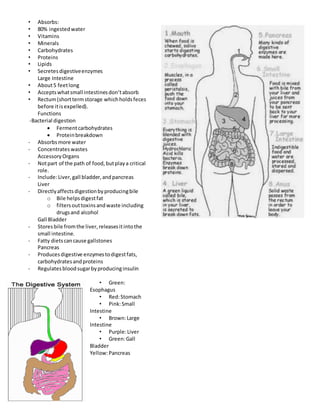
The digestive system functions to digest food and extract nutrients. It consists of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, gallbladder, liver, and pancreas. Food moves through the system where it is broken down mechanically and chemically. The small intestine absorbs nutrients from digested food into the bloodstream while the large intestine absorbs water before waste is excreted. Accessory organs like the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas produce enzymes and bile to aid in digestion.