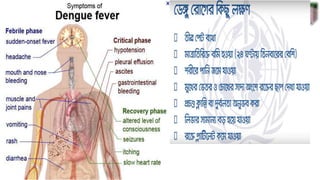
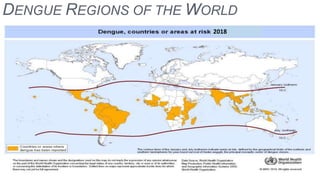
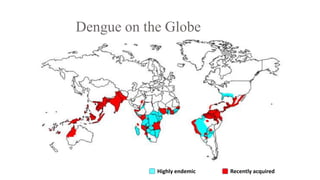
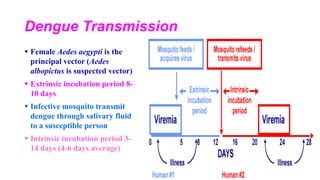
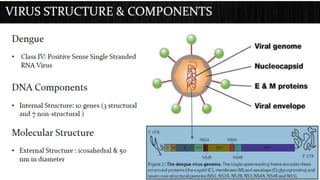
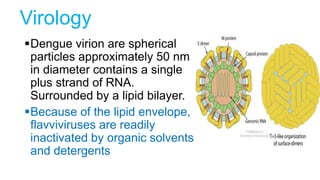
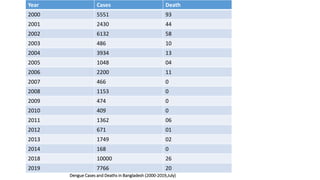
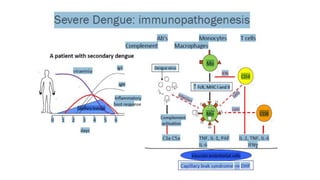
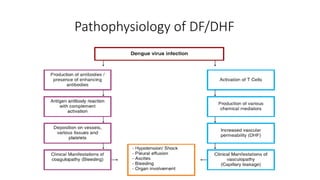
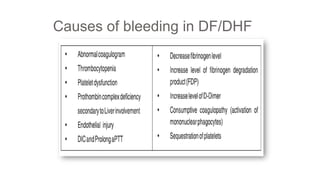
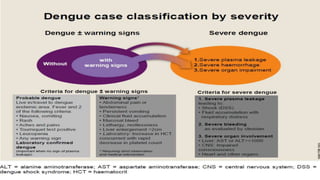
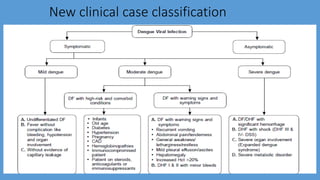
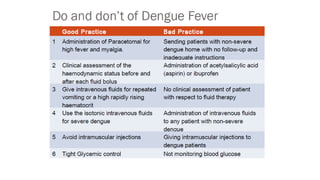
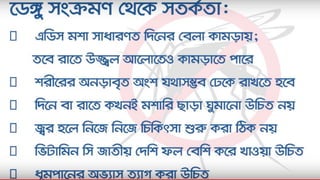
Dengue virus is a mosquito-borne virus that causes dengue fever and its more severe forms, dengue hemorrhagic fever and dengue shock syndrome. It is transmitted by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. There are four distinct serotypes of the virus. Infection with one serotype provides lifelong immunity to that serotype but only short-term immunity to the others. Dengue is widespread in tropical and subtropical parts of the world, with severe dengue being a leading cause of hospitalization and death among children in some Asian and Latin American countries. There is no vaccine available for dengue prevention, so control of the mosquito vector through environmental management and insect