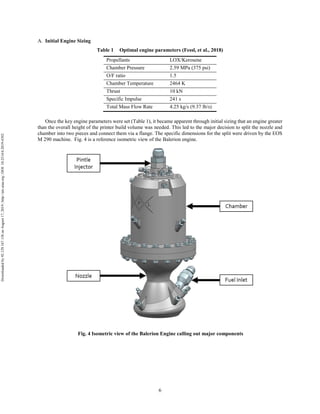
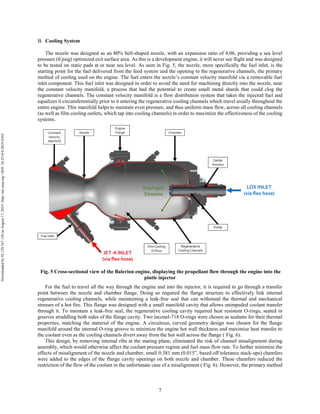
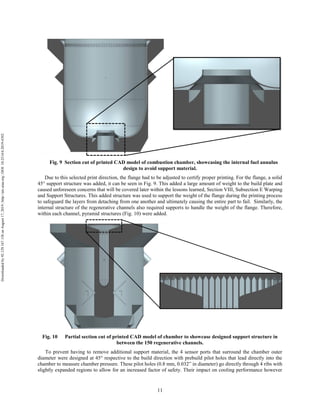
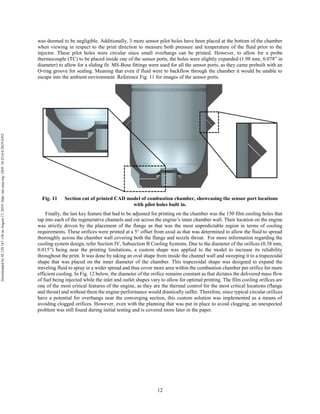
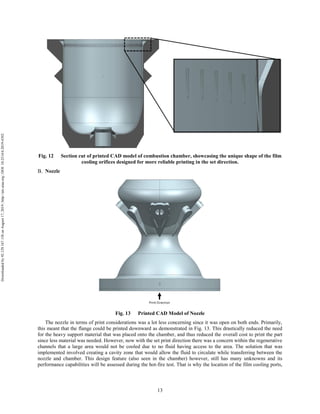
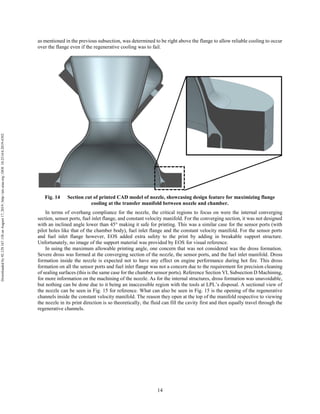
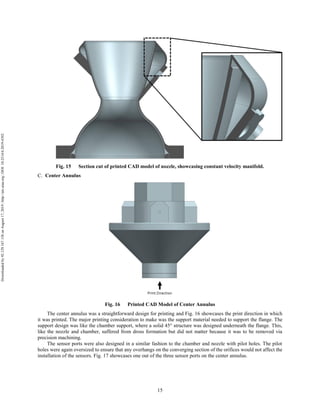
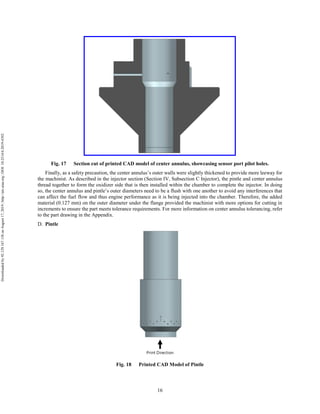
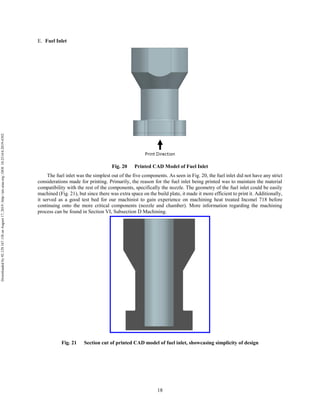
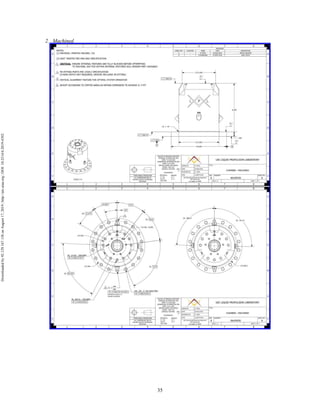
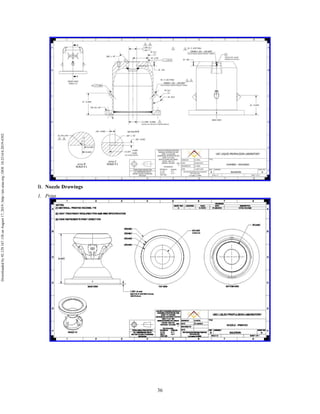
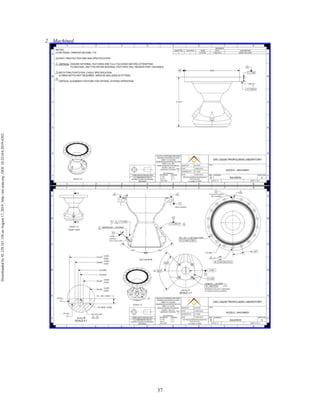
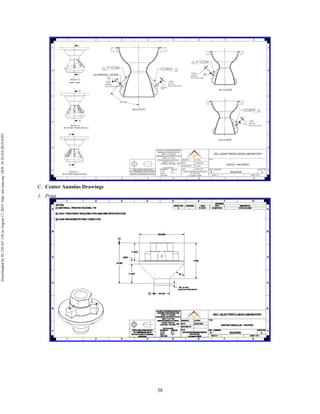
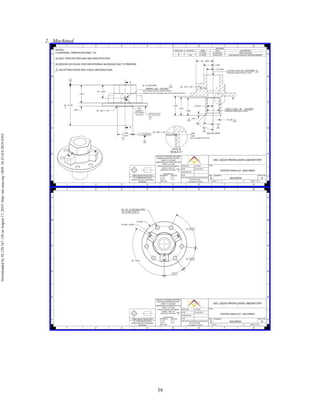
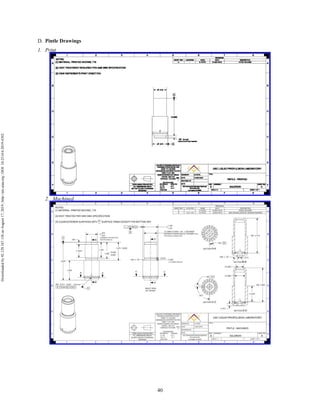
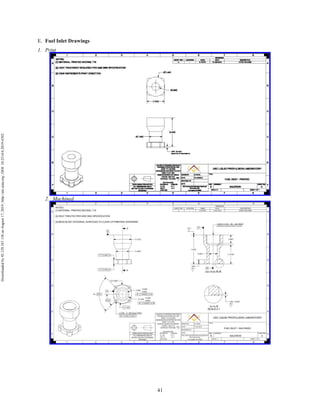
The document discusses the design and manufacturing considerations for an additively manufactured liquid rocket engine, named Balerion, developed by the Liquid Propulsion Laboratory at the University of Southern California. It highlights the challenges and solutions encountered during construction, such as post-processing techniques and material selection, emphasizing the advantages of additive manufacturing over traditional methods. The project aims to create a bi-propellant rocket engine for a reusable sounding rocket, focusing on optimizing design for performance and manufacturability.

