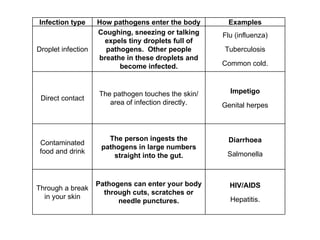
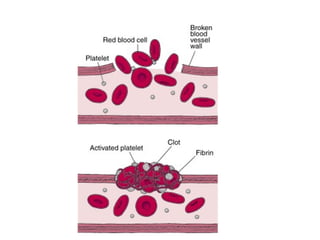
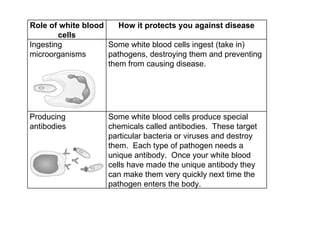
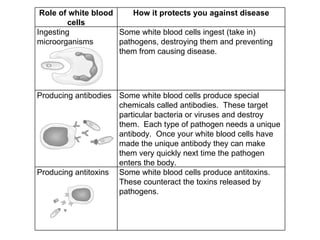
This document describes different ways pathogens can enter the body and cause infection, including through droplets from coughing/sneezing, direct contact, contaminated food/drink, and breaks in the skin. It provides examples of diseases caused by each infection type, such as influenza spreading through droplets. The document also discusses the roles of white blood cells in protecting the body from disease, including ingesting pathogens, producing antibodies, and producing antitoxins.