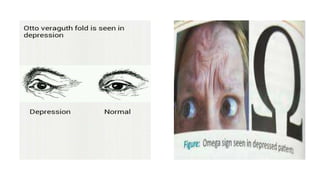
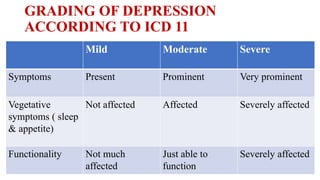
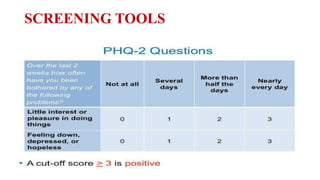
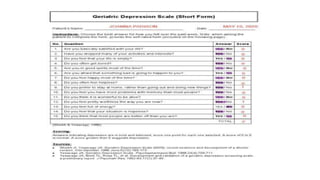
Depression is underrecognized and undertreated in older adults. It is not a normal part of aging and can worsen medical illnesses. Symptoms include depressed mood, loss of interest, changes in appetite, insomnia, fatigue, guilt, and suicidal thoughts. Depression is diagnosed if five or more symptoms are present for two weeks. Treatment involves pharmacotherapy such as SSRIs or SNRIs for at least six months, psychotherapy like CBT, and other somatic therapies for severe cases. Untreated depression can have serious consequences so screening and treatment is important for older adults.