![4
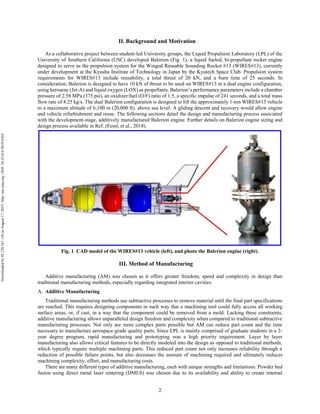
Fig. 3 Illustration of inclined angle and individual layer unsupported overhangs in reference to preceding
layers
When the inclined angle is above the minimum inclined, or critical angle, the print is in theory self-supporting and
is likely to print without major defects. As shown in Fig. 3, each layer has an overhang in reference to the layer below
it, dependent on the inclined angle and the constant layer thickness. As inclined angle decreases, unsupported overhang
length increases. A critical angle of 45° has been proposed as a “reliable building angle” to ensure defect free
fabrication (Wang, Yang, Yi, & Su, 2013). This critical angle was used for all Balerion part designs.
In the DMLS additive manufacturing process for unsupported overhangs, the main fabrication defects are dross
formation and warping that can eventually lead to layer separation and print failure. An experimental image of dross
formation can be found in Ref. (Wang, Yang, Yi, & Su, 2013, p. 1476). Dross forms in overhang areas that are only
supported by nonmelted powder instead of previously melted layers. This nonmelted support powder has “1/100th
of
the [heat conduction rate] of the solid supported zone” (Wang, Yang, Yi, & Su, 2013). This results in much more
energy input into the nonmelted powder supported zone, a larger melt pool of powder, and possible molten powder
dripping due to gravity and capillary force (Wang, Yang, Yi, & Su, 2013). Plastic deformation warping defects can
occur when thermal stress, due to rapid melt pool solidification, exceeds the strength of the material. This can also
occur in overhanging surfaces due to lack of solid surface support bonding with the previous layer (Wang, Yang, Yi,
& Su, 2013). Warping will influence the following layers, potentially leading to a lack of powder, repeated laser scans,
collisions with the powder scraper, and component breakage. Dross formation and warping can be minimized using
reduced laser deposition energy, higher scanning speed, support material addition, and a higher inclined angle (Wang,
Yang, Yi, & Su, 2013). Inversely, having an inclined angle below the critical angle value will lead to increased warping
and dross formation. To reduce unsupported overhangs and associated dross formation, interior cavities and channels
can be tear drop or diamond shaped, depending on the print direction. Small amounts of dross formation can manifest
itself as increased surface roughness or surface defects. Due to these constraints, Balerion part print directions were
considered and optimized during the design phase.
Other common possible fabrication defects in DMLS include unique non-uniform precipitate microstructure
phases. This can lead to unintended residual stresses not seen in traditional casting methods (Karimi, 2016). This is
due to the rapid cooling of the molten material of the DMLS method when compared to casting. To eliminate these
residual stresses, post-printing heat treatment is necessary. Excess porosity can also occur in laser sintering
Downloadedby92.129.167.138onAugust17,2019|http://arc.aiaa.org|DOI:10.2514/6.2019-4392](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pateletal-190826204054/85/Design-and-Additive-Manufacturing-Considerations-for-Liquid-Rocket-Engine-Development-4-320.jpg)

















![32
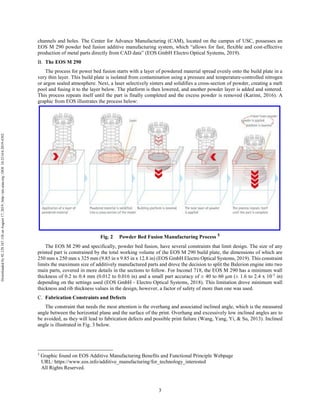
Excess Porosity
A defect found, possibly worsened by ultrasonic cleaning, were approximately 10 small open pores in the inner
chamber wall. Several open pores were located near film cooling holes, in areas of minimum thickness, and the rest
were located further up the chamber. A picture of one of these pores can be found in Fig. 38.
