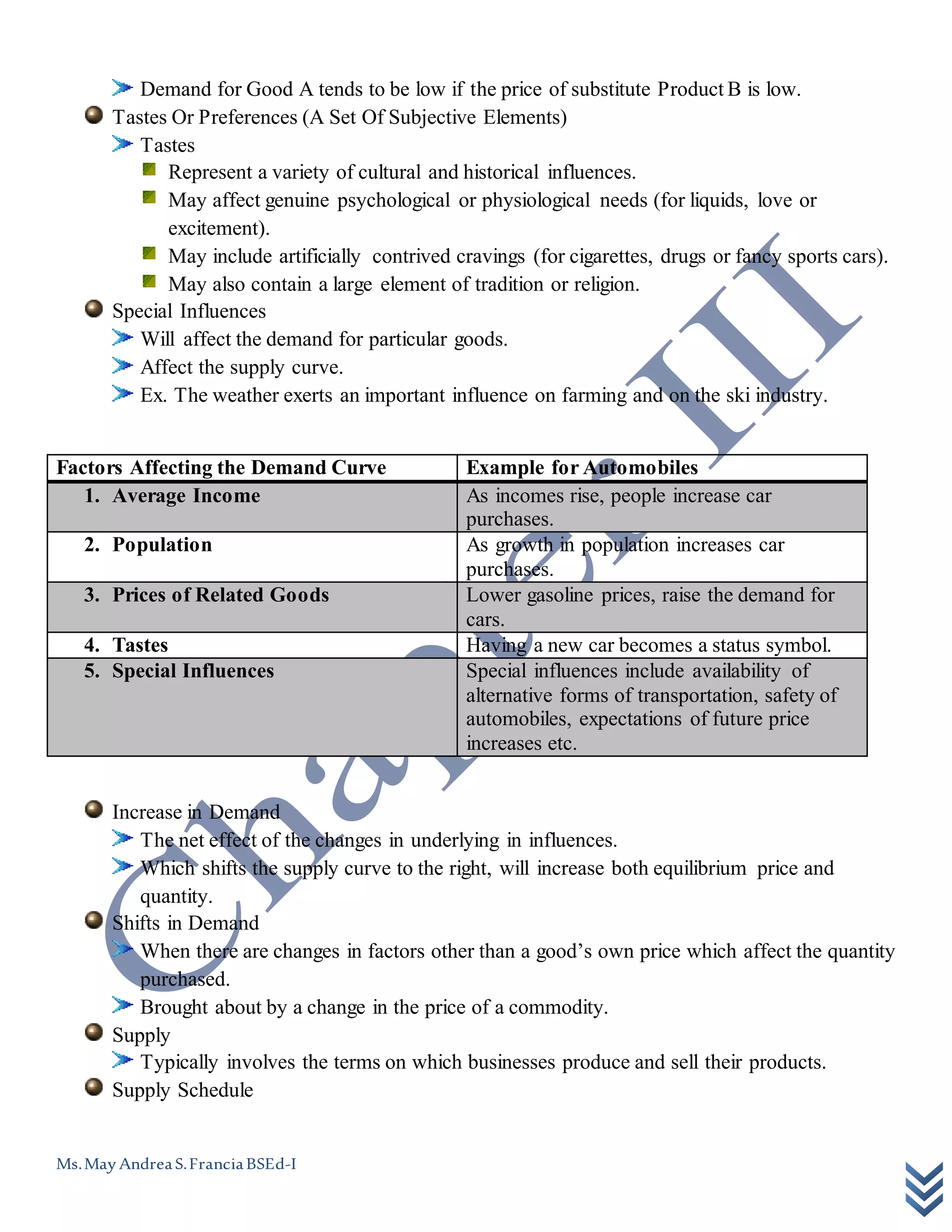
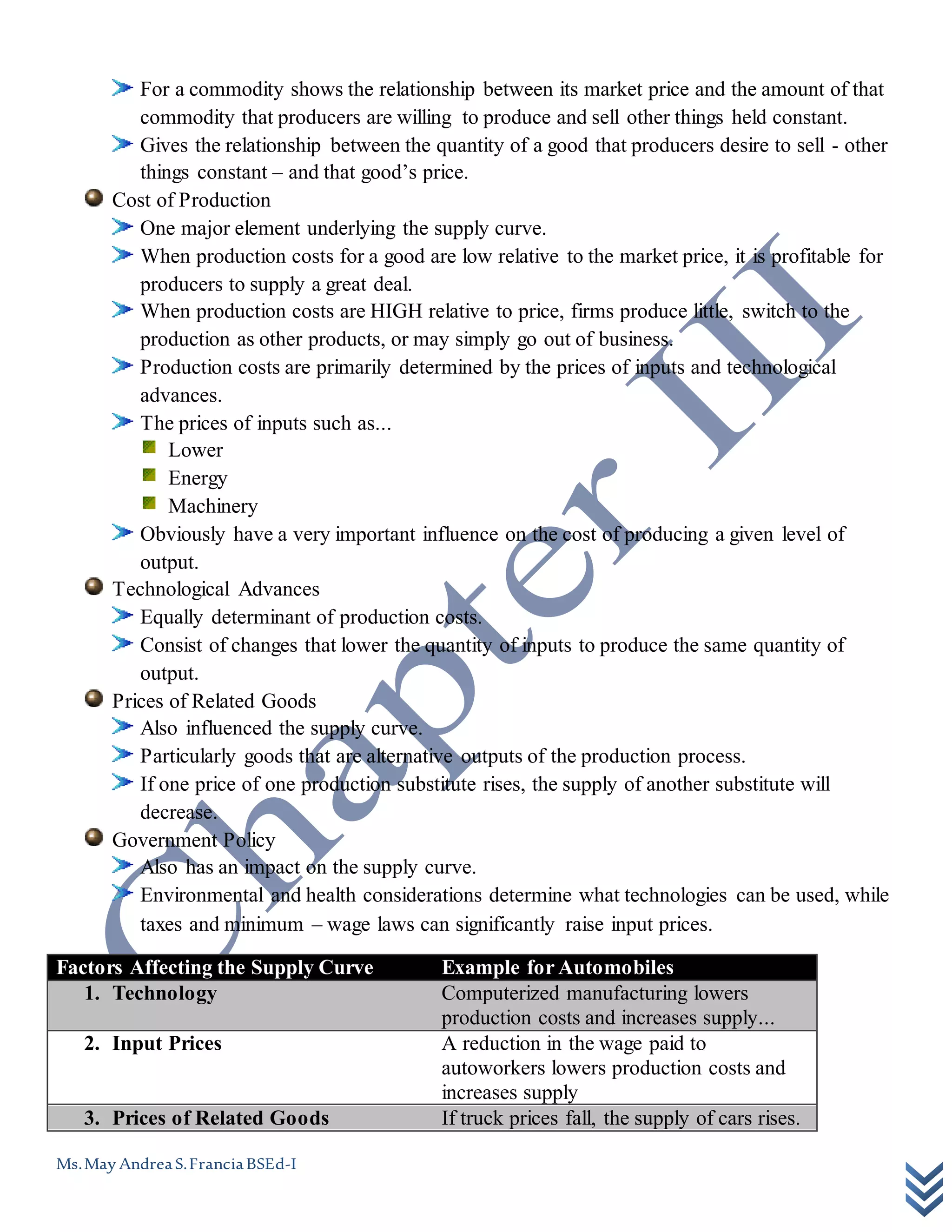
This document discusses the basic concepts of supply and demand. It defines key terms like demand curve, substitution effect, income effect, market demand, market demand curve, factors affecting demand, supply schedule, cost of production, factors affecting supply, market equilibrium, equilibrium price, demand schedule, demand curve, and the law of downward-sloping demand. It provides examples of factors that influence the demand and supply curves for automobiles.