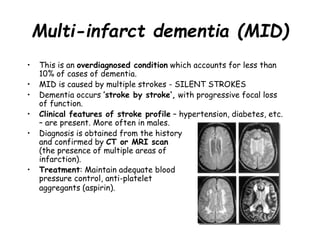
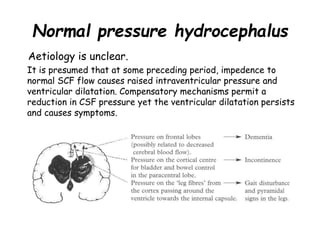
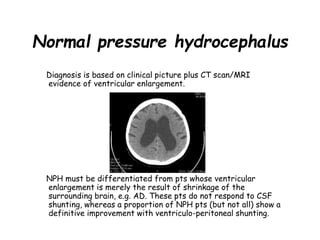
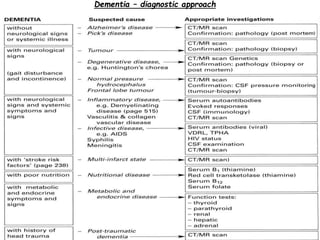
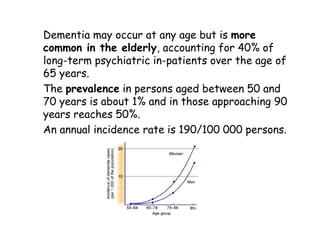
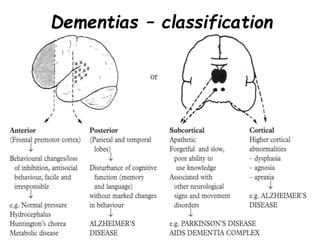
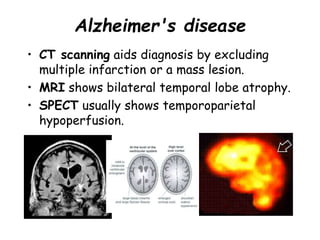
Dementia is characterized by progressive deterioration of intellect, behavior, and personality due to diffuse brain disease, especially affecting the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Memory impairment is required for diagnosis. Common causes include Alzheimer's disease, cerebrovascular disease, Lewy body disease, and frontotemporal dementia. Evaluation involves assessing cognitive function, neurological exam, imaging, and lab tests to identify underlying causes and rule out other conditions. There is no cure for dementia, but some types can be temporarily slowed with medications or treated if potentially reversible causes are identified.









![Alzheimer's disease -
treatment
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (Donepezil [Aricept],
Rivastigmine [Exelon], Galantamine [Reminyl]) have
been shown to enhance cognitive performance in early
disease. Memantine [Ebixa, Axura, Namenda] is
approved for moderate disease. However they do not
cure!
- Treat concurrent depression, anxiety and sleep
disorders. Neuroleptic use may be required for
behavioral disturbance.
- Mangement of AD requires careful advice and
counseling of the patient and family and shared care
involving the family, caregivers, GPs, hospital specialist,
and community psychiatric services.
- Long-term residential care is ofte required.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dementia-230530181929-9e59029a/85/dementia-ppt-13-320.jpg)