Fig. 38 Open pore leaks with water(left), open pore near film cooling hole (center), open pore in
chamber wall away from film cooling (right)
These pores could have been filled using hot isostatic pressing. HIP is a process that places a part in a pressure
vessel, where the component faces high temperatures and isostatic gas pressures—usually Argon—to decrease the
component’s porosity and increase strength, ductility, and fatigue life. HIP can offer many benefits to the strength of
Inconel 718 while preserving grain architecture [11]. As HIP is overall beneficial to improving the material properties
of Inconel 718, HIP will be considered for future post-print processing. However, at time of publishing the open pores
were not considered a critical failure.
Warping and Support Structures
During assembly of the engine, a warping physical deformity was discovered in the interior of the chamber. The
warping was determined to have been caused during the printing process, by the weight of the chamber flange itself
and as a result of insufficient support of the chamber during printing. Though the warping at time of publishing has
been deemed not a critical failure, it could have been avoided with proper support consideration. For example, either
sacrificial supports extruded upward from the build plate or tree branch supports would have been effective solutions
to prevent load-based warping. In the case of sacrificial supports, the support pieces would have been excellent test
coupons, which could have been used to confirm that the print meets AMS 5662 specifications. For future projects,
adding these support structures for the chamber is important to avoid warping and will be implemented.
Scanning for Tight Tolerances
As mentioned in the previous section, the failure to stay within tolerances for the O-ring grooves can be costly.
Manufacturing makes it difficult to achieve such strict tolerances and if that is the case, the part may be better off
rejected. Advanced scanning is important to accurately measure the incredibly tight tolerances of the O-ring grooves.
Using a diode arm to check any and all locations for off tolerance features can save troubles related to damaging other
expensive parts and significantly off-nominal engine performance. It is worth understanding the capabilities of the
chosen method of manufacturing and the material, as in this case, the selection of Inconel made achieving precise
tolerances a difficult task.
Downloadedby92.129.167.138onAugust17,2019|http://arc.aiaa.org|DOI:10.2514/6.2019-4392](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pateletal-190826204054/85/Design-and-Additive-Manufacturing-Considerations-for-Liquid-Rocket-Engine-Development-32-320.jpg)


![42
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the USC Department of Astronautical Engineering for supporting the activities of the
student-led Liquid Propulsion Laboratory. We would also like to thank the USC Center for Advanced Manufacturing,
and the Kaprielian Hall Machine Shop for machining the engine whilst sharing their expertise and insights throughout
the entire process. We would further like to thank Ansys and Nimbix for supporting and enabling LPL to perform
advanced 3D CFD and FEA analyses that supported the development of this engine. Finally, we would like to thank
the Aerospace Corporation for supporting LPL by providing CT scans of all the components. This allowed us to
inspect the internal geometry of each part which provided valuable data to complete a more through testing campaign.
References
[1] J. Fessl, H. Shen, P. N., T. Chen, S. Ghirnikar and M. Van Den Berghe, “Liquid Rocket Engine Design for Additive
Manufacturing,” 69th International Astronautical Congress, IAC, Bremen, Germany, 2018.
[2] EOS GmbH Electro Optical Systems, “EOS M 290 Data Sheet,” [Online], 2019, URL:
https://cdn0.scrvt.com/eos/413c861f2843b377/50cd1bf6790a/EOS_System_Data_Sheet_EOS_M_290_en_WEB.pdf.
