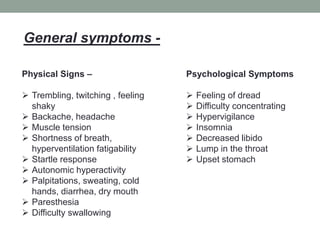
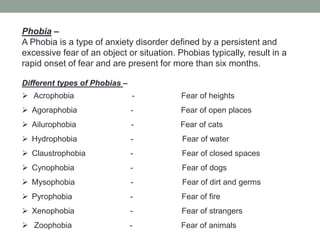
This document discusses anxiety disorders and provides information about their symptoms, types, causes, and treatment. It defines anxiety as a feeling of tension, worry, and physical changes. There are several types of anxiety disorders including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and phobias. Symptoms can include physical signs like trembling, headaches, as well as psychological symptoms like feelings of dread. The causes of anxiety disorders may include genetics, brain chemistry, environmental stress, drug use, medical conditions, and childhood trauma. Treatment involves pharmacological interventions like benzodiazepines and SSRIs as well as psychological therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy.







![Diagnostic criteria According to ICD -10 –
F40 Phobic anxiety disorders
F40.0 Agoraphobia .
.00 Without panic disorder
.01 With panic disorder
F40.1 Social phobias
F40.2 Specific (isolated) phobias
F40.8 Other phobic anxiety disorders
F40.9 Phobic anxiety disorder, unspecified
F41 Other anxiety disorders
F41.0 Panic disorder [episodic paroxysmal anxiety] .
F41.1 Generalized anxiety disorder
F41.2 Mixed anxiety and depressive disorder
F41.3 Other mixed anxiety disorders
F41.8 Other specified anxiety disorders
F41.9 Anxiety disorder, unspecified](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anxietydisorder-210625140444/85/Anxiety-disorder-10-320.jpg)