[3] P. Karimi, "SLM additive manufacturing of Alloy 718 Effect of process parameters on microstructure and properties," Masters
Thesis with Specialization of Manufacturing, Department of Engineering Science, University West, Trollhattan, Sweden,
2016.
doi: 10.13140/RG.2.2.25434.64963
[4] EOS GmbH Electro Optical Systems, "Material Data Sheet EOS NickelAlloy IN718," [Online], 2018, URL: https://ip-saas-
eos-cms.s3.amazonaws.com/public/4528b4a1bf688496/ff974161c2057e6df56db5b67f0f5595/
EOS_NickelAlloy_IN718_en.pdf.
[5] D. Wang, T. Yang, Z. Yi and X. Su, "Research on the Fabrication Quality Optimization of the Overhanging Surface in SLM
Process," The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology [Online Journal], Vol. 65, No. 9-12, 2013, pp.
1471-1484.
doi: 10.1007/s00170-012-4271-4
[6] C. Yap, C. Chua, Z. Dong, Z. Liu, D. Zhang, L. Loh and S. Sing, "Review of selective laser melting: Materials and
applications," Applied Physics Review [Online Journal], Vol. 2, No. 4, 09 December, 2015.
doi: 10.1063/1.4935926
[7] J. Targonski, M. Moruzzi, J. Fessl, P. Prochnicki and E. Perry, "The Objective and Strategy Behind the Liquid Propulsion
Laboratory at the University of Southern California," 2018 Joint Propulsion Conference, AIAA, Cincinnati, Ohio, 2018.
doi: 10.2514/6.2018-4804
[8] S. Heister, "Pintle Injectors," Handbook of Atomization and Sprays, Springer, New York, 2011, pp. 647-655.
Downloadedby92.129.167.138onAugust17,2019|http://arc.aiaa.org|DOI:10.2514/6.2019-4392](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pateletal-190826204054/85/Design-and-Additive-Manufacturing-Considerations-for-Liquid-Rocket-Engine-Development-42-320.jpg)
![43
[9] M. Moruzzi, J. Fessl, P. Prochnicki and J. Targonski, "Liquid Rocket Engine Component Water Flow Test Stand," 2018 Joint
Propulsion Conference, AIAA, Cincinnati, Ohio, 2018.
doi: 10.2514/6.2018-4599
[10] L. Murr, "A Metallographic Review of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing of Metal and Alloy Products and Components,"
Metallography, Microstructure, and Analysis [Online Journal], Vol. 7, No. 2, April 2018, pp. 103-132.
doi: 10.1007/s13632-018-0433-6
[11] K. Tan and S. Yeo, "Surface Modification of Additive Manufactured Components by Ultrasonic Cavitation Abrasive
Finishing," Wear [Online Journal], Vol. 378-379, May 2017, pp. 90-95.
doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2017.02.030
[12] V. Popovich, E. Borisov, A. Popovich, V. Sufiiarov, D. Masaylo and L. Alzina, "Impact of heat treatment on mechanical
behaviour of Inconel 718 processed with tailored microstructure by selective laser melting," Materials & Design [Online
Journal], Vol. 131, 5 October 2017, pp. 12-22.
doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2017.05.065
[13] R. Thirumalai, J. Senthilkumaar, P. Selvarani and S. Ramesh, "Machining characteristics of Inconel 718 under several cutting
conditions based on the Taguchi method," Journal of Mechanical Engineering Sciences [Online Journal], Vol. 227, No. 9,
2013, pp. 1889-1897
doi: 10.1177/0954406212466193
[14] "Guidelines for Pressure Boundary Bolted Flange Joint Assembly," American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2010,
[Online], URL: http://gost-snip.su/download/asme_pcc12010_guidelines_for_pressure_boundary_bolted_flange, [Accessed
July 2019].
Downloadedby92.129.167.138onAugust17,2019|http://arc.aiaa.org|DOI:10.2514/6.2019-4392](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pateletal-190826204054/85/Design-and-Additive-Manufacturing-Considerations-for-Liquid-Rocket-Engine-Development-43-320.jpg)